|
Hınıs
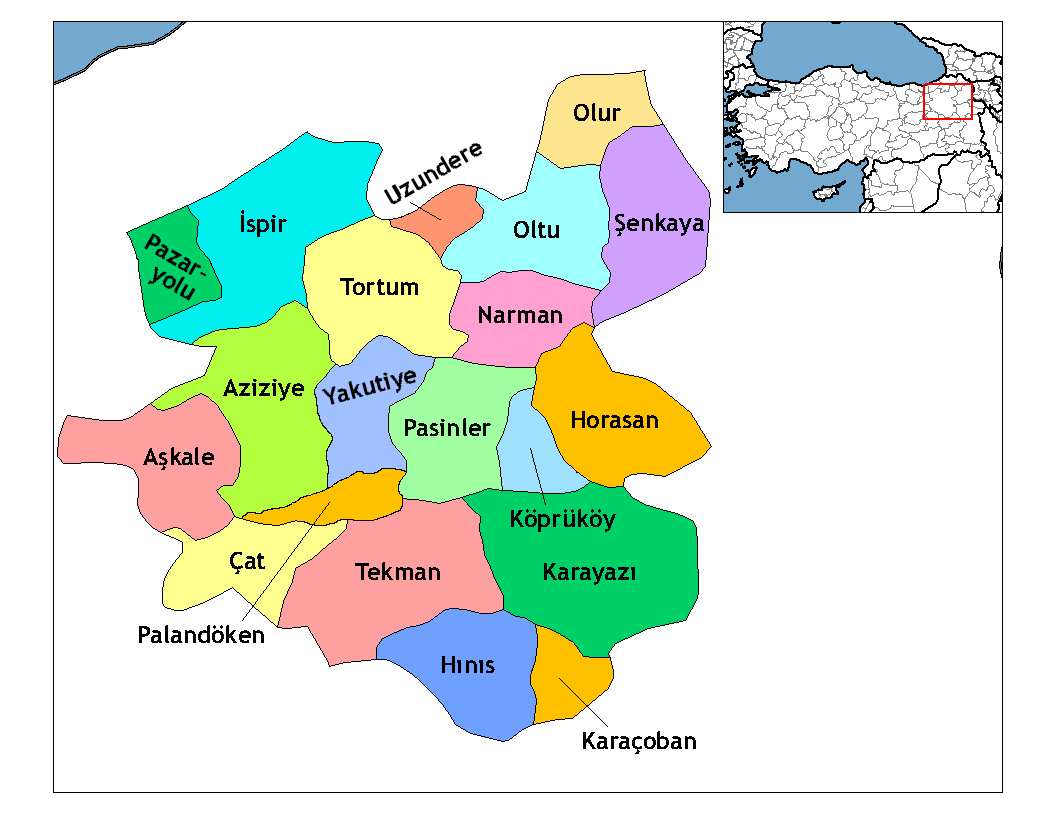
Hınıs ( ku, Xinûs, hy, Խնուս, ''Khnus'') is a town and district of Erzurum Province in the Eastern Anatolia Region of Turkey. The population is 9,792 (as of 2010). Historical monuments in the town include the castle and the Ulu Cami Mosque, said to be built in 1734 by Alaeddin, the bey of Muş. The town is populated by Kurds. The district, which is 150 km away from Erzurum to the south, that is to Muş, is very close to the Hamurpert Lake, which has an important place in history, with its location close to the Bingöl mountains. The other districts of the province, Karayazı, Karaçoban and Tekman, are the neighboring districts of Hınıs. In addition, the Varto district of Muş is only 50 km from Hınıs. Hınıs is a plain district and Hınıs Plain is one of the most fertile plains of the region. Therefore, agriculture and animal husbandry are the main sources of income in the district. It has the same characteristics as Erzurum in terms of climate and nature. Winters a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erzurum Eyalet
The Erzurum Eyalet ( ota, ایالت ارضروم, ''Eyālet-i Erżurūm'') was an eyalet of the Ottoman Empire. It was established after the conquest of Western Armenia by the Ottoman Empire. Its reported area in the 19th century was . History The eyalet was established in 1533. Early in the 17th century, the eyalet was threatened by Iran and the revolt by the province governor Abaza Mehmed Pasha. This revolt was combined with Jelali Revolts (the uprising of the provincial musketeers called the Celali), backed by Iran and lasted until 1628. It was one of the first Ottoman provinces to become a vilayet after an administrative reform in 1865, and by 1867 it had been reformed into the Erzurum Vilayet. Governors * Köprülü Fazıl Ahmed Köprülü may refer to: People * Köprülü family (Kypriljotet), an Ottoman noble family of Albanian origin ** Köprülü era (1656–1703), the period in which the Ottoman Empire's politics were set by the Grand Viziers, mainly the Köprülü ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erzurum Province
Erzurum Province ( tr, Erzurum ili) is a province of Turkey in the Eastern Anatolia Region of the country. The capital of the province is the city of Erzurum. It is bordered by the provinces of Kars and Ağrı to the east, Muş and Bingöl to the south, Erzincan and Bayburt to the west, Rize and Artvin to the north and Ardahan to the northeast. Okay Memiş was appointed as the governor of the province by a presidential decree on 27 October 2018. The province has an overall Turkish-majority. Geography The surface area of the province of Erzurum is the fourth biggest in Turkey. The majority of the province is elevated. Most plateaus are about above sea level, and the mountainous regions beyond the plateaus are and higher. Depression plains are located between the mountains and plateaus. The southern mountain ranges include the Palandöken Mountains (highest peak Büyük Ejder high) and the Şahveled Mountains (highest peak Çakmak Mountain high). The northern mountain ranges a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATD Of The Regions Of Turkey Occupied By Russian Troops During WW1 , Malta
{{disambig ...
ATD may refer to: Computing and technology * Anthropomorphic test device, also known as a crash test dummy * ''at (command)'' or @daemon (spelled "atd", lower case), a standard Unix program * Azimuth tractor drive, a drive system for tugboats Medicine and science * 1,4,6-Androstatrien-3,17-dione, estrogen inhibitor * Acute tryptophan depletion * Anti-thyroid drugs or antithyroid agent Other uses * ATD Fourth World * ''Against the Day'', a Thomas Pynchon novel * Association for Talent Development * Attention to Detail, a defunct British video game developer * the postal code of Attard Attard ( mt, Ħ'Attard) is a town in the Central Region, Malta, Central Region of Malta. Together with Balzan and Lija it forms part of "Three villages of Malta, the Three Villages" and has been inhabited since the Classical antiquity, Classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Erzurum Province
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minaret
A minaret (; ar, منارة, translit=manāra, or ar, مِئْذَنة, translit=miʾḏana, links=no; tr, minare; fa, گلدسته, translit=goldaste) is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generally used to project the Muslim call to prayer ('' adhan''), but they also served as landmarks and symbols of Islam's presence. They can have a variety of forms, from thick, squat towers to soaring, pencil-thin spires. Etymology Two Arabic words are used to denote the minaret tower: ''manāra'' and ''manār''. The English word "minaret" originates from the former, via the Turkish version (). The Arabic word ''manāra'' (plural: ''manārāt'') originally meant a "lamp stand", a cognate of Hebrew '' menorah''. It is assumed to be a derivation of an older reconstructed form, ''manwara''. The other word, ''manār'' (plural: ''manā'ir'' or ''manāyir''), means "a place of light". Both words derive from the Arabic root ''n-w-r'', which has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulu Cami
A congregational mosque or Friday mosque (, ''masjid jāmi‘'', or simply: , ''jāmi‘''; ), or sometimes great mosque or grand mosque (, ''jāmi‘ kabir''; ), is a mosque for hosting the Friday noon prayers known as ''jumu'ah''.* * * * * * * * * It can also host the Eid prayers in situations when there is no ''musalla'' or ''eidgah'' available nearby to host the prayers. In early Islamic history, the number of congregational mosques in one city was strictly limited. As cities and populations grew over time, it became more common for many mosques to host Friday prayers in the same area. Etymology The full Arabic term for this kind of mosque is ''masjid jāmi‘'' (), which is typically translated as "mosque of congregation" or "congregational mosque". "Congregational" is used to translate ''jāmi‘'' (), which comes from the Arabic root "ج - م - ع" which has a meaning ‘to bring together’ or ‘to unify’ (verbal form: and ). In Arabic, the term is typically simplifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanjak
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ) * Armenian language, Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province") * Bulgarian language, Bulgarian: окръг (''okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region") * el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province") or επαρχία (''eparchia'', meaning "eparchy") * lad, sancak , group=note (; ota, ; Modern Turkish: ''Sancak'', ) were administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire. ''Sanjak'', and the variant spellings ''sandjak'', ''sanjaq'' and ''sinjaq'', are English language, English or French language, French transliterations of the Turkish language, Turkish word ''sancak'', meaning "district", "banner (country subdivision), banner" or "flag". Sanjaks were also called by the Arabic language, Arabic word for ''banner'' or ''flag'': ''Liwa (Arabic), liwa (Liwā or Liwā’)''. Ottoman provinces (eyalets, later vilayets) were divided into sanjaks (also called ''livas'') governed by sanjakbeys (also calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulanık
Bulanık, formerly Gop or Kop ( hy, Կոփ, ku, Kop), is a town and district in Muş Province, in the Eastern Anatolian region of Turkey. History In the 19th century Bulanık was the name of the kaza. Its capital, today's Bulanık town, was called Gop, also rendered as Kop. At the end of the 19th century Gop was described as a large village with about 400 houses, all but 50 of them inhabited by Armenians. Although the soil was amongst the most fertile in the region, the inhabitants were almost destitute due to the region's insecurity and the impossibility of exporting their crops. Two miles south of the village was an Armenian monastery named Surb Daniel which contained the relics of a saint of that name. The district was formerly called Hark' and was part of Historical Armenia's Turuberan province. The earliest record of Kop is found in the 995 encyclical from Vandir monastery under the name Koghb, which was later distorted. Bulanık means "blurred" in Turkish which is a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Nazik
Lake Nazik ( tr, Nazik; hy, Նազիկ, ku, Gola Nazikê) is a freshwater lake in the Bitlis Province, eastern part of Turkey. It is located at , close to Lake Van Lake Van ( tr, Van Gölü; hy, Վանա լիճ, translit=Vana lič̣; ku, Gola Wanê) is the largest lake in Turkey. It lies in the far east of Turkey, in the provinces of Van and Bitlis in the Armenian highlands. It is a saline soda lake .... Lake Nazik is located in the elevation of about 1,816 m. It has an area of 44.5 km² and maximum depth of about 50 m. References Sports Activitiesat the Republic of Turkey Ministry of Culture and Tourism Site Nazik Landforms of Bitlis Province {{Bitlis-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Bitlis
The Principality of Bitlis, also known as the Bitlis Khanate and the Bitlis Emirate (1182–early 19th century) was a Kurdish principality originated from the ''Rojaki'' (or ''Rozagi'') tribal confederation. The Rojaki defeated the Georgian King David the Curopalate and conquered Bitlis and Sasun in the 10th century. The principality occasionally came under the rule of outsiders, such as the Aq Qoyunlu (from 1467 to 1495) and the Safavids (from 1507 to 1514). After the decline of the Aq Qoyunlu, the Rojaki princes asserted their independence. The principality supported the Ottoman Sultan Selim I and its rulers were named Noble Khans in return. In 1531, the Rojaki prince withdrew his support for the Ottomans and turned towards the Safavids instead, an event that lead to the capture of the principality by the Ottomans. A good era for the principality began in 1578, as Sultan Murad III nominated Sharaf al-Din Bitlisi the Emir of the principality. Until 1596, eighteen Rojaki princes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
