|
HMS Duke Of Kent
''Duke of Kent'' was a proposed 170-gun line of battle ship allegedly designed by future Surveyor of the Navy Joseph Tucker in 1809. Such a vessel, if built, would have become the most heavily armed ship of its time. A 1:96-scale model of the ship survives in the collection of the National Maritime Museum, Greenwich and a set of 1:48-scale drawings are in the collection of the Science Museum, London. In a 1932 work, naval historian Geoffrey Swinford Laird Clowes doubted the authorship of the drawings, stating that they may have been fabricated at a later date in an attempt to bolster Tucker's reputation as a naval architect. Design The ship was designed with four gun decks mounting a total of 170 guns and would have measured 3,700 tons burden. She would have had a three tier stern gallery and would have featured full copper sheathing and a double ship's wheel. The ''Duke of Kent'' would have been the only ship of the line built for the Royal Navy with four complete gun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Grey, 1st Duke Of Kent
Henry Grey, 1st Duke of Kent, KG, PC (16715 June 1740) was a British politician and courtier. None of his sons outlived him, so his new title became extinct on his death. Though the house he built at Wrest Park in Bedfordshire has gone, parts of his very grand garden have survived relatively untouched. Family He was a son of Anthony Grey, 11th Earl of Kent, and Mary Grey, 1st Baroness Lucas of Crudwell. He succeeded his father as 12th Earl of Kent in 1702, having succeeded his mother as 2nd Baron Lucas earlier the same year. He was the grandfather, through his daughter Anne Grey, of Henry Cavendish, the preeminent English chemist and physicist of the late 18th century. Political career Having taken his seat in the House of Lords and though regarded as lacking talent and ambitionPhilip Carter, 'Grey, Henry, duke of Kent', ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004 he, as the politically expedient candidate, was made Lord Chamberlain and a Priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
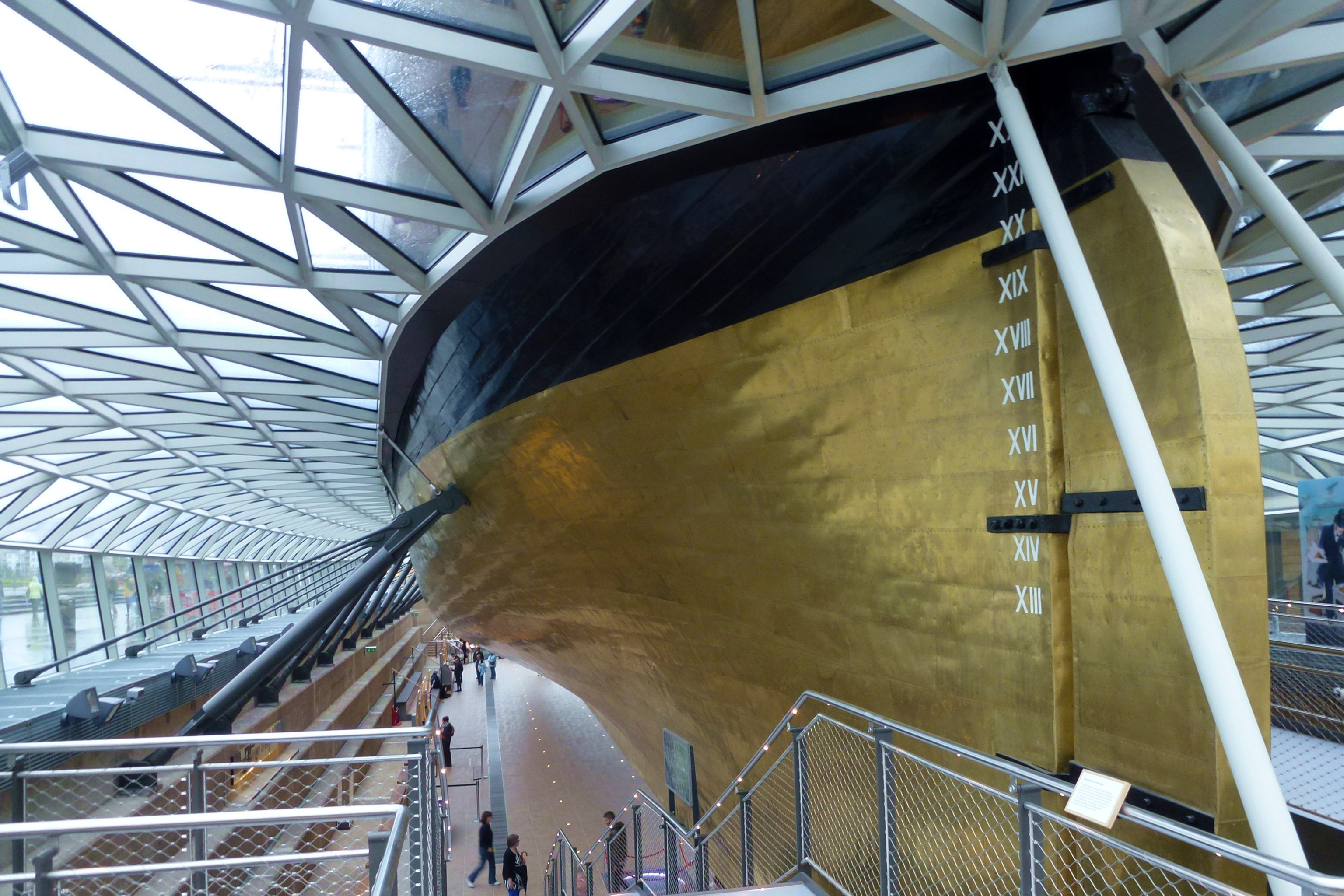
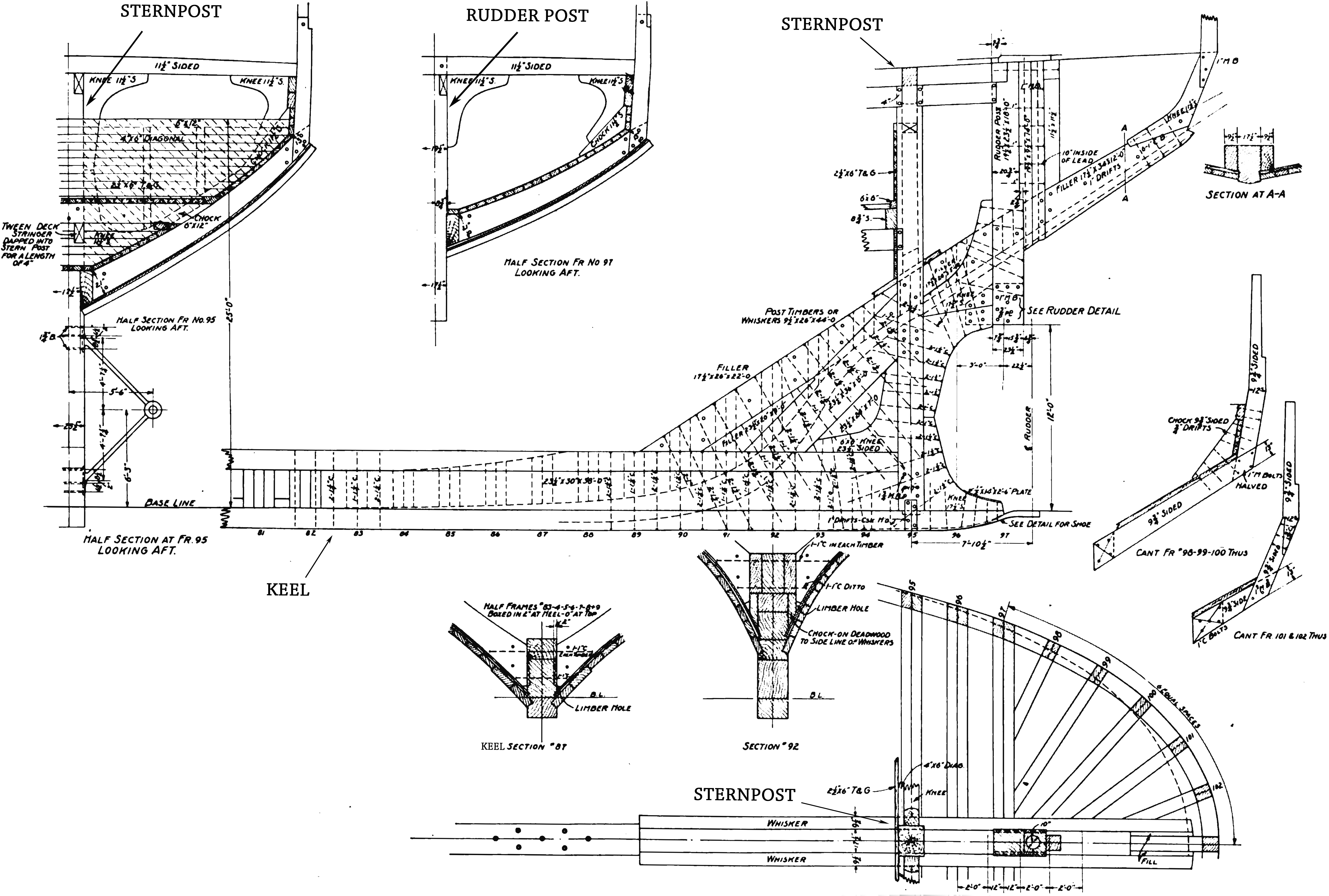
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir William Symonds
Sir William Symonds CB FRS (24 September 1782 – 30 March 1856, aboard the French steamship ''Nil'', Strait of Bonifacio, Sardinia)Complete List of Royal Society Fellows 1660-2007 page 345. was in the from 9 June 1832 to October 1847, and took part in the naval reforms instituted by the Whig First Lord of the Admiralty Sir |
Greenwich Hospital, London
Greenwich Hospital was a permanent home for retired sailors of the Royal Navy, which operated from 1692 to 1869. Its buildings, in Greenwich, London, were later used by the Royal Naval College, Greenwich and the University of Greenwich, and are now known as the Old Royal Naval College. The word "hospital" was used in its original sense of a place providing hospitality for those in need of it, and did not refer to medical care, although the buildings included an infirmary which, after Greenwich Hospital closed, operated as Dreadnought Seaman's Hospital until 1986. The foundation which operated the hospital still exists, for the benefit of former Royal Navy personnel and their dependants. It now provides sheltered housing on other sites. History The hospital was created as the Royal Hospital for Seamen at Greenwich on the instructions of Queen Mary II, who had been inspired by the sight of wounded sailors returning from the Battle of La Hogue in 1692. She ordered the King Charl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nelson Chequer
The Nelson Chequer was a colour scheme adopted by vessels of the Royal Navy, modelled on that used by Admiral Horatio Nelson in battle. It consisted of bands of black and yellow paint along the sides of the hull, broken up by black gunports. In the 18th and 19th centuries, vessels of all nations were painted in a variety of colours. Captains were allowed great latitude in the way they painted their vessels, as it aided identification in battle. Periodically the Royal Navy sought a uniform colour scheme; In 1715, an Admiralty order decreed the use of yellow and black, and a uniform colour within. However, this was generally ignored. Again in 1780 the Admiralty then issued a further order allowing captains to paint in yellow or black. Nelson favoured yellow, with black bands, he also had the underside of his gunports painted black. This meant that when the ports were closed the hull would appear striped, and when opened (ready for action) the hull would appear chequered. No che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koh-i-Noor
The Koh-i-Noor ( ; from ), also spelled Kohinoor and Koh-i-Nur, is one of the largest cut diamonds in the world, weighing . It is part of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom. The diamond is currently set in the Crown of Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother. There are multiple conflicting legends on the origin of the diamond. However, in the words of Theo Metcalfe there is 'very meager and imperfect' evidence of the early history of the Koh-i-Noor before the 1740s, that can directly tie it to any ancient diamond. There is no record of its original weight, but the earliest attested weight is 186 old carats (191 metric carats or 38.2 g). The first verifiable record of the diamond comes from a history by Muhammad Kazim Marvi of the 1740s Invasion of Northern India. Marvi notes that the Koh-i-Noor as being one of many stones on the Mughal Peacock Throne that Nader Shah looted from Delhi. The diamond then changed hands between various empires in south and west Asia, until being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Seppings
Sir Robert Seppings, FRS (11 December 176725 April 1840) was an English naval architect. His experiments with diagonal trusses in the construction of ships led to his appointment as Surveyor of the Navy in 1813, a position he held until 1835. Biography Seppings was born to Robert Seppings (1734-1781) and his wife Lydia Milligen (1740-1821), at Fakenham, Norfolk, on 11 December 1767 and was baptised three days later. In 1782 he was apprenticed in Plymouth Dock. In 1800, when he had risen to be master shipwright assistant in the yard, he invented a device which greatly reduced the time required to repair the lower portions of ships in dry dock when compared with the laborious process of lifting then in vogue. His plan was to make the keel of the ship rest upon a series of supports placed on the floor of the dock and each consisting of three parts - two being wedges arranged one on each side of the keel at right angles to it, with their thin ends together, while the third was a verti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth Dockyard
His Majesty's Naval Base, Devonport (HMNB Devonport) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Portsmouth) and is the sole nuclear repair and refuelling facility for the Royal Navy. The largest naval base in Western Europe, HMNB Devonport is located in Devonport, in the west of the city of Plymouth, England. The base began as Royal Navy Dockyard in the late 17th century, but shipbuilding ceased at Devonport in the early 1970s, although ship maintenance work has continued. The now privatised maintenance facilities are operated by Babcock International Group, who took over the previous owner Devonport Management Limited (DML) in 2007. DML had been running the Dockyard since privatisation in 1987. From 1934 until the early 21st century the naval barracks on the site was named HMS ''Drake'' (it had previously been known as HMS ''Vivid'' after the base ship of the same name). The name HMS ''Drake'' and its c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caledonia-class Ship Of The Line
The ''Caledonia''-class ships of the line were a class of nine 120-gun first rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir William Rule. A tenth ship (''Royal Frederick'') was ordered on 29 October 1827 to the same design, but was launched in 1833 as ''Queen'' to a fresh design by Sir William Symonds. Armament In the original configuration, the armament of the ''Caledonia'' class was consistent for the first three ships of the class. The exception was an increase in firepower on the poop deck from 2 to 6 18-pounder carronades. Starting with the fourth ship, the armament of the class was significantly modified to adhere to the principle of a unified caliber of 32 pound. All guns on the middle and upper gun decks were replaced with the same number of 32-pounders. Except for two 24-pounders on the middle deck that were replaced by two 8 inch shell guns. Four of the 12-pounder guns on the quarterdeck were replaced with 32-pounder carronades. The remaining two were increased to 18-po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Ship Nuestra Señora De La Santísima Trinidad
''Santísima Trinidad'' (officially named ''Nuestra Señora de la Santísima Trinidad'' by royal order on 12 March 1768, nicknamed ''La Real'', sometimes confused with the galleon ''Santísima Trinidad y Nuestra Señora del Buen Fin'') was a Spanish first-rate ship of the line with 112 guns. This was increased in 1795–96 to 130 guns by closing in the spar deck between the quarterdeck and forecastle, and to 140 guns around 1802, thus creating what was in effect a continuous fourth gundeck although the extra guns added were actually relatively small. She was the heaviest-armed ship in the world when rebuilt, and bore the most guns of any ship of the line outfitted in the Age of Sail. Design and construction She was built at Havana, Cuba, to a design by Irish naval architect Matthew Mullan (domiciled in Spain under the name Mateo Mullán) and launched in 1769 as a 112-gun three-decker (some sources say 116 or even 120 guns). She was considerably larger than her British conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship's Wheel
A ship's wheel or boat's wheel is a device used aboard a water vessel to steer that vessel and control its course. Together with the rest of the steering mechanism, it forms part of the helm. It is connected to a mechanical, electric servo, or hydraulic system which alters the horizontal angle of the vessel's rudder relative to its hull. In some modern ships the wheel is replaced with a simple toggle that remotely controls an electro-mechanical or electro-hydraulic drive for the rudder, with a rudder position indicator presenting feedback to the helmsman. History Until the invention of the ship's wheel, the helmsman relied on a tiller—a horizontal bar fitted directly to the top of the rudder post—or a whipstaff—a vertical stick acting on the arm of the ship's tiller. Near the start of the 18th century, a large number of vessels appeared using the ship's wheel design, but historians are unclear when the approach was first used. Design A traditional ship's wheel is compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Sheathing
Copper sheathing is the practice of protecting the under-water hull of a ship or boat from the corrosive effects of salt water and biofouling through the use of copper plates affixed to the outside of the hull. It was pioneered and developed by the Royal Navy during the 18th century. In antiquity, ancient Greeks used lead plates to protect the underwater hull. Development Deterioration of the hull of a wooden ship was a significant problem during the Age of Sail. Ships' hulls were under continuous attack by shipworm, barnacles and various marine weeds, all of which had some adverse effect on the ship, be it structurally, in the case of the worm, or affecting speed and handling in the case of the weeds. The most common methods of dealing with these problems were through the use of wood, and sometimes lead, sheathing. Expendable wood sheathing effectively provided a non-structural skin to the hull for the worm to attack, and could be easily replaced in dry dock at regular interva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_by_William_Bradley.jpg)


