|
H₂e-conjugation Theory
The -conjugation theory adds a third conjugation to the two generally accepted conjugations of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE), the thematic and athematic conjugations. The symbol ' refers to a particular example of a class of sounds known as "laryngeals" in the theory of PIE linguistics. History of the theory Proposed by Jay Jasanoff in 1979 and presented in its most elaborate form in Jasanoff (2003), the evidence for the "new" verbal conjugation in PIE is based on the attested existence of the similar ''ḫi''-conjugation in Hittite and other Anatolian languages. Whereas the Anatolian ''ḫi''-conjugation has traditionally been seen as an innovation in the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European family of languages, Jasanoff presents evidence and arguments to place it as a conjugation already established in PIE proper. The problem The following table serves to give an understanding of the problem that the theory tries to solve. The origin of the Hittite ''mi''-conju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Conjugation
In linguistics, conjugation () is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb ''break'' can be conjugated to form the words ''break'', ''breaks'', ''broke'', ''broken'' and ''breaking''. While English has a relatively simple conjugation, other languages such as French and Arabic are more complex, with each verb having dozens of conjugated forms. Some languages such as Georgian and Basque have highly complex conjugation systems with hundreds of possible conjugations for every verb. Verbs may inflect for grammatical categories such as person, number, gender, case, tense, aspect, mood, voice, possession, definiteness, politeness, causativity, clusivity, interrogatives, transitivity, valency, polarity, telicity, volition, mirativity, evidentiality, animacy, associativity, pluractionality, and reciprocity. Verbs may also be affected by agreement, polypersonal agreem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE or its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result. PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from 4500 BC to 2500 BC during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
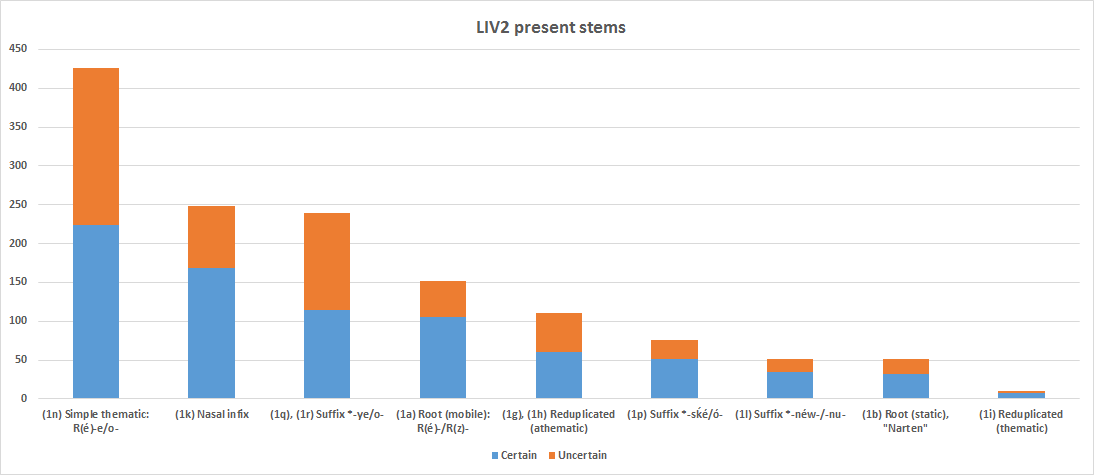
Proto-Indo-European Verbs
Proto-Indo-European verbs reflect a complex system of morphology, more complicated than the substantive, with verbs categorized according to their aspect, using multiple grammatical moods and voices, and being conjugated according to person, number and tense. In addition to finite forms thus formed, non-finite forms such as participles are also extensively used.Beekes, 18.1.1. The verbal system is clearly represented in Ancient Greek and Vedic Sanskrit, which closely correspond, in nearly all aspects of their verbal systems, and are two of the most well-understood of the early daughter languages of Proto-Indo-European. Basics Verb conjugation in Proto-Indo-European involves the interplay of six dimensions (number, person, voice, mood, aspect and tense) with the following variables identified under the ''Cowgill-Rix'' system, which is one of the methodologies proposed and applies only to certain subfamilies: Further, participles can be considered part of the verbal sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laryngeals
The laryngeal theory is a theory in the historical linguistics of the Indo-European languages positing that: * The Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) had a series of phonemes beyond those reconstructable by the comparative method. That is, the theory maintains that there were sounds in Proto-Indo-European that no longer exist in any of the daughter languages, and thus, cannot be reconstructed merely by comparing sounds among those daughter languages. * These phonemes, according to the most accepted variant of the theory, were laryngeal consonants of an indeterminate place of articulation towards the back of the mouth. The theory aims to: * Produce greater regularity in the reconstruction of PIE phonology than from the reconstruction that is produced by the comparative method. * Extend the general occurrence of the Indo-European ablaut to syllables with reconstructed vowel phonemes other than *e or *o. In its earlier form ( see below), the theory proposed two sounds in PIE. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jay Jasanoff
Jay Harold Jasanoff ( or ) is an American linguist and Indo-Europeanist, best known for his ''h2e''-conjugation theory of the Proto-Indo-European verbal system. He teaches Indo-European linguistics and historical linguistics at Harvard University. Career Jasanoff received both his bachelor's degree (in 1963) and his Ph.D. (in 1968) from Harvard. After working for one year as an assistant professor at the University of California, Berkeley, he returned to Harvard to teach as an assistant professor and, later, associate professor from 1970 to 1978. He then moved to Ithaca, New York, to teach at Cornell University, where he was promoted to full professor in linguistics. He taught at Cornell for twenty years, including a number of years as the department chair. Since 1998 he has been the Diebold Professor of Indo-European Linguistics and Philology at Harvard, and was the department chair from 1999 to 2008. In his research, he has examined, in addition to the Indo-European verb, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hittite Language
Hittite (natively / "the language of Neša", or ''nešumnili'' / "the language of the people of Neša"), also known as Nesite (''Nešite'' / Neshite, Nessite), is an extinct Indo-European language that was spoken by the Hittites, a people of Bronze Age Anatolia who created an empire centred on Hattusa, as well as parts of the northern Levant and Upper Mesopotamia. The language, now long extinct, is attested in cuneiform, in records dating from the 17th (Anitta text) to the 13th centuries BCE, with isolated Hittite loanwords and numerous personal names appearing in an Old Assyrian context from as early as the 20th century BCE, making it the earliest-attested use of the Indo-European languages. By the Late Bronze Age, Hittite had started losing ground to its close relative Luwian. It appears that in the 13th century BCE, Luwian was the most widely spoken language in the Hittite capital, Hattusa. After the collapse of the Hittite New Kingdom during the more general Late Bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolian Languages
The Anatolian languages are an extinct branch of Indo-European languages that were spoken in Anatolia, part of present-day Turkey. The best known Anatolian language is Hittite, which is considered the earliest-attested Indo-European language. Undiscovered until the late 19th and 20th centuries, they are often believed to be the earliest branch to have split from the Indo-European family. Once discovered, the presence of laryngeal consonants ''ḫ'' and ''ḫḫ'' in Hittite and Luwian provided support for the laryngeal theory of Proto-Indo-European linguistics. While Hittite attestation ends after the Bronze Age, hieroglyphic Luwian survived until the conquest of the Neo-Hittite kingdoms by Assyria, and alphabetic inscriptions in Anatolian languages are fragmentarily attested until the early first millennium AD, eventually succumbing to the Hellenization of Anatolia. Origins The Anatolian branch is often considered the earliest to have split from the Proto-Indo-European l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerzy Kuryłowicz
Jerzy Kuryłowicz (; 26 August 1895 – 28 January 1978) was a Polish linguist who studied Indo-European languages. Life Born in Stanislawow, Austria-Hungary. He was a Polish historical linguist, structuralist and language theoretician, deeply interested in the studies of Indo-European languages. He studied at the Vienna University of Economics and Business (1913–1914), and then, after World War I, continued his studies at Lwów University, where his unusual language skills drew the attention of some prominent linguists. As a result, he was granted a scholarship in Paris. This gave him an opportunity to qualify as a university professor of Indo-European linguistics soon after his return to Poland. After obtaining the title, he became a professor at the University of Lwów. Later on, in 1946-48 Kuryłowicz filled in for Dr Krzyżanowski at the Institute of English Philology in Wrocław. Finally, he moved to Kraków, where he took the chair of General Linguistics at Jagiellonian U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holger Pedersen (linguist)
Holger Pedersen (; 7 April 1867 – 25 October 1953) was a Danish linguist who made significant contributions to language science and wrote about 30 authoritative works concerning several languages. He was born in Gelballe, Denmark, and died in Hellerup, next to Copenhagen. Education and academic career ''(Principal source: Koerner 1983)'' Pedersen studied at the University of Copenhagen with Karl Verner, Vilhelm Thomsen, and Hermann Möller. He subsequently studied at the University of Leipzig with Karl Brugmann, Eduard Sievers, Ernst Windisch, and August Leskien. In the fall of 1893, Pedersen enrolled at the University of Berlin, where he studied with Johannes Schmidt. The following year he studied Celtic languages and Sanskrit with Heinrich Zimmer at the University of Greifswald. In 1895 he spent several months in the Aran Islands in Ireland to study the conservative form of Gaelic spoken there. Pedersen submitted his doctoral dissertation to the University of Copenhage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calvert Watkins
Calvert Watkins ( /ˈwɒtkɪnz/; March 13, 1933 – March 20, 2013) was an American linguist and philologist, known for his book ''How to Kill a Dragon''. He was a professor of linguistics and the classics at Harvard University and after retirement went to serve as professor-in-residence at UCLA. Early life Family Calvert Watkins was born in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania on March 13, 1933 to Ralph James Watkins, an economist and government advisor, and Willye Ward, a Spanish teacher who translated the personal memoirs of former Mexican president Gen. Antonio Lopez de Santa Anna. Much of Watkins's childhood was spent in New York City, and he graduated from Friends Seminary in Manhattan before beginning his career at Harvard University. Watkins's early exposure to Latin and Greek inspired him at the age of fifteen to decide to become an Indo-Europeanist. Education Watkins received his initial undergraduate degree from Harvard University in 1954, graduating summa cum laude, and hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alwin Kloekhorst
Alwin Kloekhorst (born in Smilde, 1978) is a Dutch linguist, Indo-Europeanist and Hittitologist. Biography Kloekhorst received his Ph.D. in 2007 at Leiden University for his thesis on Hittite. In over 1200 pages, his dissertation describes the history of Hittite in the light of its Indo-European language origin. Part One, ''Towards a Hittite Historical Grammar'', contains a description of Hittite phonology and a discussion of the sound laws and morphological changes that took place between the Proto-Indo-European and Hittite. Part Two, ''An Etymological Dictionary of the Hittite Inherited Lexicon'', contains etymological treatments of all Hittite words of Indo-European origin. One of the dissertation's most important conclusions is the confirmation that the Anatolian languages split from Proto-Indo-European before all other Indo-European branches, which have undergone a period of common innovations (see Indo-Hittite). The thesis was published in the Leiden-based Indo-European Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |