|
HMS Serapis (1782)
HMS Serapis was a fifth-rate ship of the Roebuck class designed by Sir Thomas Slade for use in the shallow coastal waters around North America. She was ordered for the Royal Navy in 1780, during the American Revolutionary War, and was 886 tons (bm) as built. When fully armed, she would have a battery of 20 x long guns on the lower deck and 22 x guns on the upper deck, but much of her service was as a transport or storeship, carrying only the 12 pound guns on her upper deck. Her first commission was brief, lasting from December 1782 to April 1783, and she did not serve again until the French Revolutionary War, when she was fitted as a storeship and sent to the West Indies. Following a spell in the Mediterranean, ''Serpais'' returned home with sick and injured on 24 May 1797, where she was immediately caught up in the fleet mutiny at the Nore. Unwilling paticipants, the crew slipped the anchor and drifted away undercover of darkness on 5 June. In March 1804, ''Serapis'' wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nore
The Nore is a long bank of sand and silt running along the south-centre of the final narrowing of the Thames Estuary, England. Its south-west is the very narrow Nore Sand. Just short of the Nore's easternmost point where it fades into the channels it has a notable point once marked by a lightship on the line where the estuary of the Thames nominally becomes the North Sea. A lit buoy today stands on this often map-marked divisor: between Havengore Creek in east Essex and Warden Point on the Isle of Sheppey in Kent. Until 1964 it marked the seaward limit of the Port of London Authority. As the sandbank was a major hazard for shipping coming in and out of London, in 1732 it received the world's first lightship. This became a major landmark, and was used as an assembly point for shipping. Today it is marked by Sea Reach No. 1 Buoy. The Nore is an anchorage, or open roadstead, used by the Royal Navy's North Sea Fleet, and to its local Command. It was the site of a notorious mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
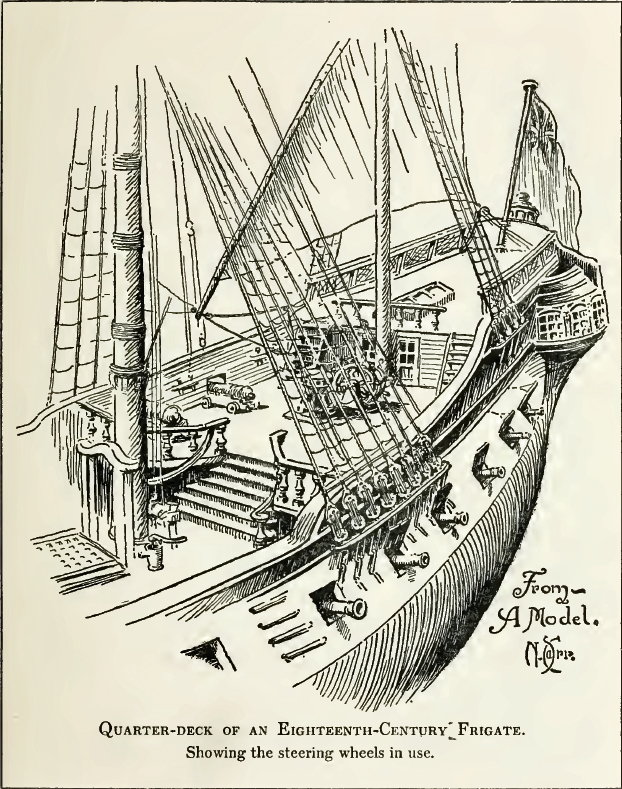
Quarter Deck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on board, and the word is still used to refer to such an area on a ship or even in naval establishments on land. Many such facilities have areas decorated like shipboard quarterdecks. In the 20th century the word came to be applied to the area at the stern of the ship, often (on naval vessels) used for secondary weapons and (on battleships) seaplane catapults. In modern military designs the stern has been roofed over by the helicopter deck but a large space remains underneath which is typically used for sonar equipment or small boats and which is still referred to as the quarterdeck in Commonwealth navies. Ceremonial use There are ancient traditions of offering special deference to the quarterdeck. Greek, Roman, and Carthaginian warships all c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-decker
A two-decker is a sail warship which carried her guns on two fully armed decks. Usually additional guns were carried on the upper works (forecastle and quarterdeck), but this was not a continuous battery and thus not counted as a full gun deck. Two-deckers ranged all the way from the small 40-gun Fifth rate up to 80- or even 90-gun ships of the line, with the third-rate of seventy-four guns, or " seventy-four", being the archetype. See also *Three-decker A three-decker was a sailing warship which carried her principal carriage-mounted guns on three fully armed decks. Usually additional (smaller) guns were carried on the upper works (forecastle and quarterdeck), but this was not a continuous b ... Naval sailing ship types {{navy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Of Hold
Depth(s) may refer to: Science and mathematics * Three-dimensional space * Depth (ring theory), an important invariant of rings and modules in commutative and homological algebra * Depth in a well, the measurement between two points in an oil well * Color depth (or "number of bits" or "bit depth"), in computer graphics * Market depth, in financial markets, the size of an order needed to move the market a given amount * Moulded depth, a nautical measurement * Sequence depth, or coverage, in genetic sequencing * Depth (coordinate), a type of vertical distance * Tree depth Art and entertainment * ''Depth'' (video game), an Indie video game * ''Depths'' (novel), a 2004 novel by Henning Mankell * ''Depths'' (Oceano album), 2009 * ''Depths'' (Windy & Carl album), 1998 * "Depths" (''Law & Order: Criminal Intent''), an episode of ''Law & Order: Criminal Intent'' * ''Depth'', the Japanese title for the PlayStation game released in Europe under the name ''Fluid'' * Depth, an as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer extremities of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship (or boat), the more initial stability it has, at the expense of secondary stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position. A ship that heels on her ''beam ends'' has her deck beams nearly vertical. Typical values Typical length-to-beam ratios ( aspect ratios) for small sailboats are from 2:1 (dinghies to trailerable sailboats around ) to 5:1 (racing sailboats over ). Large ships have widely varying beam ratios, some as large as 20:1. Rowing shells designed for flatwater racing may have length to beam ratios as high as 30:1, while a cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in South West England. The wider Bristol Built-up Area is the eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom. Iron Age hillforts and Roman villas were built near the confluence of the rivers Frome and Avon. Around the beginning of the 11th century, the settlement was known as (Old English: 'the place at the bridge'). Bristol received a royal charter in 1155 and was historically divided between Gloucestershire and Somerset until 1373 when it became a county corporate. From the 13th to the 18th century, Bristol was among the top three English cities, after London, in tax receipts. A major port, Bristol was a starting place for early voyages of exploration to the New World. On a ship out of Bristol in 1497, John Cabot, a Venetia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilhouse
Hilhouse (also spelled ''Hillhouse'') was a shipbuilder in Bristol, England, who built merchantman and men-of-war during the 18th and 19th centuries. The company subsequently became Charles Hill & Sons in 1845. The company, and its successor Charles Hill & Sons, were the most important shipbuilders in Bristol, and taking the concern together built over 560 ships over their 200 years of existence. History Origins The shipbuilding concern Hilhouse and Company was first established in 1772 by James Martin Hilhouse (1749–1822), after inheriting a fortune from his father, James Hilhouse, a Bristol Sheriff and councillor who also ran a successful privateering venture. The company acquired the large Hotwells drydock, built by the engineer William Champion in 1765 on the north side of the River Avon, to build merchantman and undertake ship repair work. From 1778, Hilhouse secured Admiralty contracts for warships following the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel Laying
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship. Keel laying is one of the four specially celebrated events in the life of a ship; the others are launching, commissioning and decommissioning. In earlier times, the event recognized as the keel laying was the initial placement of the central timber making up the backbone of a vessel, called the keel. As steel ships replaced wooden ones, the central timber gave way to a central steel beam. Modern ships are most commonly built in a series of pre-fabricated, complete hull sections rather than around a single keel. The event recognized as the keel laying is the first joining of modular components, or the lowering of the first module into place in the building dock. It is now often called "keel authentication", and is the ceremonial beginning of the ship's life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiralty In The 18th Century
The Glorious Revolution of 1688 rearranged the political map of Europe, and led to a series of wars with France that lasted well over a century. This was the classic age of sail; while the ships themselves evolved in only minor ways, technique and tactics were honed to a high degree, and the battles of the Napoleonic Wars entailed feats that would have been impossible for the fleets of the 17th century. Because of parliamentary opposition, James II fled the country. The landing of William III and the Glorious Revolution itself was a gigantic effort involving 100 warships and 400 transports carrying 11,000 infantry and 4,000 horses. It was not opposed by the English or Scottish fleets. Historical overview Naval operations in the War of the Spanish Succession (1702–13) were with the Dutch against the Spanish and French. They were at first focused on the acquisition of a Mediterranean base, culminating in an alliance with Portugal and the capture of Gibraltar (1704) and Port Mah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermuda
) , anthem = "God Save the King" , song_type = National song , song = " Hail to Bermuda" , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , mapsize2 = , map_caption2 = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title2 = English settlement , established_date2 = 1609 (officially becoming part of the Colony of Virginia in 1612) , official_languages = English , demonym = Bermudian , capital = Hamilton , coordinates = , largest_city = Hamilton , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2016 , government_type = Parliamentary dependency under a constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Rena Lalgie , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Edward David Burt , legislature = Parliament , upper_house = Senate , lower_house = House of Assembly , area_km2 = 53.2 , area_sq_mi = 20.54 , area_rank = , percent_water = 27 , elevation_max_m = 79 , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walcheren Expedition
The Walcheren Campaign ( ) was an unsuccessful British expedition to the Netherlands in 1809 intended to open another front in the Austrian Empire's struggle with France during the War of the Fifth Coalition. Sir John Pitt, 2nd Earl of Chatham, was the commander of the expedition, with the missions of capturing Flushing and Antwerp in the Netherlands and enabling navigation of the Scheldt River. Some 39,000 soldiers, 15,000 horses together with field artillery and two siege trains crossed the North Sea and landed at Walcheren on 30July. This was the largest British expedition of that year, larger than the army serving in the Peninsular War in Portugal. Nevertheless, it failed to achieve any of its goals. The Walcheren Campaign involved little fighting, but heavy losses from the sickness popularly dubbed "Walcheren Fever". Although more than 4,000 British troops died during the expedition, only 106 died in combat; the survivors withdrew on 9December. Background In July 1809, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)

