|
Hypothyreosis
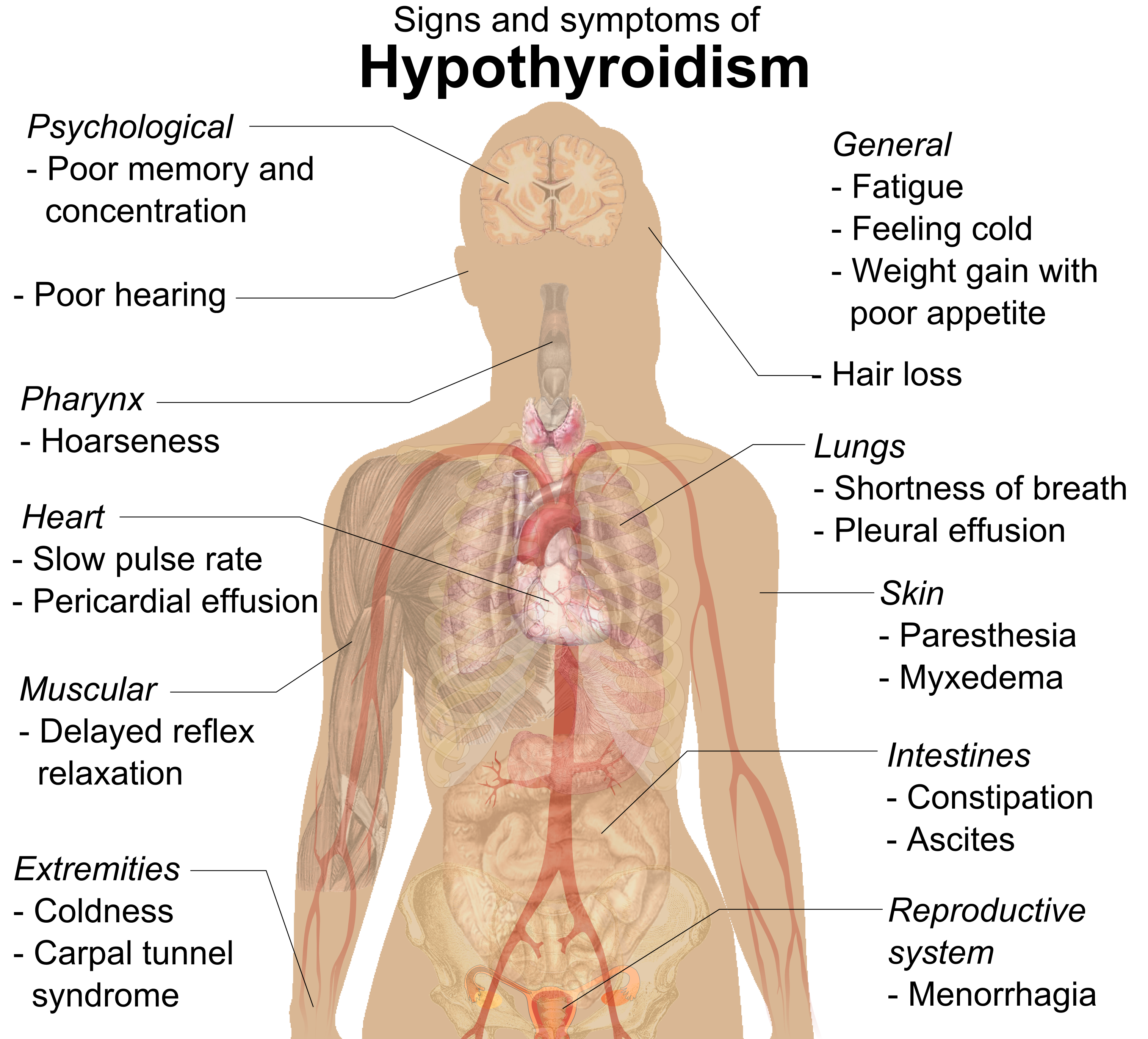
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus or the anterior pituitary gland, certain medications, a lack of a functioning thyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OxfordDictionaries
Lexico was a dictionary website that provided a collection of English and Spanish dictionaries produced by Oxford University Press (OUP), the publishing house of the University of Oxford. While the dictionary content on Lexico came from OUP, this website was operated by Dictionary.com, whose eponymous website hosts dictionaries by other publishers such as Random House. The website was closed and redirected to Dictionary.com on 26 August 2022. Before the Lexico site was launched, the ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' and ''New Oxford American Dictionary'' were hosted by OUP's own website Oxford Dictionaries Online (ODO), later known as Oxford Living Dictionaries. The dictionaries' definitions have also appeared in Google definition search and the Dictionary application on macOS, among others, licensed through the Oxford Dictionaries API. History In the 2000s, OUP allowed access to content of the ''Compact Oxford English Dictionary of Current English'' on a website called AskOxfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine, also known as -thyroxine, is a manufactured form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4). It is used to treat hypothyroidism, thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism), including a severe form known as myxedema coma. It may also be used to treat and prevent certain types of thyroid tumors. It is not indicated for weight loss. Levothyroxine is taken by mouth or given by intravenously, intravenous injection. Maximum effect from a specific dose can take up to six weeks to occur. Side effects from excessive doses include weight loss, trouble tolerating heat, sweating, anxiety, trouble sleeping, tremor, and fast heart rate. Use is not recommended in people who have had a recent myocardial infarction, heart attack. Use during pregnancy has been found to be safe. Dosing should be based on regular measurements of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and T4 levels in the blood. Much of the effect of levothyroxine is following its conversion to triiodothyronine (T3). Levot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond. The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and maternal attachment behaviours, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms. Structure T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine-131
Iodine-131 (131I, I-131) is an important radioisotope of iodine discovered by Glenn Seaborg and John Livingood in 1938 at the University of California, Berkeley. It has a radioactive decay half-life of about eight days. It is associated with nuclear energy, medical diagnostic and treatment procedures, and natural gas production. It also plays a major role as a radioactive isotope present in nuclear fission products, and was a significant contributor to the health hazards from open-air atomic bomb testing in the 1950s, and from the Chernobyl disaster, as well as being a large fraction of the contamination hazard in the first weeks in the Fukushima nuclear crisis. This is because 131I is a major fission product of uranium and plutonium, comprising nearly 3% of the total products of fission (by weight). See fission product yield for a comparison with other radioactive fission products. 131I is also a major fission product of uranium-233, produced from thorium. Due to its mode of be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine Deficiency
Iodine deficiency is a lack of the trace element iodine, an essential nutrient in the diet. It may result in metabolic problems such as goiter, sometimes as an endemic goiter as well as congenital iodine deficiency syndrome due to untreated congenital hypothyroidism, which results in developmental delays and other health problems. Iodine deficiency is an important global health issue, especially for fertile and pregnant women. It is also a preventable cause of intellectual disability. Iodine is an essential dietary mineral for neurodevelopment among children. The thyroid hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine contain iodine. In areas where there is little iodine in the diet, typically remote inland areas where no marine foods are eaten, iodine deficiency is common. It is also common in mountainous regions of the world where food is grown in iodine-poor soil. Prevention includes adding small amounts of iodine to table salt, a product known as ''iodized salt''. Iodine compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Iodine Deficiency Syndrome
Congenital iodine deficiency syndrome is a medical condition present at birth marked by impaired physical and mental development, due to insufficient thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism) often caused by insufficient dietary iodine during pregnancy. It is one cause of underactive thyroid function at birth, called congenital hypothyroidism, historically referred to as cretinism (obsolete). If untreated, it results in impairment of both physical and mental development. Symptoms may include goiter, poor length growth in infants, reduced adult stature, thickened skin, hair loss, enlarged tongue, a protruding abdomen; delayed bone maturation and puberty in children; and mental deterioration, neurological impairment, impeded ovulation, and infertility in adults. In developed countries, thyroid function testing of newborns has assured that in those affected, treatment with the thyroid hormone thyroxine is begun promptly. This screening and treatment have virtually eliminated the consequences o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Development
Child development involves the Human development (biology), biological, developmental psychology, psychological and emotional changes that occur in human beings between birth and the conclusion of adolescence. Childhood is divided into 3 stages of life which include early childhood, middle childhood, and late childhood (preadolescence). Early childhood typically ranges from infancy to the age of 6 years old. During this period, development is significant, as many of life's milestones happen during this time period such as first words, learning to crawl, and learning to walk. There is speculation that middle childhood/preadolescence or ages 6–12 are the most crucial years of a child's life. Adolescence is the stage of life that typically starts around the major onset of puberty, with markers such as menarche and spermarche, typically occurring at 12–13 years of age. It has been defined as ages 10 to 19 by the World Health Organization. In the course of development, the individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goiter
A goitre, or goiter, is a swelling in the neck resulting from an enlarged thyroid gland. A goitre can be associated with a thyroid that is not functioning properly. Worldwide, over 90% of goitre cases are caused by iodine deficiency. The term is from the Latin ''gutturia'', meaning throat. Most goitres are not cancerous (benign), though they may be potentially harmful. Signs and symptoms A goitre can present as a palpable or visible enlargement of the thyroid gland at the base of the neck. A goitre, if associated with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, may be present with symptoms of the underlying disorder. For hyperthyroidism, the most common symptoms are associated with adrenergic stimulation: tachycardia (increased heart rate), palpitations, nervousness, tremor, increased blood pressure and heat intolerance. Clinical manifestations are often related to hypermetabolism, (increased metabolism), excessive thyroid hormone, an increase in oxygen consumption, metabolic changes in pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weight Gain
Weight gain is an increase in body weight. This can involve an increase in muscle mass, fat deposits, excess fluids such as water or other factors. Weight gain can be a symptom of a serious medical condition. Description Weight gain occurs when more energy (as calories from food and beverage consumption) is gained than the energy expended by life activities, including normal physiological processes and physical exercise. If enough weight is gained due to increased body fat deposits, one may become overweight or obese, generally defined as having more body fat (adipose tissue) than is considered good for health. The Body Mass Index (BMI) measures body weight in proportion to height, and defines optimal, insufficient, and excessive weight based on the ratio. Having excess adipose tissue (fat) is a common condition, especially where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary. Overweight and obesity may increase the risk of several diseases, such as diabetes, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slow Heart Rate
Bradycardia (also sinus bradycardia) is a slow resting heart rate, commonly under 60 beats per minute (BPM) as determined by an electrocardiogram. It is considered to be a normal heart rate during sleep, in young and healthy or elderly adults, and in athletes. In some people, bradycardia below 60 BPM may be associated with fatigue, weakness, dizziness, sweating, and fainting. The term "relative bradycardia" is used to refer to a heart rate slower than an individual's typical resting heart rate. Athletes may have athletic heart syndrome, which includes bradycardia as part of the cardiovascular adaptations to training and participation. The word "bradycardia" is from the Greek βραδύς ''bradys'' "slow", and καρδία ''kardia'' "heart". Classification Sinus Atrial bradycardias are divided into three types. The first, respiratory sinus arrhythmia, is usually found in young and healthy adults. Heart rate increases during inhalation and decreases during exhalation. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve after rest or sleep, or occurs independently of physical or mental exertion, it may be a symptom of a medical condition that may become severe or progressive. Fatigue can be a feature of a mental disorder such as depression; may be associated with conditions of chronic pain such as fibromyalgia; it may also feature in conditions of chronic low-level inflammation, and be a disease-related symptom in many other conditions. Fatigue often has no known cause, and is recognised as being very complex in nature. Fatigability describes a susceptibility to fatigue. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of cognitive activity which impairs cognitive abil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Intolerance
Cold sensitivity or cold intolerance is unusual discomfort felt by some people when in a cool environment. There is much variation in the sensitivity to cold experienced by different people, with some putting on many layers of clothing while others in the same environment feel comfortable in one layer. Cold sensitivity may be a symptom of hypothyroidism, anemia, fibromyalgia or vasoconstriction. Vitamin B12 deficiency usually accompanies cold intolerance as well. There are other conditions that may cause a cold intolerance, including low body weight, high body temperature and low blood pressure. There may also be differences in people in the expression of uncoupling proteins, thus affecting their amount of thermogenesis. Psychology may also play a factor in perceived temperature. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |