|
Härsbacka Mine
Härsbacka mine ( sv, Härsbacka gruva) is a quartz and feldspar mine. It was once Sweden's foremost quartz mine. The mine was closed in 1946. The quartz and feldspar mined in Härsbacka are the main constituent of a large pegmatite dyke. This pegmatite dyke dips about 60 to 70° to the southeast and has a maximum thickness of 37 m. While quartz and feldspar are mostly mixed, pure zones of either occur. Most feldspar is pink microclineperthite and much lesser amounts are white oligoclase. There are lesser quantities of biotite, garnet, molybdenite and fluorite. About 230,000 tons of quartz have been mined in total from Härsbacka mine. In 1947 the mine was bought by Statens Vattenfallverk to turn it into an oil storage depot and it functioned as such until 1985 when it was emptied. Since 1997 the mine is fully flooded by groundwater. In 2021 the Geological Survey of Sweden Geological Survey of Sweden ( sv, Sveriges geologiska undersökning, SGU) is a Swedish government agency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Sweden
The municipalities of Sweden ( sv, Sveriges kommuner) are its lower-level local government entities. There are 290 municipalities which are responsible for a large proportion of local services, including schools, emergency services and physical planning. Foundation The Local Government Act of 1991 specifies several responsibilities for the municipalities, and provides outlines for local government, such as the process for electing the municipal assembly. It also regulates a process (''laglighetsprövning'', "legality trial") through which any citizen can appeal the decisions of a local government to a county court. Municipal government in Sweden is similar to city commission government and cabinet-style council government. A legislative municipal assembly ''(kommunfullmäktige)'' of between 31 and 101 members (always an odd number) is elected from party-list proportional representation at municipal elections, held every four years in conjunction with the national general ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives. All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different species are pyrope, almandine, spessartine, grossular (varieties of which are hessonite or cinnamon-stone and tsavorite), uvarovite and andradite. The garnets make up two solid solution series: pyrope-almandine-spessartine (pyralspite), with the composition range ; and uvarovite-grossular-andradite (ugrandite), with the composition range . Etymology The word ''garnet'' comes from the 14th-century Middle English word ''gernet'', meaning 'dark red'. It is borrowed from Old French ''grenate'' from Latin ''granatus,'' from ''granum'' ('grain, seed'). This is possibly a reference to ''mela granatum'' or even ''pomum granatum'' ('pomegranate', ''Punica granatum''), a plant whose fruits contain abundant and vivid red seed covers ( arils), whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Mines In Sweden
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz Mines In Sweden
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral defining the val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underground Mines In Sweden
Underground most commonly refers to: * Subterranea (geography), the regions beneath the surface of the Earth Underground may also refer to: Places * The Underground (Boston), a music club in the Allston neighborhood of Boston * The Underground (Stoke concert venue), a club/music venue based in Hanley, Stoke-on-Trent * Underground Atlanta, a shopping and entertainment district in the Five Points neighborhood of downtown Atlanta, Georgia * Buenos Aires Underground, a rapid transit system * London Underground, a rapid transit system Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Underground'' (1928 film), a drama by Anthony Asquith * ''Underground'' (1941 film), a war drama by Vincent Sherman * ''Underground'' (1970 film), a war drama starring Robert Goulet * ''Underground'' (1976 film), a documentary about the radical organization the Weathermen * ''Underground'' (1989 film), a film featuring Melora Walters * ''Underground'' (1995 film), a film by Emir Kusturica * ''The Underground'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feldspar Mines In Sweden
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldspars and the ''alkali'' (potassium-sodium) feldspars. Feldspars make up about 60% of the Earth's crust, and 41% of the Earth's continental crust by weight. Feldspars crystalize from magma as both intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks and are also present in many types of metamorphic rock. Rock formed almost entirely of calcic plagioclase feldspar is known as anorthosite. Feldspars are also found in many types of sedimentary rocks. Compositions The feldspar group of minerals consists of tectosilicates, silicate minerals in which silicon ions are linked by shared oxygen ions to form a three-dimensional network. Compositions of major elements in common feldspars can be expressed in terms of three endmembers: * potassium feldspar (K-spar) en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1946 Disestablishments In Sweden
Events January * January 6 - The 1946 North Vietnamese parliamentary election, first general election ever in Vietnam is held. * January 7 – The Allies recognize the Austrian republic with its 1937 borders, and divide the country into four Allied-occupied Austria, occupation zones. * January 10 ** The first meeting of the United Nations is held, at Methodist Central Hall Westminster in London. ** ''Project Diana'' bounces radar waves off the Moon, measuring the exact distance between the Earth and the Moon, and proves that communication is possible between Earth and outer space, effectively opening the Space Age. * January 11 - Enver Hoxha declares the People's Republic of Albania, with himself as prime minister of Albania, prime minister. * January 16 – Charles de Gaulle resigns as head of the Provisional Government of the French Republic, French provisional government. * January 17 - The United Nations Security Council holds its first session, at Church House, Westmin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1895 Establishments In Sweden
Events January–March * January 5 – Dreyfus affair: French officer Alfred Dreyfus is stripped of his army rank, and sentenced to life imprisonment on Devil's Island. * January 12 – The National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty is founded in England by Octavia Hill, Robert Hunter and Canon Hardwicke Rawnsley. * January 13 – First Italo-Ethiopian War: Battle of Coatit – Italian forces defeat the Ethiopians. * January 17 – Félix Faure is elected President of the French Republic, after the resignation of Jean Casimir-Perier. * February 9 – Mintonette, later known as volleyball, is created by William G. Morgan at Holyoke, Massachusetts. * February 11 – The lowest ever UK temperature of is recorded at Braemar, in Aberdeenshire. This record is equalled in 1982, and again in 1995. * February 14 – Oscar Wilde's last play, the comedy ''The Importance of Being Earnest'', is first shown at St J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the water table. Groundwater is recharged from the surface; it may discharge from the surface naturally at springs and seeps, and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal, and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology, also called groundwater hydrology. Typically, groundwater is thought of as water flowing through shallow aquifers, but, in the technical sense, it can also contain soil moisture, perma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Storage Depot
An oil terminal (also called a tank farm, tankfarm, oil installation or oil depot) is an industrial facility for the storage of oil, petroleum and petrochemical products, and from which these products are transported to end users or other storage facilities. An oil terminal typically has a variety of above or below ground tankage; facilities for inter-tank transfer; pumping facilities; loading gantries for filling road tankers or barges; ship loading/unloading equipment at marine terminals; and pipeline connections. History Originally, open pits and cubic reservoirs were used for industrial oil storage. The structure was pioneered by Russian engineer Vladimir Shukhov during his work for Branobel oil company. He published an article "Mechanical structures in oil industry" ("") in 1883, mathematically proving that cylindrical shape would require the least amount of steel, modelling structural stresses specific to oil storage. Shukhov also developed construction methods, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
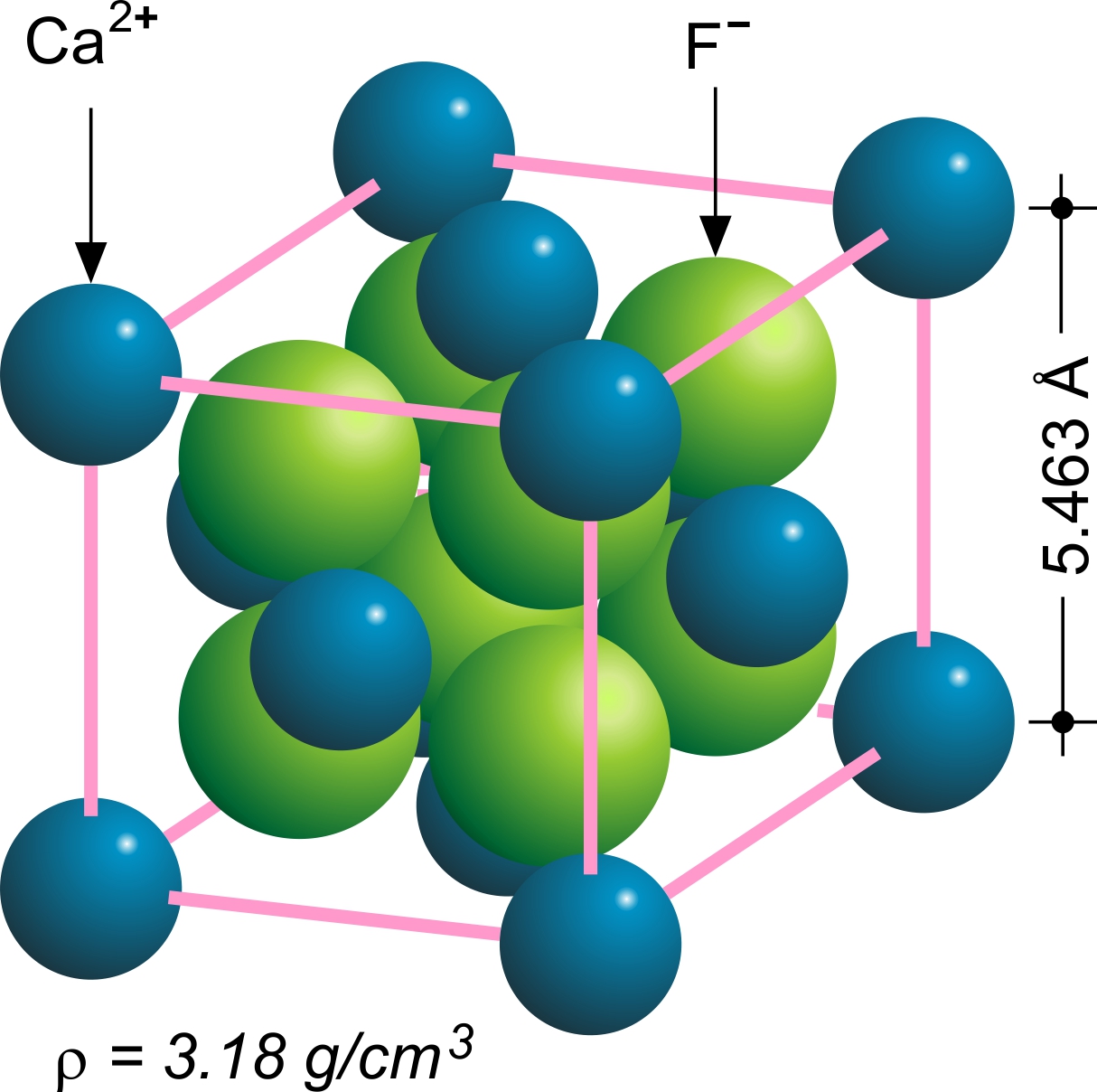
Fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 4 as fluorite. Pure fluorite is colourless and transparent, both in visible and ultraviolet light, but impurities usually make it a colorful mineral and the stone has ornamental and lapidary uses. Industrially, fluorite is used as a flux for smelting, and in the production of certain glasses and enamels. The purest grades of fluorite are a source of fluoride for hydrofluoric acid manufacture, which is the intermediate source of most fluorine-containing fine chemicals. Optically clear transparent fluorite lenses have low dispersion, so lenses made from it exhibit less chromatic aberration, making them valuable in microscopes and telescopes. Fluorite optics are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |