|
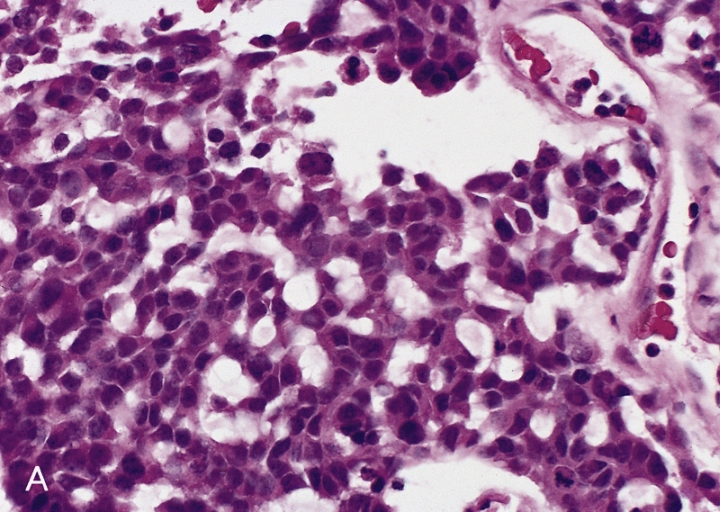
H295R
H295R (also referred to as NCI-H295R) is an angiotensin-II-responsive steroid-producing adrenocortical cell line. It was initially isolated in 1980 from a 48-year-old female patient diagnosed with adrenocortical carcinoma Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) is an aggressive cancer originating in the cortex (steroid hormone-producing tissue) of the adrenal gland. Adrenocortical carcinoma is remarkable for the many hormonal syndromes that can occur in patients with ster .... The initial polyclonal populations of tumor cells obtained from the patients' tumor were cultured and the resultant cell line was called NCI-H295. Because of slow growth rates and easy detachment of the original NCI-H295 strains, efforts were made to select a population of cells with better monolayer attachment and more rapid growth. Three strains were developed, based on the serum supplement used for growth, which have been termed H295R-S1, H295R-S2 and H295R-S3. All three strains grow as adherent monolayer culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenocortical Carcinoma
Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) is an aggressive cancer originating in the cortex (steroid hormone-producing tissue) of the adrenal gland. Adrenocortical carcinoma is remarkable for the many hormonal syndromes that can occur in patients with steroid hormone-producing ("functional") tumors, including Cushing's syndrome, Conn syndrome, virilization, and feminization. Adrenocortical carcinoma has often invaded nearby tissues or metastasized to distant organs at the time of diagnosis, and the overall 5-year survival rate is about 50%. Adrenocortical carcinoma is a rare tumor, with incidence of one to two per million population annually. It has a bimodal distribution by age, with cases clustering in children under 5 and in adults 30–40 years old. The widely used angiotensin-II-responsive steroid-producing cell line H295R was originally isolated from a tumor diagnosed as adrenocortical carcinoma. Signs and symptoms Adrenocortical carcinoma may present differently in children an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiotensin
Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex to promote sodium retention by the kidneys. An oligopeptide, angiotensin is a hormone and a dipsogen. It is derived from the precursor molecule angiotensinogen, a serum globulin produced in the liver. Angiotensin was isolated in the late 1930s (first named 'angiotonin' or 'hypertensin') and subsequently characterized and synthesized by groups at the Cleveland Clinic and Ciba laboratories. Precursor and types Angiotensinogen Angiotensinogen is an α-2-globulin synthesized in the liver and is a precursor for angiotensin, but has also been indicated as having many other roles not related to angiotensin peptides. It is a member of the serpin family of proteins, leading to another name: Serpin A8, although it is not known to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cholestane. ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenal Cortex
The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of an adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones. It is also a secondary site of androgen synthesis. – "Adrenal Gland" Layers The adrenal cortex comprises three main zones, or layers that are regulated by distinct hormones as noted below. This ''anatomic zonation'' can be appreciated at the microscopic level, where each zone can be recognized and distinguished from one another based on structural and anatomic characteristics. ;Zona glomerulosa :The outermost layer, the zona glomerulosa is the main site for the production of aldosterone, a mineralocorticoid. The synthesis and secretion of aldosterone are mainly regulated by the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. The zona glomerulosa cells express a specific enzyme aldosterone synthase (also known as CYP11B2). Aldosterone is largel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Line
An immortalised cell line is a population of cells from a multicellular organism which would normally not proliferate indefinitely but, due to mutation, have evaded normal cellular senescence and instead can keep undergoing division. The cells can therefore be grown for prolonged periods ''in vitro''. The mutations required for immortality can occur naturally or be intentionally induced for experimental purposes. Immortal cell lines are a very important tool for research into the biochemistry and cell biology of multicellular organisms. Immortalised cell lines have also found uses in biotechnology. An immortalised cell line should not be confused with stem cells, which can also divide indefinitely, but form a normal part of the development of a multicellular organism. Relation to natural biology and pathology There are various immortal cell lines. Some of them are normal cell lines (e.g. derived from stem cells). Other immortalised cell lines are the ''in vitro'' equivalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid Hormones
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Within those two classes are five types according to the receptors to which they bind: glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids (both corticosteroids) and androgens, estrogens, and progestogens (sex steroids). Vitamin D derivatives are a sixth closely related hormone system with homologous receptors. They have some of the characteristics of true steroids as receptor ligands. Steroid hormones help control metabolism, inflammation, immune functions, salt and water balance, development of sexual characteristics, and the ability to withstand injury and illness. The term steroid describes both hormones produced by the body and artificially produced medications that duplicate the action for the naturally occurring steroids. Synthesis The natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Cell Lines
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate Phenomenon, phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only Extant taxon, extant member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrinology
Endocrinology (from '' endocrine'' + '' -ology'') is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental events proliferation, growth, and differentiation, and the psychological or behavioral activities of metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sleep, digestion, respiration, excretion, mood, stress, lactation, movement, reproduction, and sensory perception caused by hormones. Specializations include behavioral endocrinology and comparative endocrinology. The endocrine system consists of several glands, all in different parts of the body, that secrete hormones directly into the blood rather than into a duct system. Therefore, endocrine glands are regarded as ductless glands. Hormones have many different functions and modes of action; one hormone may have several effects on different target organs, and, conversely, one target orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |