|
Hypozeuxis
Hypozeuxis is a rhetorical term for an expression or sentence where every clause has its own independent subject and predicate. If the same words are repeated in each clause, it is also an example of anaphora. *"We shall fight on the beaches. We shall fight on the landing grounds. We shall fight in the fields and in the streets. We shall fight in the hills." (Winston Churchill) The opposite of hypozeuxis is hyperzeuxis, which may also be a form of zeugma or syllepsis. See also * Glossary of rhetorical terms Owing to its origin in ancient Greece and Rome, English rhetorical theory frequently employs Greek and Latin words as terms of art. This page explains commonly used rhetorical terms in alphabetical order. The brief definitions here are intended to ... References Rhetorical techniques {{rhetorics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Rhetorical Terms
Owing to its origin in ancient Greece and Rome, English rhetorical theory frequently employs Greek and Latin words as terms of art. This page explains commonly used rhetorical terms in alphabetical order. The brief definitions here are intended to serve as a quick reference rather than an in-depth discussion. For more information, click the terms. A *''Absurdity.'' The exaggeration of a point beyond belief. *''Accumulatio.'' The emphasis or summary of previously made points or inferences by excessive praise or accusation. *'' Acutezza.'' Wit or wordplay used in rhetoric. *'' Ad hominem.'' Rebutting an argument by attacking the character, motive, or other attribute of the person making it rather than the substance of the argument itself. *'' Adianoeta.'' A phrase carrying two meanings: an obvious meaning and a second, more subtle and ingenious one. *'' Adjunction.'' When a verb is placed at the beginning or the end of a sentence instead of in the middle. For example (from ''Rhetoric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeugma And Syllepsis
In rhetoric, zeugma (; from the Ancient Greek , , lit. "a yoking together"Liddell, H. G. & al. ''A Greek-English Lexicon''"" Perseus Project. Retrieved 24 January 2013.) and syllepsis (; from the Ancient Greek , , lit. "a taking together"''Random House Dictionary''"Syllepsis" 2013. Retrieved 24 January 2013.) are figures of speech in which a single phrase or word joins different parts of a sentence. Definition In current usage, there are multiple and sometimes conflicting definitions for zeugma and syllepsis. This article categorizes these two figures of speech into four types, based on four definitions: Type 1 Grammatical syllepsis (sometimes also called ''zeugma''): where a single word is used in relation to two other parts of a sentence although the word grammatically or logically applies to only one. By definition, grammatical syllepsis will often be grammatically "incorrect" according to traditional grammatical rules. However, such solecisms are sometimes not errors bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syllepsis
In rhetoric, zeugma (; from the Ancient Greek , , lit. "a yoking together"Liddell, H. G. & al. ''A Greek-English Lexicon''"" Perseus Project. Retrieved 24 January 2013.) and syllepsis (; from the Ancient Greek , , lit. "a taking together"''Random House Dictionary''"Syllepsis" 2013. Retrieved 24 January 2013.) are figures of speech in which a single phrase or word joins different parts of a sentence. Definition In current usage, there are multiple and sometimes conflicting definitions for zeugma and syllepsis. This article categorizes these two figures of speech into four types, based on four definitions: Type 1 Grammatical syllepsis (sometimes also called ''zeugma''): where a single word is used in relation to two other parts of a sentence although the word grammatically or logically applies to only one. By definition, grammatical syllepsis will often be grammatically "incorrect" according to traditional grammatical rules. However, such solecisms are sometimes not errors bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Rhetorical Terms
Owing to its origin in ancient Greece and Rome, English rhetorical theory frequently employs Greek and Latin words as terms of art. This page explains commonly used rhetorical terms in alphabetical order. The brief definitions here are intended to serve as a quick reference rather than an in-depth discussion. For more information, click the terms. A *''Absurdity.'' The exaggeration of a point beyond belief. *''Accumulatio.'' The emphasis or summary of previously made points or inferences by excessive praise or accusation. *'' Acutezza.'' Wit or wordplay used in rhetoric. *'' Ad hominem.'' Rebutting an argument by attacking the character, motive, or other attribute of the person making it rather than the substance of the argument itself. *'' Adianoeta.'' A phrase carrying two meanings: an obvious meaning and a second, more subtle and ingenious one. *'' Adjunction.'' When a verb is placed at the beginning or the end of a sentence instead of in the middle. For example (from ''Rhetoric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
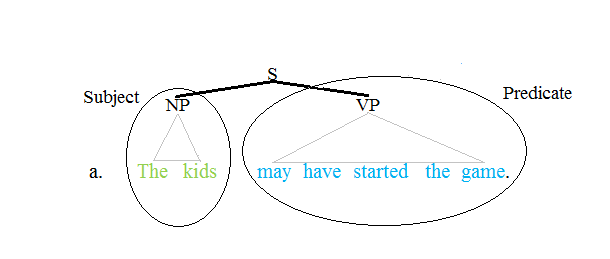
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in one of two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject, and the other views it as just the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake''. By the second definition, the predicate of the same sentence is just the content verb ''likes'', whereby ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the arguments of this predicate. Differences between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of predicates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphora (rhetoric)
In rhetoric, an anaphora (, "carrying back") is a rhetorical device that consists of repeating a sequence of words at the beginnings of neighboring clauses, thereby lending them emphasis. In contrast, an epistrophe (or epiphora) is repeating words at the clauses' ends. The combination of anaphora and epistrophe results in symploce. Functions Other than the function of emphasizing ideas, the use of anaphora as a rhetorical device adds rhythm to a word as well as making it more pleasurable to read and easier to remember. Anaphora is repetition at the beginning of a sentence to create emphasis. Anaphora serves the purpose of delivering an artistic effect to a passage. It is also used to appeal to the emotions of the audience in order to persuade, inspire, motivate and encourage them. In Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.'s famous "I Have a Dream" speech, he uses anaphora by repeating "I have a dream" eight times throughout the speech. Usage Today, anaphora is seen in many different c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
We Shall Fight On The Beaches
"We shall fight on the beaches" is a common title given to a speech delivered by the British Prime Minister Winston Churchill to the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom on 4 June 1940. This was the second of three major speeches given around the period of the Battle of France; the others are the "Blood, toil, tears and sweat" speech of 13 May 1940, and the "This was their finest hour" speech of 18 June 1940. Events developed dramatically over the five-week period, and although broadly similar in themes, each speech addressed a different military and diplomatic context. In this speech, Churchill had to describe a great military disaster, and warn of a possible invasion attempt by Nazi Germany, without casting doubt on eventual victory. He also had to prepare his domestic audience for France's falling out of the war without in any way releasing France to do so, and wished to reiterate a policy and an aim unchangeddespite the intervening eventsfrom his speec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, during the Second World War, and again from 1951 to 1955. Apart from two years between 1922 and 1924, he was a Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of Parliament (MP) from 1900 to 1964 and represented a total of five UK Parliament constituency, constituencies. Ideologically an Economic liberalism, economic liberal and British Empire, imperialist, he was for most of his career a member of the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party, which he led from 1940 to 1955. He was a member of the Liberal Party (UK), Liberal Party from 1904 to 1924. Of mixed English and American parentage, Churchill was born in Oxfordshire to Spencer family, a wealthy, aristocratic family. He joined the British Army in 1895 and saw action in British Raj, Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |