|
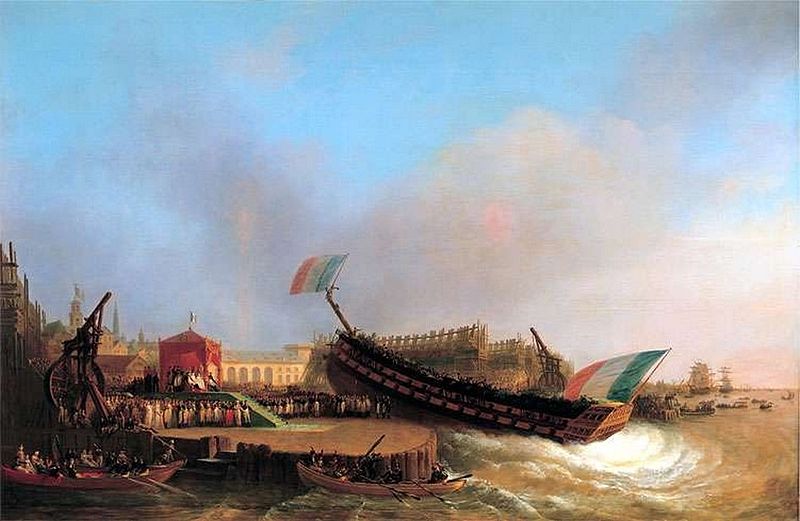
HMS Girdle Ness
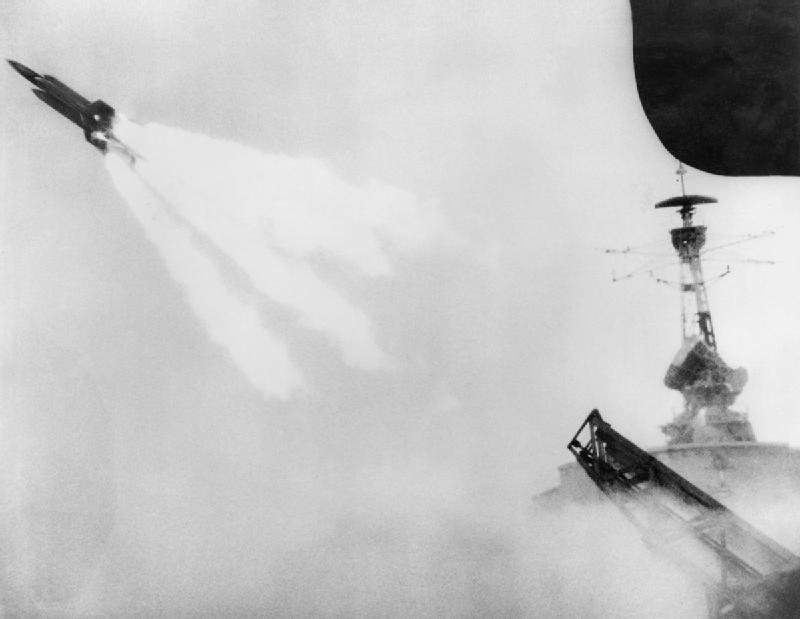
HMS ''Girdle Ness'' was a constructed for the Royal Navy that entered service in 1945. Originally named ''Penlee Point'', the vessel was designed as a maintenance ship for landing craft in the Pacific Theatre of World War II but used as an accommodation ship at Rosyth Dockyard. Renamed ''Girdle Ness'', the ship was taken out of service in 1953 and converted for use in support of missile trials in the development of the Seaslug missile in the early 1960s. After trials of the missile were completed, ''Girdle Ness'' was placed in reserve before becoming an accommodation ship as part of the shore establishment at Rosyth. The vessel was stricken in 1970. Description and early service Following setbacks in the Pacific theatre of operations which led to the loss of naval bases, the Royal Navy required more depot and repair ships for the fleet to replace shore facilities.Mitchell and Sawyer, p. 39 As part of the war construction programme, the Royal Navy ordered a series of vessels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burrard Dry Dock
Burrard Dry Dock Ltd. was a Canadian shipbuilding company headquartered in North Vancouver (city), North Vancouver, British Columbia. Together with the neighbouring North Van Ship Repair yard and the Yarrow Shipbuilders#Yarrows in Canada, Yarrows Ltd. yard in Esquimalt, British Columbia, Esquimalt, which were eventually absorbed, Burrard built over 450 ships, including many warships built and refitted for the Royal Navy and Royal Canadian Navy in the First World War, First and Second World Wars. History * 1894 – Alfred "Andy" Wallace begins building wooden fish boats at False Creek area of Vancouver, British Columbia. These boatworks burned down in 1909 and was abandoned. * 1905 – Wallace Shipyards is incorporated. The following year the company establishes a new, larger shipyard at the foot of Lonsdale Avenue in North Vancouver. * 1911 – July 11, the shipyard is destroyed by fire but is immediately rebuilt. * 1914–18 – During the First World War, Wallace Shipyards is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull (keel). The draught of the vessel is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if deployed. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The related term air draft is the maximum height of any part of the vessel above the water. The more heavily a vessel is loaded, the deeper it sinks into the water, and the greater its draft. After construction, the shipyard creates a table showing how much water the vessel displaces based on its draft and the density of the water (salt or fresh). The draft can also be used to determine the weight of cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water, accounting for the content of the ship's bunkers, and using Archimedes' principle. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMNB Devonport
His Majesty's Naval Base, Devonport (HMNB Devonport) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Portsmouth) and is the sole nuclear repair and refuelling facility for the Royal Navy. The largest naval base in Western Europe, HMNB Devonport is located in Devonport, in the west of the city of Plymouth, England. The base began as Royal Navy Dockyard in the late 17th century, but shipbuilding ceased at Devonport in the early 1970s, although ship maintenance work has continued. The now privatised maintenance facilities are operated by Babcock International Group, who took over the previous owner Devonport Management Limited (DML) in 2007. DML had been running the Dockyard since privatisation in 1987. From 1934 until the early 21st century the naval barracks on the site was named HMS ''Drake'' (it had previously been known as HMS ''Vivid'' after the base ship of the same name). The name HMS ''Drake'' and its c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserve Fleet
A reserve fleet is a collection of naval vessels of all types that are fully equipped for service but are not currently needed; they are partially or fully decommissioned. A reserve fleet is informally said to be "in mothballs" or "mothballed"; an equivalent expression in unofficial modern US naval usage is "ghost fleet". In earlier times, especially in British usage, the ships were said to be "laid up in ordinary". Overview Such ships are held in reserve against a time when it may be necessary to call them back into service. They are usually tied up in backwater areas near naval bases or shipyards in order to speed the reactivation process. They may be modified for storage during such a period, for instance by having rust-prone areas sealed off or wrapped in plastic or, in the case of sailing warships, the masts removed. While being held in the reserve fleet, ships typically have a minimal crew (known informally as a skeleton crew) to ensure that they stay in somewhat usable co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Commissioning
Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to placing a warship in active duty with its country's military forces. The ceremonies involved are often rooted in centuries-old naval tradition. Ship naming and launching endow a ship hull with her identity, but many milestones remain before she is completed and considered ready to be designated a commissioned ship. The engineering plant, weapon and electronic systems, galley, and other equipment required to transform the new hull into an operating and habitable warship are installed and tested. The prospective commanding officer, ship's officers, the petty officers, and seamen who will form the crew report for training and familiarization with their new ship. Before commissioning, the new ship undergoes sea trials to identify any deficiencies needing corre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceremonial Ship Launching
Ceremonial ship launching involves the performance of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back thousands of years, to accompany the physical process with ceremonies which have been observed as public celebration and a solemn blessing, usually but not always, in association with the launch itself. Ship launching imposes stresses on the ship not met during normal operation and, in addition to the size and weight of the vessel, represents a considerable engineering challenge as well as a public spectacle. The process also involves many traditions intended to invite good luck, such as christening by breaking a sacrificial bottle of champagne over the bow as the ship is named aloud and launched. Methods There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching". The oldest, most familiar, and most widely used is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel Laying
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship. Keel laying is one of the four specially celebrated events in the life of a ship; the others are launching, commissioning and decommissioning. In earlier times, the event recognized as the keel laying was the initial placement of the central timber making up the backbone of a vessel, called the keel. As steel ships replaced wooden ones, the central timber gave way to a central steel beam. Modern ships are most commonly built in a series of pre-fabricated, complete hull sections rather than around a single keel. The event recognized as the keel laying is the first joining of modular components, or the lowering of the first module into place in the building dock. It is now often called "keel authentication", and is the ceremonial beginning of the ship's life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Ship
An auxiliary ship is a naval ship designed to support combatant ships and other naval operations. Auxiliary ships are not primary combatant vessels, though they may have some limited combat capacity, usually for purposes of self-defense. Auxiliary ships are extremely important for navies of all sizes because if they were not present the primary fleet vessels would be unsupported. Thus, virtually every navy maintains an extensive fleet of auxiliary ships. However, the composition and size of these auxiliary fleets vary depending on the nature of each navy and its primary mission. Smaller coastal navies tend to have smaller auxiliary vessels focusing primarily on littoral and training support roles. Larger blue-water navies tend to have larger auxiliary fleets comprising longer-range fleet support vessels designed to provide support far beyond territorial waters. Roles Replenishment One of the most direct ways that auxiliary ships support the fleet is by providing under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
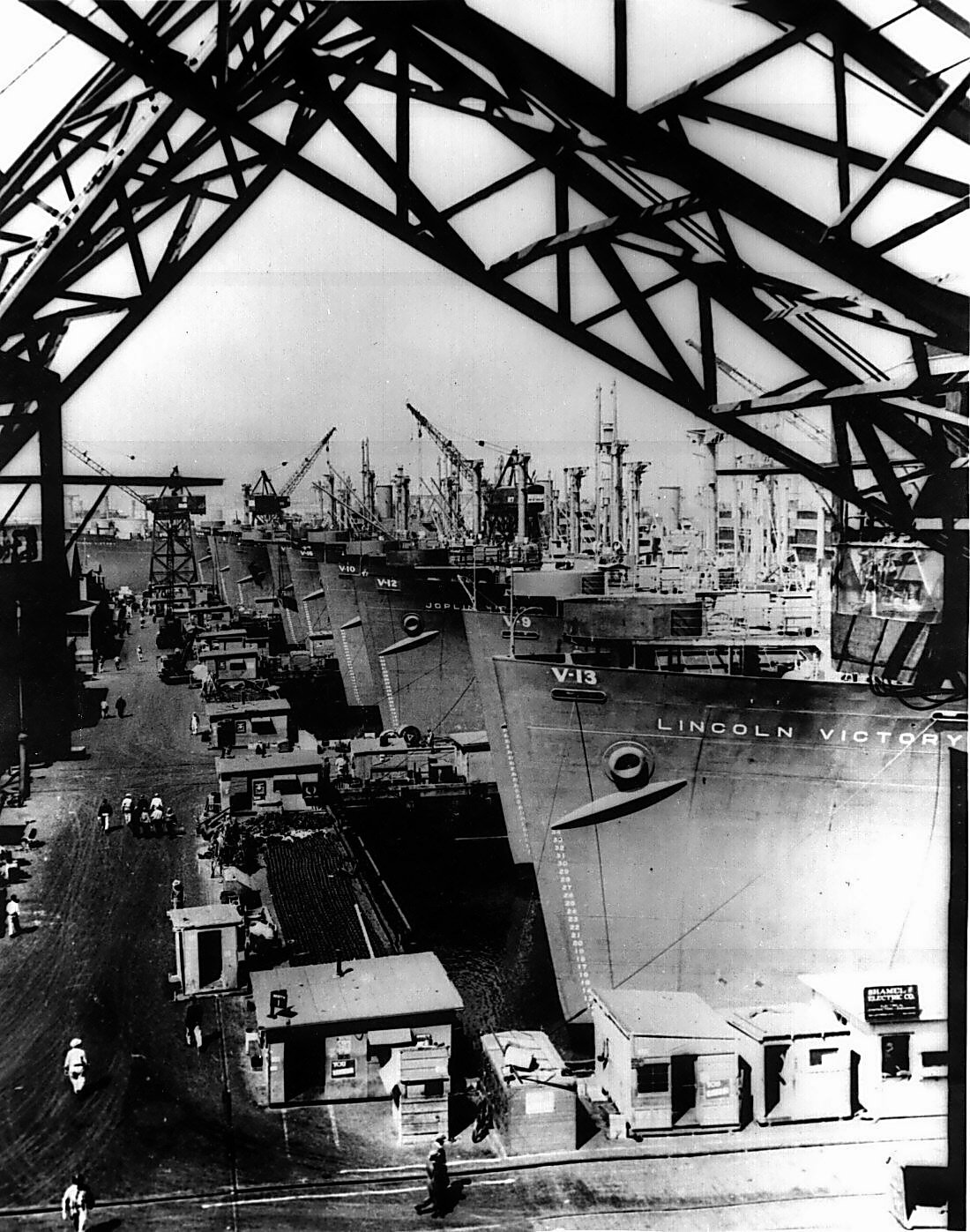
Victory Ship
The Victory ship was a class of cargo ship produced in large numbers by North American shipyards during World War II to replace losses caused by German submarines. They were a more modern design compared to the earlier Liberty ship, were slightly larger and had more powerful steam turbine engines giving higher speed to allow participation in high speed convoys and make them more difficult targets for German U-boats. A total of 531 Victory ships were built in between 1944 and 1946. VC2 design One of the first acts of the United States War Shipping Administration upon its formation in February 1942 was to commission the design of what came to be known as the Victory class. Initially designated EC2-S-AP1, where EC2 = Emergency Cargo, type 2 (Load Waterline Length between ), S = steam propulsion with AP1 = one aft propeller (EC2-S-C1 had been the designation of the Liberty ship design), it was changed to VC2-S-AP1 before the name "Victory Ship" was officially adopted on 28 Apr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Ship
The Fort ships were a class of 198 cargo ships built in Canada during World War II for use by the United Kingdom under the Lend-Lease scheme. They all had names prefixed with "Fort" when built. The ships were in service between 1942 and 1985, with two still listed on shipping registers until 1992. A total of 53 were lost during the war due to accidents or enemy action. One of these, , was destroyed in 1944 by the detonation of 1,400 tons of explosive on board her. This event, known as the Bombay Explosion, killed over 800 people and sank thirteen ships. Fort ships were ships transferred to the British Government and the Park ships were those employed by the Canadian Government, both had the similar design. Description The Fort ships were long with a beam of . They were assessed at . The ships were of three types, the "North Sands" type, which were of riveted construction, and the "Canadian" and "Victory" types, which were of welded construction. They were built by eighteen di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains, and borders the province of Alberta to the east and the Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north. With an estimated population of 5.3million as of 2022, it is Canada's third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria and its largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver is the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada; the 2021 census recorded 2.6million people in Metro Vancouver. The first known human inhabitants of the area settled in British Columbia at least 10,000 years ago. Such groups include the Coast Salish, Tsilhqotʼin, and Haida peoples, among many others. One of the earliest British settlements in the area was Fort Victoria, established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. The Greater Vancouver, Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2.6million in 2021, making it the List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada#List, third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Greater Vancouver, along with the Fraser Valley Regional District, Fraser Valley, comprises the Lower Mainland with a regional population of over 3 million. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada, with over 5,700 people per square kilometre, and fourth highest in North America (after New York City, San Francisco, and Mexico City). Vancouver is one of the most Ethnic origins of people in Canada, ethnically and Languages of Canada, linguistically diverse cities in Canada: 49.3 percent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_underway_c1947.jpg)
_underway_2009.jpg)





