|
AIDS In Uganda
The very high rate of HIV infection experienced in Uganda during the 1980s and early 1990s created an urgent need for people to know their HIV status. The only option available to them was offered by the National Blood Transfusion Service, which carries out routine HIV tests on all the blood that is donated for transfusion purposes. The great need for testing and counseling resulted in a group of local non-governmental organizations such as The AIDS Support Organisation (TASO), Uganda Red Cross, Nsambya Home Care, the National Blood Bank, the Uganda Virus Research Institute together with the Ministry of Health establishing the AIDS Information Centre in 1990. This organization worked to provide HIV testing and counseling services with the knowledge and consent of the client involved. In Uganda, HIV/AIDS has been approached as more than a health issue and in 1992 a Multi-sectoral AIDS Control Approach was adopted. In addition, the Uganda AIDS Commission, also founded in 1992, has help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa: Due to the historical .... The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The southern part of the country includes a substantial portion of Lake Victoria, shared with Kenya and Tanzania. Uganda is in the African Great Lakes region. Uganda also lies within the Nile, Nile basin and has a varied but generally a modified equatorial climate. It has a population of around 49 million, of which 8.5 million live in the Capital city, capital and largest city of Kampala. Uganda is named after the Buganda kingdom, which encompasses a large portion of the south of the country, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
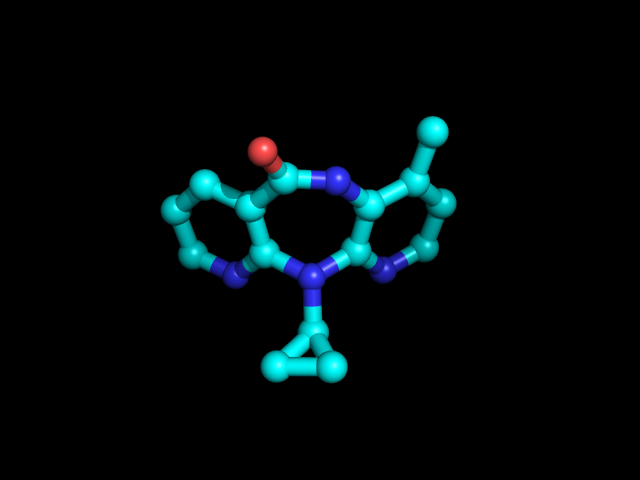
Nevirapine
Nevirapine (NVP), sold under the brand name Viramune among others, is a medication used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS, specifically HIV-1. It is generally recommended for use with other antiretroviral medications. It may be used to prevent mother to child spread during birth but is not recommended following other exposures. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include rash, headache, nausea, feeling tired, and liver problems. The liver problems and skin rash may be severe and should be checked for during the first few months of treatment. It appears to be safe for use during pregnancy. It is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) and works by blocking the function of reverse transcriptase. Nevirapine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. Medical uses Nevirapine is used in people six years of age and older infected with HIV- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fred Nalugoda
Fred Nalugoda is a public health researcher studying HIV/AIDS in rural Uganda for over 20 years, mainly through surveillance and field work. He currently serves as the Program Director of a research station in Kalisizo in Uganda as part of his continued work at the Rakai Health Sciences Program (RHSP). Education Nalugoda holds a bachelor's degree in statistics, and later went on to receive a master's degree in health sciences from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, under the Fogarty AIDS International Training and Research Program. He has served as the Head of Grants, Science and Training at the RHSP while returning to Makerere University to pursue a doctorate degree in public health. In 2015, he graduated from Makerere University, in the school of Philosophy, studying public health, biostatistics, and epidemiology. Rakai Health Sciences Program The Rakai Health Sciences Program represents a group of scientists, investigators and clinicians performing a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roy Mugerwa
Roy D. Mugerwa (January 2, 1942 – April 19, 2019) was a Ugandan physician, cardiologist and researcher. His contribution to the world of academics include being a Professor Emeritus at Makerere University College of Health Sciences in Kampala, cardiology in Uganda, researching HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis, and his efforts to find an effective HIV vaccine. Background Dr. Mugerwa was born on January 2, 1942, to Yowana Ziryawula and Maria Namatovu. He pursued his education at St. Mary's College Kisubi for both the O-Level and A-Level and was at the top of his class for all six years. Upon graduation, he admitted to Makerere University, Uganda's oldest and largest public university, and completed both undergraduate and masters programs. He received training in medicine and cardiology at Mulago Hospital and also pursued higher level instruction in the United States, United Kingdom, and the Netherlands. He then returned to Uganda and developed a career in Kampala, serving a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philly Lutaaya
Philly Bongoley Lutaaya (19 October 1951 – 15 December 1989) was a Ugandan musician who was the first prominent Ugandan to give a human face to HIV/ AIDS. He became a national hero because he was the first Ugandan to declare that he was HIV – positive. That was in 1988, when HIV still carried a lot of stigma. Before dying of AIDS, Lutaaya spent his remaining time writing songs about his battle with AIDS, releasing his last album ''Alone and Frightened'', including his famous song "Alone", influenced by Swedish duo Roxette's hit song ''It Must Have Been Love'', as well as touring churches and schools throughout Uganda to spread a message of prevention and hope. Lutaaya was popular in Uganda in the 1960s, and in the 1970s he toured the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, and Japan. In the mid 1980s, he settled in Stockholm, Sweden. There he recorded his hit album '' Born in Africa'', which is still popular in Uganda. Lutaaya's ''Christmas Album'', produced in 1986, rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Konde-Lule
Joseph Konde-Lule is a retired Ugandan medical sociologist and epidemiologist who conducted extensive work regarding HIV risk behaviors in rural Uganda. Background Joseph Konde-Lule holds degrees as a Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery as well as a Master of Public Health. He was an associate professor in the Department of Epidemiology & Biostatistics, now under the School of Public Health, at Makerere University in Uganda from 1977 until 2014. He additionally served as the first head of the department. Throughout his career, Konde-Lule has amassed over seventy-two publications to his name, many of them focusing on understanding social determinants of HIV and its spread within Uganda. His career in public health research began with his thesis which focused on syphilis prevalence and how understanding of the virus, or lack thereof, was allowing it to continue to spread within communities. He later applied this research background to understanding HIV/AIDS prevalenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noerine Kaleeba
Noerine Kaleeba is a Ugandan physiotherapist, educator and AIDS activist. She is the co-founder of the AIDS activism group " The AIDS Support Organization" (TASO). She is currently a program development adviser for the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). She is also the Patron of TASO. Background Noerine Kaleeba specialised in orthopaedics, physiotherapy and community rehabilitation at Makerere University in Kampala, and the Robert Jones & Agnes Hunt Orthopaedic & District Hospital in Oswestry, England. She has worked as a physiotherapist at Mulago Hospital, and was the principal of Mulago School of Physiotherapy until 1987. TASO In June 1986, Kaleeba received a call that her husband, Christopher, had become very sick while he was in England working on his masters in sociology and political science. He was diagnosed with AIDS. He died in January 1987, which caused Kaleeba to co-found a support group that same year, The AIDS Support Organization (TASO). The goal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gideon Byamugisha
Reverend Canon Gideon Byamugisha (born 1959) is an Anglican priest in Uganda with a parish outside of Kampala. In 1992, he became the first religious leader in Africa to publicly announce that he was HIV positive.HIV-positive religious leaders break their silence Mg.co.za (17 March 2008). Retrieved on 26 November 2012. In 2009, Byamugisha received the 26th annual "in recognition of his work to uphold the dignity and human rights of people living with HIV/AIDS". Byamugisha co-founded the African Network of Religious Leaders Living with and Personally Affected HIV and Aids ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health In Uganda
Health in Uganda refers to the health of the population of Uganda. The average life expectancy at birth of Uganda has increased from 59.9 years in 2013 to 63.4 years in 2019. This is lower than in any other country in the East African Community except Burundi. As of 2017, females had a life expectancy higher than their male counterparts of 69.2 versus 62.3. It is projected that by 2100, males in Uganda will have an expectancy of 74.5 and females 83.3. Uganda's population has steadily increased from 36.56 million in 2016 to an estimate of 42.46 in 2021. The fertility rate of Ugandan women slightly increased from an average of 6.89 babies per woman in the 1950s to about 7.12 in the 1970s before declining to an estimate 5.32 babies in 2019. This figure is higher than most world regions including South East Asia, Middle East and North Africa, Europe and Central Asia and America. The under-5-mortality-rate for Uganda has decreased from 191 deaths per 1000 live births in 1970 to 45.8 d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janet Museveni
Janet Kainembabazi Museveni (''née'' Kataaha; born June 24, 1948) is a Ugandan politician who has been the First Lady of Uganda since 1986. She is married to President Yoweri Museveni, with whom she has four children. She has been Cabinet Minister of Education and Sports in the Ugandan Cabinet, since 6 June 2016, although her own education record is questioned. She previously served as Minister for Karamoja Affairs in the Cabinet of Uganda from 27 May 2011 until 6 June 2016. She also served as the elected Member of Parliament representing Ruhaama County in Ntungamo District, between 2011 and 2016. She published her autobiography, ''My Life's Journey'', in 2011. Early life and marriage Janet Kainembabazi Kataaha was born in Kajara County, Ntungamo District to Mr. Edward Birori and Mrs. Mutesi. She attended Kyamate Primary School, and Bweranyangi Girls' Senior Secondary School in Uganda. She was awarded a Master of Arts in Organisational Leadership and Management on 30th Octo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evangelicalism
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual experiences personal conversion; the authority of the Bible as God's revelation to humanity (biblical inerrancy); and spreading the Christian message. The word ''evangelical'' comes from the Greek (''euangelion'') word for " good news". Its origins are usually traced to 1738, with various theological streams contributing to its foundation, including Pietism and Radical Pietism, Puritanism, Quakerism, Presbyterianism and Moravianism (in particular its bishop Nicolaus Zinzendorf and his community at Herrnhut).Brian Stiller, ''Evangelicals Around the World: A Global Handbook for the 21st Century'', Thomas Nelson, USA, 2015, pp. 28, 90. Preeminently, John Wesley and other early Methodists were at the root of sparking this new movement during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PEPFAR
The United States President's Emergency Plan For AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) is a United States governmental initiative to address the global HIV/AIDS epidemic and help save the lives of those suffering from the disease. Launched by U.S. President George W. Bush in 2003, as of May 2020, PEPFAR has provided about $90 billion in cumulative funding for HIV/AIDS treatment, prevention, and research since its inception, making it the largest global health program focused on a single disease in history until the COVID-19 pandemic. PEPFAR is implemented by a combination of U.S. government agencies in over 50 countries and overseen by the Global AIDS Coordinator at the U.S. Department of State. As of 2021, PEPFAR has saved over 20 million lives, primarily in Sub-Saharan Africa. History PEPFAR began with President George W. Bush and his wife, Laura, and their interests in AIDS prevention, Africa, and what Bush termed “compassionate conservatism.” According to his 2010 memoir, ''Decision Poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)