|
Hypocalcuria
Hypocalciuria is a low level of calcium in the urine. It is a significant risk factor for predicting eclampsia in pregnancy. The most common causes for hypocalciuria is either thiazide diuretics or reduced dietary intake of calcium. The other cause is Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH). Low dietary sodium causes hypocalciuria. It is also common in patients with Gitelman syndrome Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. The disorder is caused by disease-causing .... References Medical signs {{med-sign-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
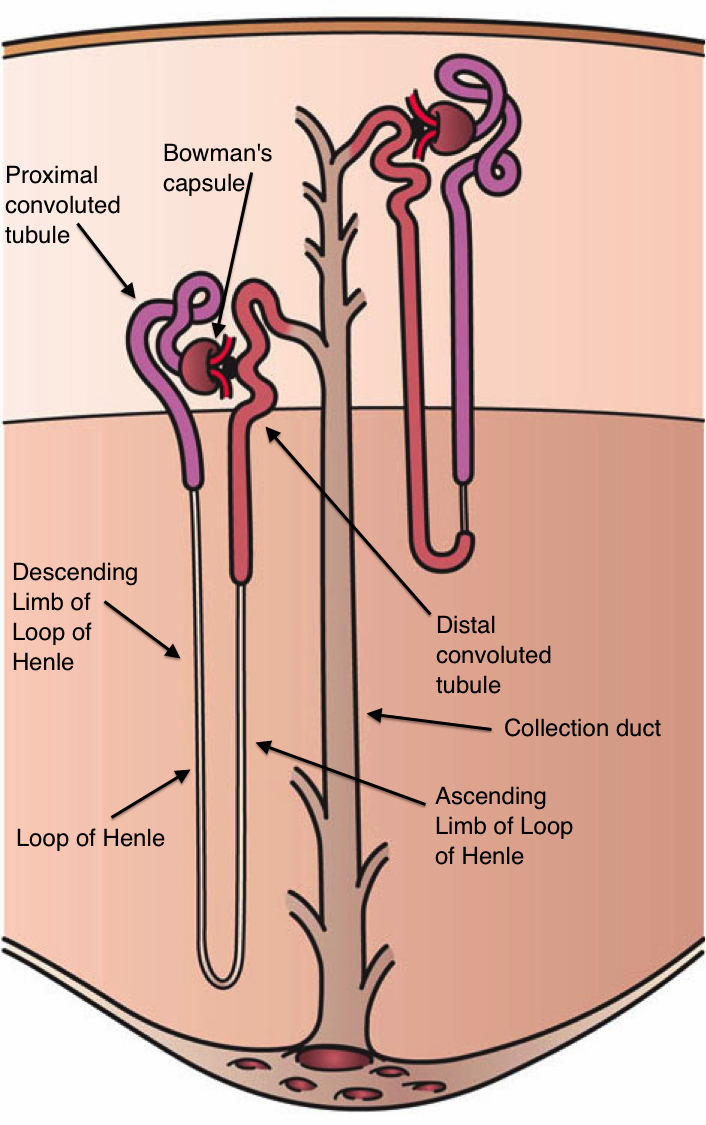
Gitelman Syndrome
Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. The disorder is caused by disease-causing variants in both alleles of the ''SLC12A3'' gene''.'' The ''SLC12A3'' gene encodes the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter (also known as NCC, NCCT, or TSC), which can be found in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. The distal convoluted tubule of the kidney plays an important homeostatic role in sodium and chloride absorption as well as of the reabsorption of magnesium and calcium. Genetic mutations of NCC, lead to loss of function and subsequently, reduced transport of sodium and chloride via NCC. Secondary derangement of calcium, magnesium, and potassium concentrations are caused by secondary effects in the distal tubule and collecting duct. The effect is an electrolyte imbalance similar to that seen with thiazide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium In The Urine
Urinary calcium is calcium in the urine. It is termed -calcuria or -calciuria as a suffix. Normal amount In a urinalysis, the normal amount of urinary calcium can be measured in amount per time (commonly per 24 hours). It can also be measured in amount per mass of creatinine, which avails for estimating the urinary calcium excretion in a spot urine sample, because urinary creatinine clearance is relatively unaffected by differences in free water clearance which occurs, for example, in dehydration and which would distort the interpretation of the urinary calcium in a spot urine sample. Normally, in an average adult, the amount of calcium excreted in the urine is 100–250 mg over a 24-hour period.medscape.com > Urine Calcium: Laboratory Measurement and Clinical UtilityBy Kevin F. Foley, PhD, DABCC; Lorenzo Boccuzzi, DO. Posted: 12/26/2010; Laboratory Medicine. 2010;41(11):683-686. © 2010 American Society for Clinical Pathology. In turn citing: *Wu HBA. Tietz Guide to Clinical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection. Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often used as a synonym. The main difference lies in the realm of practice: medicine (clinical practice) versus public health. As an example from clinical practice, low ingestion of dietary sources of vitamin C is a known risk factor for developing scurvy. Specific to public health policy, a determinant is a health risk that is general, abstract, related to inequalities, and difficult for an individual to control. For example, poverty is known to be a determinant of an individual's standard of health. Correlation vs causation Risk factors or determinants are correlational and not necessarily causal, because correlation does not prove causation. For example, being young cannot be said to cause measles, but young people have a higher rate of meas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclampsia
Eclampsia is the onset of seizures (convulsions) in a woman with pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is one of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy that presents with three main features: new onset of high blood pressure, large amounts of protein in the urine or other organ dysfunction, and edema. The diagnostic criteria for pre-eclampsia is high blood pressure occurring after 20 weeks gestation or during the second half of pregnancy. Most often it occurs during the 3rd trimester of pregnancy and may occur before, during, or after childbirth, delivery. The seizures are of the tonic–clonic type and typically last about a minute. Following the seizure, there is either a postictal period, period of confusion or coma. Other complications include aspiration pneumonia, cerebral hemorrhage, kidney failure, pulmonary edema, HELLP syndrome, coagulopathy, placental abruption and cardiac arrest. Low dose aspirin is recommended to prevent pre-eclampsia and eclampsia in those at high risk. Oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An '' embryo'' is the term for the developing offspring during the first seven weeks following implantation (i.e. ten weeks' gestational age), after which the term ''fetus'' is used until birth. Signs an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiazide
Thiazide () refers to both a class of sulfur-containing organic molecules and a class of diuretics based on the chemical structure of benzothiadiazine. The thiazide drug class was discovered and developed at Merck and Co. in the 1950s. The first approved drug of this class, chlorothiazide, was marketed under the trade name Diuril beginning in 1958. In most countries, thiazides are the least expensive antihypertensive drugs available. Thiazide organic molecules are bi-cyclic structures that contain adjacent sulfur and nitrogen atoms on one ring. Confusion sometimes occurs because thiazide-like diuretics such as indapamide are referred to as thiazides despite not having the thiazide chemical structure. When used this way, "thiazide" refers to a drug which acts at the thiazide receptor. The thiazide receptor is a sodium-chloride transporter that pulls NaCl from the lumen in the distal convoluted tubule. Thiazide diuretics inhibit this receptor, causing the body to release NaCl and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH) is an inherited condition that can cause hypercalcemia, a serum calcium level typically above 10.2 mg/dL; although uncommon. It is also known as familial benign hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FBHH) where there is usually a family history of hypercalcemia which is mild, a urine calcium to creatinine ratio <0.01, and urine calcium <200 mg/day. Signs and symptoms Most cases of familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia are asymptomatic. Laboratory signs of FHH include: * High blood levels of calcium (hypercalcemia) * A low amount of calcium excreted in the urine (Ca excretion rate < 0.02 mmol/L) * High blood levels of magnesium (hypermagnesemia) ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |