|
HMS Proteus (N29)
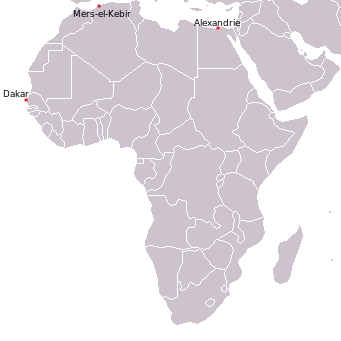
HMS ''Proteus'' was a Parthian class submarine, ''Parthian''-class submarine designed and built by Vickers Shipbuilding and Engineering in Barrow-in-Furness for the Royal Navy. She was laid down on 18 July 1928, launched on 22 August 1929 and completed on 17 June 1930. Like other submarines in her class she served on the China Station before the war. In the Second World War, mainly based at Alexandria in the Mediterranean, ''Proteus'' sank 15 enemy vessels and damaged several others during her service. Wartime service In July 1939, ''Proteus'' began a refit at Singapore Naval Base. After trials, she arrived in Hong Kong in January 1940 where she carried out her first war patrol, before being ordered to the Mediterranean on 2 April, arriving in Alexandria on 3 May. On 4 July 1940 in the aftermath of the British attack on Mers-el-Kébir, ''Proteus'' torpedoed and sank the Vichy , An Admiralty order that French ships were not to be attacked except in self-defence was not received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Shipbuilding And Engineering
Vickers Shipbuilding and Engineering, Ltd (VSEL) was a shipbuilding company based at Barrow-in-Furness, Cumbria in northwest England that built warships, civilian ships, submarines and armaments. The company was historically the Naval Construction Works of Vickers Armstrongs and has a heritage of building large naval warships and armaments. Through a complicated history the company's shipbuilding division is now BAE Systems Submarine Solutions and the armaments division is now part of BAE Systems Land & Armaments. History The company was founded in 1871 by James Ramsden as the Iron Shipbuilding Company, but its name was soon changed to Barrow Shipbuilding Company. In 1897, ''Vickers & Sons'' bought the ''Barrow Shipbuilding Company'' and its subsidiary the ''Maxim Nordenfelt Guns and Ammunition Company'', becoming ''Vickers, Sons and Maxim, Limited''. The shipyard at Barrow became the Naval Construction & Armaments Company. In 1911 the company was renamed ''Vickers Ltd'', and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack On Mers-el-Kébir
The Attack on Mers-el-Kébir (Battle of Mers-el-Kébir) on 3 July 1940, during the Second World War, was a British naval attack on neutral French Navy ships at the naval base at Mers El Kébir, near Oran, on the coast of French Algeria. The attack was the main part of Operation Catapult, a British plan to neutralise or destroy neutral French ships to prevent them from falling into German hands after the Allied defeat in the Battle of France. The British bombardment of the base killed 1,297 French servicemen, sank a battleship and damaged five other ships, for a British loss of five aircraft shot down and two crewmen killed. The attack by air and sea was conducted by the Royal Navy, after France had signed armistices with Germany and Italy, coming into effect on 25 June. Of particular significance to the British were the five battleships of the and es and the two fast battleships of the , the second largest force of capital ships in Europe after the Royal Navy. The British War Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Clyde
The River Clyde ( gd, Abhainn Chluaidh, , sco, Clyde Watter, or ) is a river that flows into the Firth of Clyde in Scotland. It is the ninth-longest river in the United Kingdom, and the third-longest in Scotland. It runs through the major city of Glasgow. Historically, it was important to the British Empire because of its role in shipbuilding and trade. To the Romans, it was , and in the early medieval Cumbric language, it was known as or . It was central to the Kingdom of Strathclyde (). Etymology The exact etymology of the river's name is unclear, though it is known that the name is ancient: It was called or by the Britons and by the Romans. It is therefore likely that the name comes from a Celtic language—most likely Old British. But there is more than one old Celtic word that the river's name could plausibly derive from. One possible root is the Common Brittonic , meaning 'loud' or 'loudly'. More likely, the river was named after a local Celtic goddess, '' Clōta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonport Naval Base
Devonport Naval Base is the home of the Royal New Zealand Navy, located at Devonport, New Zealand on Auckland's North Shore. It is currently the only base of the navy that operates ships, and has been in use as a navy base since 1841. The base consists of HMNZS ''Philomel'' (the administration centre for the base), the Fleet Support Organisation, and the Fleet Personnel and Training Organisation. Operation All operational units of the Royal New Zealand Navy are based at Devonport. The Navy's munitions are stored and maintained at Kauri Point Armament Depot in Auckland. Senior naval staff are located at the NZDF headquarters in Wellington. The operational headquarters, and the effective fleet commander, the Maritime Component Commander are both located at Headquarters Joint Forces New Zealand adjacent to Trentham Military Camp in the Upper Hutt suburb of Trentham. Within the Royal New Zealand Navy many land-based facilities and services ensure support for ships and pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diving Plane
Diving planes, also known as hydroplanes, are control surfaces found on a submarine which allow the vessel to pitch its bow and stern up or down to assist in the process of submerging or surfacing the boat, as well as controlling depth when submerged. Bow and stern planes Diving planes are usually fitted in two pairs, the '' bow planes'' at the front of the submarine and the ''stern planes'' at the rear. The stern planes function in much the same way as an aircraft's elevator. As the planes are a long distance fore-and-aft from the hull's centre of buoyancy, they introduce a pitching moment. Ballast tanks within the submarine adjust buoyancy to be neutral, making the boat controllable. The position of the planes controls the pitch of the boat and, with the forward motion of the boat, this controls depth. If not carefully controlled, this could lead to a 'porpoising' motion whereby the planesman continually hunts for a stable combination of depth and pitch. For easier berth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramming
In warfare, ramming is a technique used in air, sea, and land combat. The term originated from battering ram, a siege weapon used to bring down fortifications by hitting it with the force of the ram's momentum, and ultimately from male sheep. Thus, in warfare, ramming refers to hitting a target by running oneself into the target. Today, hand-held battering rams are one tool among many used by law enforcement and military personnel for door breaching. Forcible entry by criminals has been implemented using such methods as Ram-raiding, vehicles rammed into buildings. Naval warfare Navies in antiquity commonly used the ram: the "beak" ( la , rostrum) became an important part of the armament of the galleys of Imperial Rome. The Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks used their trireme vessels for ramming as well. In History of China#Ancient China, ancient China, rams were largely unknown, as the lack of a keel and the flat shape of the junk (ship), junk's bow was not conducive to constructi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lefkada
Lefkada ( el, Λευκάδα, ''Lefkáda'', ), also known as Lefkas or Leukas (Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: Λευκάς, ''Leukás'', modern pronunciation ''Lefkás'') and Leucadia, is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea on the west coast of Greece, connected to the mainland by a long causeway and floating bridge. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Lefkada. It is situated on the northern part of the island, approximately 25 minutes by automobile away from Aktion National Airport. The island is part of the regional unit of Lefkada. Geography Lefkada measures from north to south, and from east to west. The area of the island is about , the area of the municipality (including the islands Kalamos, Kastos and several smaller islets) is . Its highest point is the mountain Stavrota, above sea level, situated in the middle of the island. The east coast section of the island has small resorts of Lygia, Nikiana and Perigiali, all north of Nidri, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hm Submarine Proteus, Returns Home With A Record Of Her Mediterranean Successes
HM or hm may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''HM'' (magazine), a Christian hard rock magazine * Hidden Machine, a type of item in Pokémon Businesses * H&M, a Swedish clothing company * Hindustan Motors, an automobile manufacturer of India * Air Seychelles (IATA airline code) Other uses * Heard Island and McDonald Islands (ISO 3166 digram and FIPS PUB 10-4 territory code) ** .hm, the Internet country code top-level domain ostensibly for the above * Hectometre, hm, an SI unit of length * Henry Molaison Henry Gustav Molaison (February 26, 1926 – December 2, 2008), known widely as H.M., was an American who had a bilateral medial temporal lobe, temporal lobectomy to surgically resect the anterior two thirds of his Hippocampus, hippocampi, p ..., aka Patient H.M., a man with anterograde amnesia * His or Her Majesty, a form of address for various monarchs * Hindley–Milner type system, in mathematics * Hospital corpsman, in the United States Navy * Sisters of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Loch
The Holy Loch ( gd, An Loch Sianta/Seunta) is a sea loch, a part of the Cowal peninsula coast of the Firth of Clyde, in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. The "Holy Loch" name is believed to date from the 6th century, when Saint Munn landed there after leaving Ireland. Kilmun Parish Church and Argyll Mausoleum is said to stand where Saint Munn's church was once located. Robertson's Yard at Sandbank, a village on the loch, was a major wooden boat building company in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. During World War II, the loch was used as a British Royal Navy submarine base. From 1961 to 1992, it was used as a United States Navy ballistic missile submarine base. In 1992, the Holy Loch base was deemed unnecessary following the demise of the Soviet Union and subsequently closed. Geography Open on the Firth of Clyde at its eastern end, the Sea Loch is approximately wide and between long, varying with the tide. The town of Dunoon on the Cowal peninsula lies on the shores of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth Naval Base
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is located on the eastern shore of Portsmouth Harbour, north of the Solent and the Isle of Wight. Until the early 1970s, it was officially known as Portsmouth Royal Dockyard (or HM Dockyard, Portsmouth); thereafter the term 'Naval Base' gained currency, acknowledging a greater focus on personnel and support elements alongside the traditional emphasis on building, repairing and maintaining ships. In 1984 Portsmouth's Royal Dockyard function was downgraded and it was formally renamed the 'Fleet Maintenance and Repair Organisation' (FMRO). The FMRO was privatized in 1998, and for a time (from 2002 to 2014), shipbuilding, in the form of block construction, returned. Around 2000, the designation HMS ''Nelson'' (which until then had been specific to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–Libya border, the south, Niger to Libya–Niger border, the southwest, Algeria to Algeria–Libya border, the west, and Tunisia to Libya–Tunisia border, the northwest. Libya is made of three historical regions: Tripolitania, Fezzan, and Cyrenaica. With an area of almost 700,000 square miles (1.8 million km2), it is the fourth-largest country in Africa and the Arab world, and the List of countries and outlying territories by total area, 16th-largest in the world. Libya has the List of countries by proven oil reserves, 10th-largest proven oil reserves in the world. The largest city and capital, Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli, is located in western Libya and contains over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



