|
HMAS Vendetta (D69)
HMAS ''Vendetta'' (D69/I69) (formerly HMS ''Vendetta'' (FA3/F29/D69)) was a V-class destroyer that served in the Royal Navy and the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). One of 25 V class ships ordered for the Royal Navy during World War I, ''Vendetta'' entered service in 1917. During World War I, ''Vendetta'' participated in the Second Battle of Heligoland Bight, and operated against Bolshevik forces during the British Baltic Campaign. Most of the ship's post-war career was spent operating in the Mediterranean. In 1933, ''Vendetta'' was one of five destroyers selected for transfer to the RAN. Over the next six years, the ship was either involved in peacetime activities or was in reserve, but when World War II started, she was assigned to the Mediterranean as part of the ' Scrap Iron Flotilla'. During the Greek Campaign, ''Vendetta'' was involved in the transportation of Allied troops to Greece, then the evacuation to Crete. After, the destroyer served with the Tobruk Ferry Service, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairfield Shipbuilding & Engineering Company
The Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company, Limited was a Scottish shipbuilding company in the Govan area on the Clyde in Glasgow. Fairfields, as it is often known, was a major warship builder, turning out many vessels for the Royal Navy and other navies through the First World War and the Second World War. It also built many transatlantic liners, including record-breaking ships for the Cunard Line and Canadian Pacific, such as the Blue Riband-winning sisters RMS ''Campania'' and RMS ''Lucania''. At the other end of the scale, Fairfields built fast cross-channel mail steamers and ferries for locations around the world. These included ships for the Bosporus crossing in Istanbul and some of the early ships used by Thomas Cook for developing tourism on the River Nile. John Elder & Co and predecessors Millwright Randolph & Elliott Charles Randolph founded the company as Randolph & Co. He had been an apprentice at the Clyde shipyard of Robert Napier, and at William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Australian Navy
The Royal Australian Navy (RAN) is the principal naval force of the Australian Defence Force (ADF). The professional head of the RAN is Chief of Navy (CN) Vice Admiral Mark Hammond AM, RAN. CN is also jointly responsible to the Minister of Defence (MINDEF) and the Chief of Defence Force (CDF). The Department of Defence as part of the Australian Public Service administers the ADF. Formed in 1901, as the Commonwealth Naval Forces (CNF), through the amalgamation of the colonial navies of Australia following the federation of Australia. Although it was originally intended for local defence, it became increasingly responsible for regional defence as the British Empire started to diminish its influence in the South Pacific. The Royal Australian Navy was initially a green-water navy, and where the Royal Navy provided a blue-water force to the Australian Squadron, which the Australian and New Zealand governments helped to fund, and that was assigned to the Australia Station. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
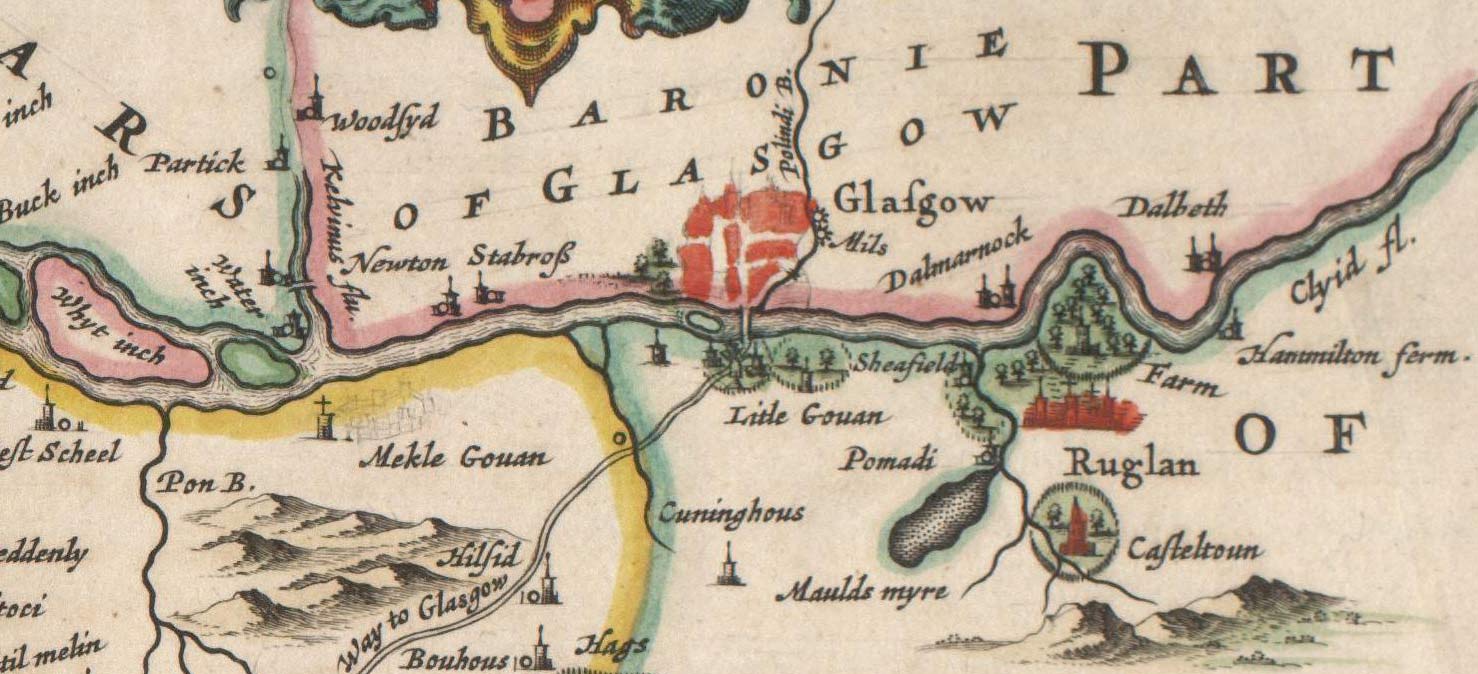
Govan
Govan ( ; Cumbric?: ''Gwovan'?''; Scots: ''Gouan''; Scottish Gaelic: ''Baile a' Ghobhainn'') is a district, parish, and former burgh now part of south-west City of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated west of Glasgow city centre, on the south bank of the River Clyde, opposite the mouth of the River Kelvin and the district of Partick. Historically it was part of the County of Lanark. In the early medieval period, the site of the present Govan Old churchyard was established as a Christian centre for the Brittonic Kingdom of Alt Clut (Dumbarton Rock) and its successor realm, the Kingdom of Strathclyde. This latter kingdom, established in the aftermath of the Viking siege and capture of Alt Clut by Vikings from Dublin in AD 870, created the sandstone sculptures known today as the Govan Stones. Govan was the site of a ford and later a ferry which linked the area with Partick for seasonal cattle drovers. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, textile mills and coal mining were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairfield Shipbuilding And Engineering Company, Limited
The Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company, Limited was a Scottish shipbuilding company in the Govan area on the Clyde in Glasgow. Fairfields, as it is often known, was a major warship builder, turning out many vessels for the Royal Navy and other navies through the First World War and the Second World War. It also built many transatlantic liners, including record-breaking ships for the Cunard Line and Canadian Pacific, such as the Blue Riband-winning sisters RMS ''Campania'' and RMS ''Lucania''. At the other end of the scale, Fairfields built fast cross-channel mail steamers and ferries for locations around the world. These included ships for the Bosporus crossing in Istanbul and some of the early ships used by Thomas Cook for developing tourism on the River Nile. John Elder & Co and predecessors Millwright Randolph & Elliott Charles Randolph founded the company as Randolph & Co. He had been an apprentice at the Clyde shipyard of Robert Napier, and at William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-pounder Pom-pom
The 2-pounder gun, officially the QF 2-pounder ( QF denoting "quick firing") and universally known as the pom-pom, was a British autocannon, used as an anti-aircraft gun by the Royal Navy.British military of the period traditionally denoted smaller guns in terms of the approximate weight of the standard projectile, rather than by its bore diameter, which in this case was 40 mm. References to 40-mm anti-aircraft guns invariably mean the Bofors gun, while references to 2-pounder anti-aircraft guns mean this gun. The name came from the sound that the original models make when firing. This QF 2-pounder was not the same gun as the Ordnance QF 2-pounder, used by the British Army as an anti-tank gun and a tank gun, although they both fired , projectiles. Predecessors - Boer War and the Great War QF 1 pounder The first gun to be called a pom-pom was the 37 mm Nordenfelt-Maxim or "QF 1-pounder" introduced during the Second Boer War, the smallest artillery piece of that war. It fire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney Heads
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountains to the west, Hawkesbury to the north, the Royal National Park to the south and Macarthur to the south-west. Sydney is made up of 658 suburbs, spread across 33 local government areas. Residents of the city are known as "Sydneysiders". The 2021 census recorded the population of Greater Sydney as 5,231,150, meaning the city is home to approximately 66% of the state's population. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017. Nicknames of the city include the 'Emerald City' and the 'Harbour City'. Aboriginal Australians have inhabited the Greater Sydney region for at least 30,000 years, and Aboriginal engravings and cultural sites are common throughout Greater Sydney. The traditional custodians of the land on which modern Sydney stands are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scuttled
Scuttling is the deliberate sinking of a ship. Scuttling may be performed to dispose of an abandoned, old, or captured vessel; to prevent the vessel from becoming a navigation hazard; as an act of self-destruction to prevent the ship from being captured by an enemy force (or, in the case of a vessel engaged in illegal activities, by the authorities); as a blockship to restrict navigation through a channel or within a harbor; to provide an artificial reef for divers and marine life; or to alter the flow of rivers. Notable historical examples Skuldelev ships (around 1070) The Skuldelev ships, five Viking ships, were sunk to prevent attacks from the sea on the Danish city of Roskilde. The scuttling blocked a major waterway, redirecting ships to a smaller one that required considerable local knowledge. Cog near Kampen (early 15th century) In 2012, a cog preserved from the keel up to the decks in the silt was discovered alongside two smaller vessels in the river IJssel in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
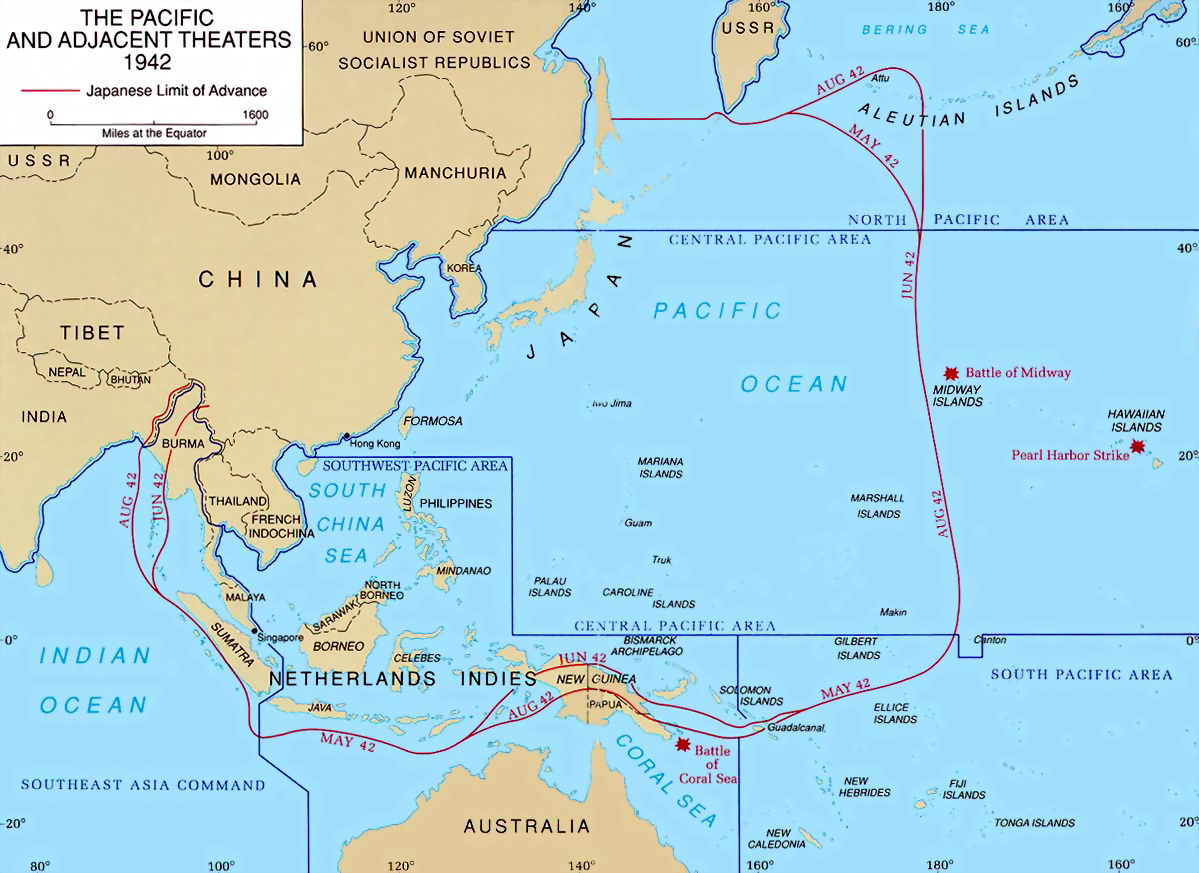
Battle Of Singapore
The Fall of Singapore, also known as the Battle of Singapore,; ta, சிங்கப்பூரின் வீழ்ச்சி; ja, シンガポールの戦い took place in the South–East Asian theatre of the Pacific War. The Empire of Japan captured the British stronghold of Singapore, with fighting lasting from 8 to 15 February 1942. Singapore was the foremost British military base and economic port in South–East Asia and had been of great importance to British interwar defence strategy. The capture of Singapore resulted in the largest British surrender in its history. Prior to the battle, Japanese General Tomoyuki Yamashita had advanced with about 30,000 men down the Malayan Peninsula in the Malayan campaign. The British erroneously considered the jungle terrain impassable, leading to a swift Japanese advance as Allied defences were quickly outflanked. The British Lieutenant-General, Arthur Percival, commanded 85,000 Allied troops at Singapore, although many units ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Tobruk
The siege of Tobruk lasted for 241 days in 1941, after Axis forces advanced through Cyrenaica from El Agheila in Operation Sonnenblume against Allied forces in Libya, during the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) of the Second World War. In late 1940, the Allies had defeated the Italian 10th Army during Operation Compass and trapped the remnants at Beda Fomm. During early 1941, much of the Western Desert Force (WDF) was sent to the Greek and Syrian campaigns. As German troops and Italian reinforcements reached Libya, only a skeleton Allied force remained, short of equipment and supplies. The defenders quickly became known as the Rats of Tobruk. Operation ''Sonnenblume'' forced the Allies into a retreat to the Egyptian border. A garrison, consisting mostly of the 9th Australian Division (Lieutenant-General Leslie Morshead) remained at Tobruk, to deny the port to the Axis, while the WDF reorganised and prepared a counter-offensive. The Axis siege of Tobruk began on 10 Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobruk Ferry Service
The Tobruk Ferry Service (also known as the Tobruk Ferry Run) was the name given to the force of Royal Navy and Royal Australian Navy ships involved in the supply of Allied forces during the Siege of Tobruk. History The aim of the Ferry Service was to keep the besieged Allied forces supplied with ammunition, gun barrels, and medical supplies, while evacuating wounded personnel. The initial supply runs to Tobruk were performed by the ships of the 10th Destroyer Flotilla (which included the Australian 'Scrap Iron Flotilla') operating independently. A typical run saw a destroyer leave Alexandria early in the morning, after spending the night loading, then sail for Tobruk, where the ship would arrive around midnight. After supplies were unloaded and wounded loaded, the destroyer would sail for Mersa Matruh, where the wounded were exchanged for more supplies. The destroyer would return to Tobruk for a second evening, then head back to Alexandria. The danger of attack by air and sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Campaign
The German invasion of Greece, also known as the Battle of Greece or Operation Marita ( de , Unternehmen Marita, links = no), was the attack of Greece by Italy and Germany during World War II. The Italian invasion in October 1940, which is usually known as the Greco-Italian War, was followed by the German invasion in April 1941. German landings on the island of Crete (May 1941) came after Allied forces had been defeated in mainland Greece. These battles were part of the greater Balkans Campaign of the Axis powers and their associates. Following the Italian invasion on 28 October 1940, Greece, with British air and material support, repelled the initial Italian attack and a counter-attack in March 1941. When the German invasion, known as Operation Marita, began on 6 April, the bulk of the Greek Army was on the Greek border with Albania, then a vassal of Italy, from which the Italian troops had attacked. German troops invaded from Bulgaria, creating a second front. Greece recei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrap Iron Flotilla
The Scrap Iron Flotilla was an Australian destroyer group that operated in the Mediterranean and Pacific during World War II. The name was bestowed upon the group by Nazi Propaganda Minister Joseph Goebbels. The flotilla consisted of five Royal Australian Navy (RAN) destroyers. The five ships of the flotilla had been Royal Navy ships that had been built and served during the First World War and transferred to the RAN in the 1930s. HMAS ''Waterhen'' was sunk in the Mediterranean in 1941, HMAS ''Vampire'' was sunk in the Indian Ocean in 1942, and HMAS ''Voyager'' was sunk near Timor in 1942. HMAS ''Stuart'' and HMAS ''Vendetta'' survived the war. The story of the ships in the flotilla, up to 1943, was recounted in the book ''Scrap-Iron Flotilla'' by John F. Moyes, who served as a Sub-Lieutenant RANVR on HMAS ''Voyager'' later in the war, and collected many stories from the crews. Moyes was on HMAS ''Voyager'' when she was sunk, but survived. The flotilla * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |