|
HMS Weston
HMS ''Weston'' was a ''Shoreham''-class sloop of the British Royal Navy. ''Weston'' was built at Devonport Dockyard in 1931–1933. ''Weston'' served on the Africa Station and in the Red Sea in the 1930s. In the Second World War, she was used for convoy escort duties, operating in British waters and in the North Atlantic, sinking the German submarine in 1940, and later in West African waters. The ship was laid up in reserve after the end of the war in Europe and was scrapped in 1947. Construction and design The British Admiralty ordered four sloops as part of the 1930 construction programme, with three ordered from Devonport and one from Chatham dockyard. Classified as repeat ''Shoreham'' or ''Falmouth''-class ships, they, like the four ''Shoreham''-class sloops ordered under the 1929 construction programme, were a lengthened and improved version of the of the 1928 programme, which were themselves a modification of the . They were intended for a dual role of patrol servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMNB Devonport
His Majesty's Naval Base, Devonport (HMNB Devonport) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Portsmouth) and is the sole nuclear repair and refuelling facility for the Royal Navy. The largest naval base in Western Europe, HMNB Devonport is located in Devonport, in the west of the city of Plymouth, England. The base began as Royal Navy Dockyard in the late 17th century, but shipbuilding ceased at Devonport in the early 1970s, although ship maintenance work has continued. The now privatised maintenance facilities are operated by Babcock International Group, who took over the previous owner Devonport Management Limited (DML) in 2007. DML had been running the Dockyard since privatisation in 1987. From 1934 until the early 21st century the naval barracks on the site was named HMS ''Drake'' (it had previously been known as HMS ''Vivid'' after the base ship of the same name). The name HMS ''Drake'' and its c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saluting Gun
A salute is usually a formal hand gesture or other action used to display respect in military situations. Salutes are primarily associated with the military and law enforcement, but many civilian organizations, such as Girl Guides, Boy Scouts and the Salvation Army use formal salutes. Ordinary civilians also salute informally to greet or acknowledge the presence of another person; such as a tip of the hat or a hand wave to a friend or neighbour. Military salutes Throughout history, military organizations have used many methods to perform salutes. Depending on the situation a salute could be a hand or body gesture, cannon or rifle shots, hoisting of flags, removing headgear, or other means of showing respect or deference. Hand salutes Origins According to historical reconstruction, the ancient Roman military salute (''salutatio militaris'') was analogous to the current military salute. According to some modern military manuals, the modern Western salute originated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander-in-Chief, Africa (Royal Navy)
The Commander-in-Chief, Africa was the last title of a Royal Navy's formation commander located in South Africa from 1795 to 1939. Under varying titles, it was one of the longest-lived formations of the Royal Navy. It was also often known as the Cape of Good Hope Station. History From 1750 to 1779 the Cape of Good Hope became strategically important due to the increasing competition between France and Great Britain for control of the seas. In 1780 Holland joined the American Revolutionary War in alliance with France and Spain against Great Britain; the British Government were aware of the consequences should the Cape of Good Hope fall and the impact it would have on its trade links with India and put a plan into place to capture the Cape and circumvent its use by the enemy. The first attempt was subject to prolonged delays and the fact that the French were able to reinforce their defences enabled them to successfully defend it from the British attack. From 1781 to 1791 various att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navy News
''Navy News'' is the official newspaper of the British Royal Navy, produced by a small team of editorial and support staff and published by the Ministry of Defence on a monthly basis. The content of the newspaper is varied, ranging from information for all serving personnel of whatever rank or specialisation to Sea Cadets and former shipmates. Members of the public with an interest in the Royal Navy, Royal Marines and the Fleet Air Arm also have access to the newspaper. The newspaper is distributed free to serving personnel (ratio 1:5), and is available to members of the public through subscription or through a newsagent. Up to 35,000 copies are printed each month. ''Navy News'' includes sections on news; special features; sport; book reviews; association news; people; charity work; Fleet Focus (where the ships are deployed); 2-6 (for serving personnel); letters and the very popular noticeboard (on which readers can search for old shipmates, notify deaths and reunions or ask a qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council. Portsmouth is the most densely populated city in the United Kingdom, with a population last recorded at 208,100. Portsmouth is located south-west of London and south-east of Southampton. Portsmouth is mostly located on Portsea Island; the only English city not on the mainland of Great Britain. Portsea Island has the third highest population in the British Isles after the islands of Great Britain and Ireland. Portsmouth also forms part of the regional South Hampshire conurbation, which includes the city of Southampton and the boroughs of Eastleigh, Fareham, Gosport, Havant and Waterlooville. Portsmouth is one of the world's best known ports, its history can be traced to Roman times and has been a significant Royal Navy dockyard and base for centuries. Portsm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymouth's early history extends to the Bronze Age when a first settlement emerged at Mount Batten. This settlement continued as a trading post for the Roman Empire, until it was surpassed by the more prosperous village of Sutton founded in the ninth century, now called Plymouth. In 1588, an English fleet based in Plymouth intercepted and defeated the Spanish Armada. In 1620, the Pilgrim Fathers departed Plymouth for the New World and established Plymouth Colony, the second English settlement in what is now the United States of America. During the English Civil War, the town was held by the Roundhead, Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646. Throughout the Industrial Revolution, Plymouth grew as a commercial shipping port, handling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnes Weston
Dame Agnes Elizabeth Weston, GBE (26 March 1840 – 23 October 1918), also known as Aggie Weston, was an English philanthropist noted for her work with the Royal Navy. For over twenty years, she lived and worked among the sailors of the Royal Navy. The result of her powerful influence is evidenced in the widespread reform which took place in the habits of hundreds of men to whom her name was a talisman for good. In her day, one man in six in the navy was a total abstainer. Weston's work included her monthly letters to sailors, ''Ashore and Afloat'', which she edited, and the "Sailors' Rests", which she established in Portsmouth. She was the first woman given a full ceremonial Royal Navy funeral. Early life Weston was born on 26 March 1840 in London, the daughter of a barrister. In 1851 she, her mother and siblings were living in Weston, Bath. She was influenced from her teenage years onward by the Reverend James Fleming, curate of St Stephen, Lansdown, in the parish of Walcot, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weston-Super-Mare
Weston-super-Mare, also known simply as Weston, is a seaside town in North Somerset, England. It lies by the Bristol Channel south-west of Bristol between Worlebury Hill and Bleadon Hill. It includes the suburbs of Mead Vale, Milton, Oldmixon, West Wick, Worlebury, Uphill and Worle. Its population at the 2011 census was 76,143. Since 1983, Weston has been twinned with Hildesheim in Germany. The local area has been occupied since the Iron Age. It was still a small village until the 19th century when it developed as a seaside resort. A railway station and two piers were built. In the second half of the 20th century it was connected to the M5 motorway but the number of people holidaying in the town declined and some local industries closed, although the number of day visitors has risen. Attractions include The Helicopter Museum, Weston Museum, and the Grand Pier. Cultural venues include The Playhouse, the Winter Gardens and the Blakehay Theatre. The Bristol Channel has a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-frequency Direction Finding
High-frequency direction finding, usually known by its abbreviation HF/DF or nickname huff-duff, is a type of radio direction finder (RDF) introduced in World War II. High frequency (HF) refers to a radio band that can effectively communicate over long distances; for example, between U-boats and their land-based headquarters. HF/DF was primarily used to catch enemy radios while they transmitted, although it was also used to locate friendly aircraft as a navigation aid. The basic technique remains in use to this day as one of the fundamental disciplines of signals intelligence, although typically incorporated into a larger suite of radio systems and radars instead of being a stand-alone system. Earlier systems used a mechanically rotated antenna or solenoid and an operator listening for peaks or nulls in the signal, which often took considerable time to determine the bearing on the order of a minute or more. Later systems used a set of antennas to receive the same signal in slightly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
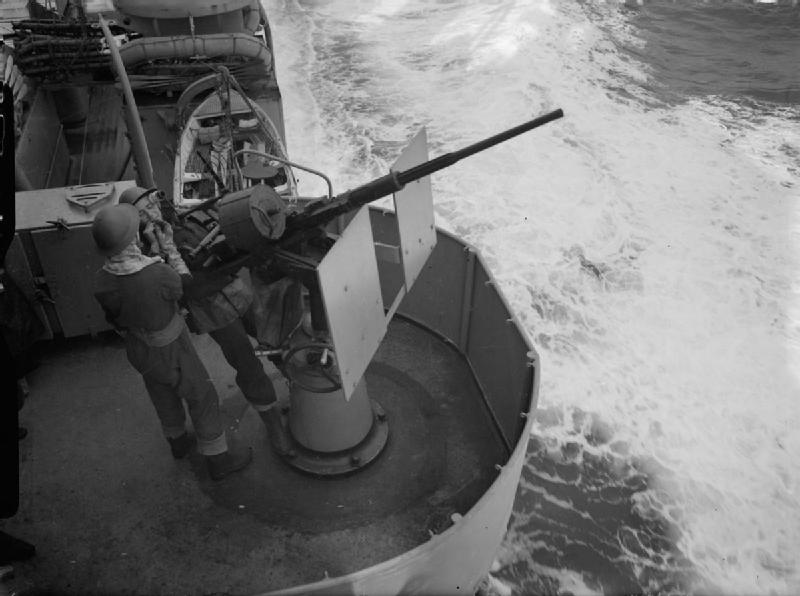
Oerlikon 20 Mm
The Oerlikon 20 mm cannon is a series of autocannons, based on an original German Becker Type M2 20 mm cannon design that appeared very early in World War I. It was widely produced by Oerlikon Contraves and others, with various models employed by both Allied and Axis forces during World War II. Many versions of the cannon are still used today. Blowback-operated models History Origins During World War I, the German industrialist Reinhold Becker developed a 20 mm caliber cannon, known now as the 20 mm Becker using the advanced primer ignition blowback (API blowback) method of operation. This used a 20×70mmRB cartridge and had a cyclic rate of fire of 300 rpm. It was used on a limited scale as an aircraft gun on ''Luftstreitkräfte'' warplanes, and an anti-aircraft gun towards the end of that war. Because the Treaty of Versailles banned further production of such weapons in Germany, the patents and design works were transferred in 1919 to the Swiss firm SEMAG (''Seeba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennant Number
In the Royal Navy and other navies of Europe and the Commonwealth of Nations, ships are identified by pennant number (an internationalisation of ''pendant number'', which it was called before 1948). Historically, naval ships flew a flag that identified a flotilla or type of vessel. For example, the Royal Navy used a red burgee for torpedo boats and a pennant with an H for torpedo boat destroyers. Adding a number to the type-identifying flag uniquely identified each ship. In the current system, a letter prefix, called a ''flag superior'', identifies the type of ship, and numerical suffix, called a flag inferior, uniquely identifies an individual ship. Not all pennant numbers have a flag superior. Royal Navy systems The Royal Navy first used pennants to distinguish its ships in 1661 with a proclamation that all of his majesty's ships must fly a union pennant. This distinction was further strengthened by a proclamation in 1674 which forbade merchant vessels from flying any pennants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



2009.jpg)