|
HMS Hyaena (1778)
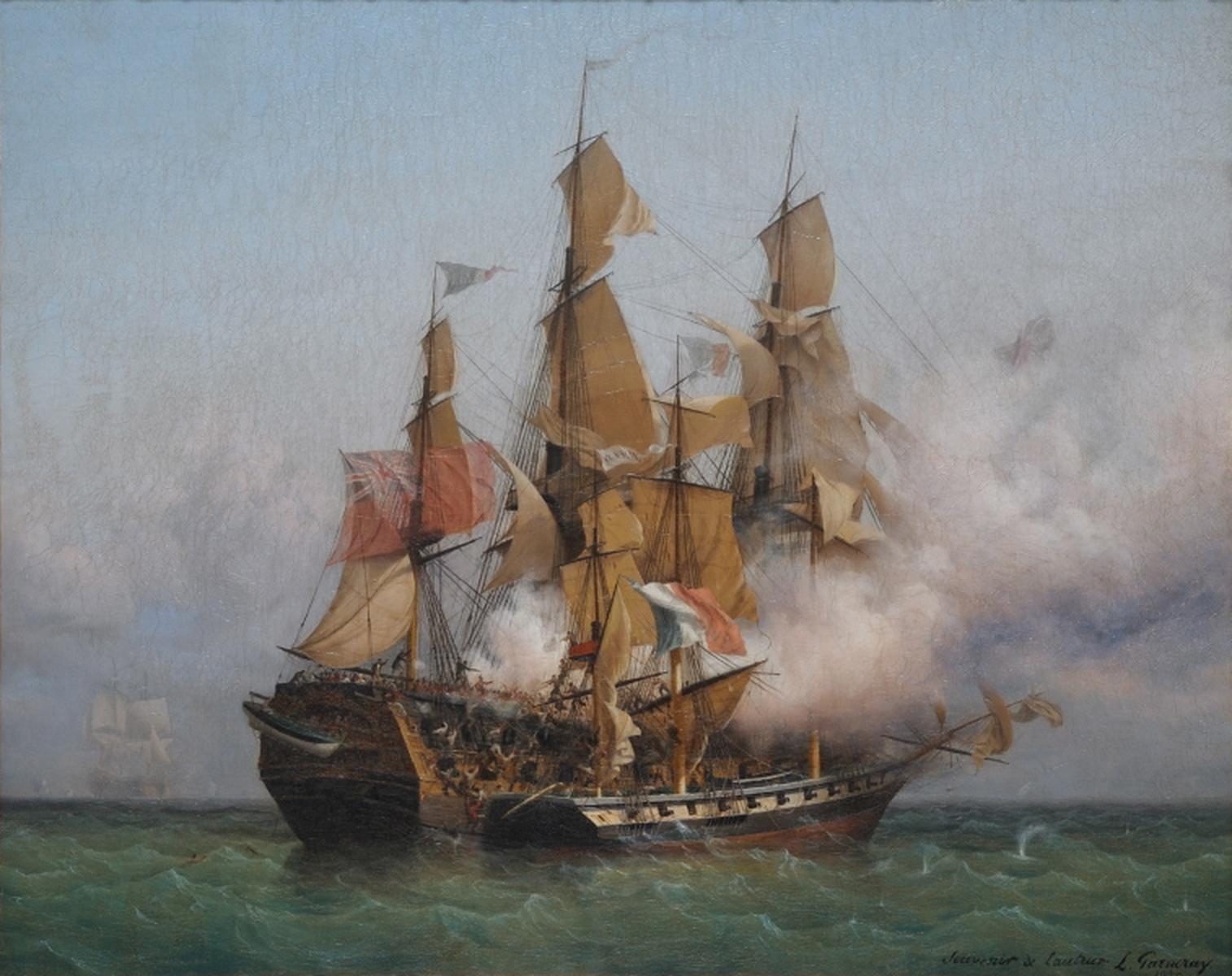
HMS ''Hyaena'' (HMS ''Hyæna'') was a 24-gun ''Porcupine''-class post-ship of the Royal Navy launched in 1778. The French captured her in 1793, took her into service as ''Hyène'', and then sold her. She became a privateer that the British captured in 1797. The Royal Navy took her back into service as ''Hyaena'' and she continued to serve until the Navy sold her in 1802. The ship's new owner, Daniel Bennett, renamed her ''Recovery''. Between 802 and 1813, she made seven voyages as a whaler in the British southern whale fishery. She was broken up later in 1813. Early service Launched in March 1778, she was commissioned in January 1779 for service in British home waters and the Caribbean, under the command of Captain Edward Thompson. She saw active service in the blockade and capture of French-controlled Gorée in April 1779, and eight months later was part of Admiral George Rodney's fleet which sailed to the naval relief of Gibraltar in January 1780. ''Hyaena'' then retur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil And Naval Ensign Of France
Civil may refer to: *Civic virtue, or civility *Civil action, or lawsuit *Civil affairs *Civil and political rights *Civil disobedience *Civil engineering *Civil (journalism), a platform for independent journalism *Civilian, someone not a member of armed forces *Civil law (other), multiple meanings *Civil liberties *Civil religion *Civil service *Civil society *Civil war *Civil (surname) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Maritime Museum
The National Maritime Museum (NMM) is a maritime museum in Greenwich, London. It is part of Royal Museums Greenwich, a network of museums in the Maritime Greenwich World Heritage Site. Like other publicly funded national museums in the United Kingdom, it has no general admission charge; there are admission charges for most side-gallery temporary exhibitions, usually supplemented by many loaned works from other museums. Creation and official opening The museum was created by the National Maritime Museum Act 1934 under a Board of Trustees, appointed by HM Treasury. It is based on the generous donations of Sir James Caird (1864–1954). King George VI formally opened the museum on 27 April 1937 when his daughter Princess Elizabeth accompanied him for the journey along the Thames from London. The first director was Sir Geoffrey Callender. Collection Since the earliest times Greenwich has had associations with the sea and navigation. It was a landing place for the Romans, Henry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deptford Dockyard
Deptford Dockyard was an important naval dockyard and base at Deptford on the River Thames, operated by the Royal Navy from the sixteenth to the nineteenth centuries. It built and maintained warships for 350 years, and many significant events and ships have been associated with it. Founded by Henry VIII in 1513, the dockyard was the most significant royal dockyard of the Tudor period and remained one of the principal naval yards for three hundred years. Important new technological and organisational developments were trialled here, and Deptford came to be associated with the great mariners of the time, including Francis Drake and Walter Raleigh. The yard expanded rapidly throughout the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, encompassing a large area and serving for a time as the headquarters of naval administration, and the associated Victualling Yard became the Victualling Board's main depot. Tsar Peter the Great visited the yard officially incognito in 1698 to learn shipbuildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Copenhagen (1801)
The Battle of Copenhagen of 1801 (Danish: ''Slaget på Reden''), also known as the First Battle of Copenhagen to distinguish it from the Second Battle of Copenhagen in 1807, was a naval battle in which a British fleet fought and defeated a smaller force of the Dano-Norwegian Navy anchored near Copenhagen on 2 April 1801. The battle came about over British fears that the powerful Danish fleet would ally with France, and a breakdown in diplomatic communications on both sides. As the British ships entered the harbour of the Danish fleet, several of its ships stationed in the city's inlet forming a blockade. The Danish fleet defended the capital with these ships and bastions on both sides of the harbour inlet. It was the second attempt by the British to try to prevent a Franco-Danish alliance, as the British had already entered Øresund with a fleet in August 1800, in order to persuade Denmark not to ally with France. The Danes agreed to the British terms upon hearing news of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval General Service Medal (1847)
__NOTOC__ The Naval General Service Medal (NGSM) was a campaign medal approved in 1847, and issued to officers and men of the Royal Navy in 1849. The final date for submitting claims was 1 May 1851.British Battles and Medals, page 34. Admiral Thomas Bladen Capel was one of the members of the board that authorised the medal. The NGSM was awarded retrospectively for various naval actions during the period 1793–1840, a period that included the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars and the Anglo-American War of 1812. Each battle or campaign covered by the medal was represented by a clasp on the ribbon. The medal was never issued without a clasp, 231 of which were sanctioned.British Battles and Medals, page 33. The clasps covered a variety of actions, from boat service, ship to ship skirmishes, to major fleet actions such as the Battle of Trafalgar. This medal and its army counterpart, the Military General Service Medal, were amongst the first real British campaign medals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Île De Batz
The Île de Batz ( br, Enez Vaz) is an island off Roscoff in Brittany, France. Administratively, it is a commune in the Finistère department of Brittany in north-western France. Climate Île de Batz has a oceanic climate ( Köppen climate classification ''Cfb''). The average annual temperature in Île de Batz is . The average annual rainfall is with December as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around , and lowest in February, at around . The highest temperature ever recorded in Île de Batz was on 18 August 1932; the coldest temperature ever recorded was on 14 February 1929 and 18 December 1927. Population Inhabitants of Île-de-Batz are called in French ''Batziens'' or ''Îliens''. At the census of 1999 the island had a population of 575, and in 2005 it had an estimated population of 594. Sights *Jardin Georges Delaselle *Lighthouse A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Malo
Saint-Malo (, , ; Gallo: ; ) is a historic French port in Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany, on the English Channel coast. The walled city had a long history of piracy, earning much wealth from local extortion and overseas adventures. In 1944, the Allies heavily bombarded Saint-Malo, which was garrisoned by German troops. The city changed into a popular tourist centre, with a ferry terminal serving the Channel Islands of Jersey and Guernsey, as well as the Southern English settlements of Portsmouth, Hampshire and Poole, Dorset. The famous transatlantic single-handed yacht race Route du Rhum, which takes place every four years in November, is between Saint Malo and Pointe-à-Pitre in Guadeloupe. Population The population in 2017 was 46,097 – though this can increase to up to 300,000 in the summer tourist season. With the suburbs included, the metropolitan area's population is approximately 133,000 (2017). The population of the commune more than doubled in 1967 with the merging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as a letter of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes, and taking prize crews as prisoners for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Privateering allowed sovereigns to raise revenue for war by mobilizing privately owned armed ships and sailors to supplement state power. For participants, privateerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flush-deck
Flush deck is a term in naval architecture. It can refer to any deck of a ship which is continuous from stem to stern. History The flush deck design originated with rice ships built in Bengal Subah, Mughal India (modern Bangladesh), resulting in hulls that were stronger and less leak-prone than stepped deck ships.. This was a key innovation in shipbuilding. The British East India Company duplicated the flush deck design in the 1760s, leading to significant improvements in seaworthiness of British ships during the Industrial Revolution. Two different meanings of "flush" "Flush deck" with "flush" in its generic meaning of "even or level; forming an unbroken plane", is sometimes applied to vessels, as in describing yachts lacking a raised pilothouse for instance. "Flush deck aircraft carrier" uses "flush deck" in this generic sense. "Flush deck" in its more specific maritime-architecture sense denotes (for instance) the flush deck destroyers described above: the flush decks are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Concorde (1791)
''Concorde'' was a 40-gun frigate of the French Navy. The Royal Navy captured her in August 1800. Service history On 27 May 1793, ''Concorde'' captured the 24-gun ; she became the privateer ''Hyene'', which the Royal Navy recaptured in 1797. ''Concorde'' took part in the Expédition d'Irlande, and on 12 October 1798, in aftermath of the Battle of Tory Island. ''Concorde'' was part of a squadron of three frigates, ''Concorde'' under Commodore Jean-François Landolphe, under Captain Jean-Daniel Coudin, and under Captain Pierre Jurien, with Landolphe as the overall commander, that left Rochefort on 6 March 1799. Eluding the British blockade off Rochefort, the squadron sailed southwards until it reached the coast of West Africa. There, Landolphe's ships began an extended commerce raiding operation, inflicting severe damage on the West African trade. During this time, the squadron captured the Portuguese island of Prince (Príncipe).Fonds, Vol. 1, p.244. Eventually the stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hargood
Admiral of the White Sir William Hargood (6 May 1762 – 12 December 1839) was a British naval officer who served with distinction through the American War of Independence, the French Revolutionary War and the Napoleonic Wars, during which he gained an unfortunate reputation for bad luck, which seemed to reverse following his courageous actions at the battle of Trafalgar in command of HMS ''Belleisle''. Military service Born in 1762 into a Royal Navy Dockyard family, the son of a Clerk of the Survey, Hargood was able to secure a position as a midshipman on HMS ''Triumph'', on which he served from 1775 until the following year, in which time he made a convoy to Newfoundland, and then moved to HMS ''Bristol'' in which he saw the West Indies and American Eastern Seaboard, being heavily in involved in the landing at Fort Moultrie in 1776. In 1781, Hargood was a lieutenant, serving in the sloop HMS ''Port Royal'' when Pensacola fell to the Spanish despite his best efforts to ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Press-gang
Impressment, colloquially "the press" or the "press gang", is the taking of men into a military or naval force by compulsion, with or without notice. European navies of several nations used forced recruitment by various means. The large size of the British Royal Navy in the Age of Sail meant impressment was most commonly associated with Great Britain and Ireland. It was used by the Royal Navy in wartime, beginning in 1664 and during the 18th and early 19th centuries as a means of crewing warships, although legal sanction for the practice can be traced back to the time of Edward I of England. The Royal Navy impressed many merchant sailors, as well as some sailors from other, mostly European, nations. People liable to impressment were "eligible men of seafaring habits between the ages of 18 and 55 years". Non- seamen were sometimes impressed as well, though rarely. In addition to the Royal Navy's use of impressment, the British Army also experimented with impressment from 1778 to 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


_and_USS_Somers_(DD-301)_underway_off_San_Diego%2C_in_1928_(NH_81279).jpg)
