|
Hypobetalipoproteinemia
Hypobetalipoproteinemia is a disorder consisting of low levels of LDL cholesterol or apolipoprotein B, below the 5th percentile. The patient can have hypobetalipoproteinemia and simultaneously have high levels of HDL cholesterol. Notably, in people who do not have the genetic disorder hypobetalipoproteinemia, a very low cholesterol level (less than 100 mg/dl) may be a marker for poor nutrition, wasting disease, cancer, hyperthyroidism, and liver disease. In 1997 a study showed that Japanese Centenarians had tenfold increase of hypobetalipoproteinemia compared with controls. Causes One form is thought to be caused by mutated apolipoprotein B. Another form is associated with microsomal triglyceride transfer protein which causes abetalipoproteinemia. A third form, chylomicron retention disease (CRD), is associated with SARA2. Diagnosis Typically in hypobetalipoproteinemia, plasma cholesterol levels will be around 80–120 mg/dL, LDL cholesterol will be around 50–80&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chylomicron Retention Disease
Chylomicron retention disease is a disorder of fat absorption. It is associated with SAR1B. Mutations in SAR1B prevent the release of chylomicrons in the circulation which leads to nutritional and developmental problems. It is a rare autosomal recessive disorder with around 40 cases reported worldwide. Since the disease allele is recessive, parents usually do not show symptoms. Without functional chylomicrons, certain fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin D and vitamin E cannot be absorbed. Chylomicrons have a crucial role in fat absorption and transport, thus a deficiency in chylomicron functioning reduces available levels of dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins. History Chylomicron Retention Disease, also called Anderson's disease, is an autosomal recessive lipid malabsorption syndrome characterized by abnormally low amounts of cholesterol in the blood. This disease most frequently is diagnosed in infants. Charlotte Anderson first published a description of the disorder in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
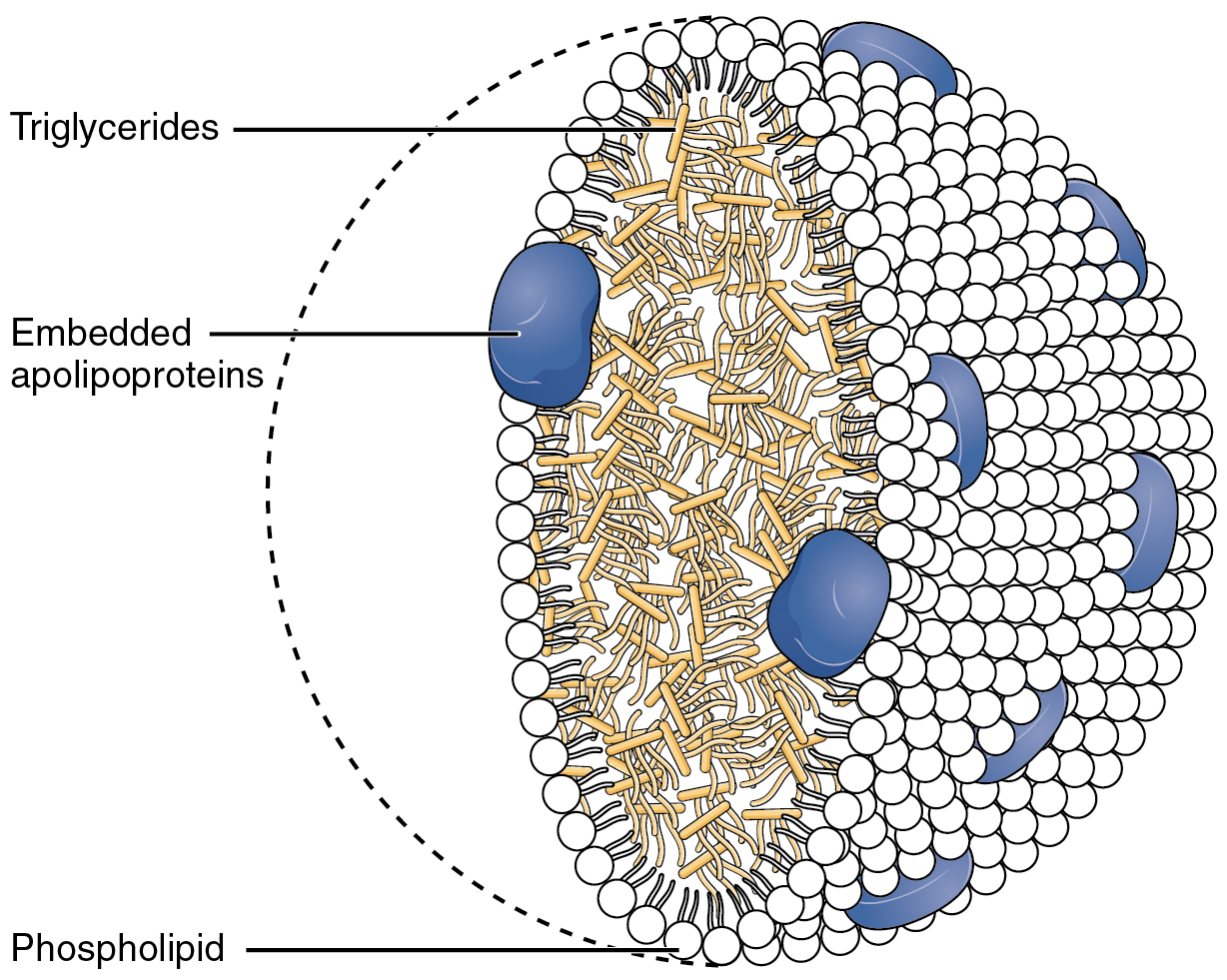
Apolipoprotein B
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene. Function Apolipoprotein B is the primary apolipoprotein of chylomicrons, VLDL, Lp(a), IDL, and LDL particles (LDL—commonly known as "bad cholesterol" when in reference to both heart disease and vascular disease in general), which is responsible for carrying fat molecules (lipids), including cholesterol, around the body to all cells within all tissues. While all the functional roles of ApoB within the LDL (and all larger) particles remain somewhat unclear, it is the primary organizing protein (of the entire complex shell enclosing/carrying fat molecules within) component of the particles and is absolutely required for the formation of these particles. What is also clear is that the ApoB on the LDL particle acts as a ligand for LDL receptors in various cells throughout the body (i.e., less formally, ApoB indicates fat carrying particles are ready to enter any cells with ApoB receptors and deliver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LDL Cholesterol
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall density naming convention), very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL delivers fat molecules to cells. LDL is involved in atherosclerosis, a process in which it is oxidized within the walls of arteries. Overview Lipoproteins transfer lipids (fats) around the body in the extracellular fluid, making fats available to body cells for receptor-mediated endocytosis. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins, typically 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by a single apolipoprotein B for LDL and the larger particles). A single LDL particle is about 220–275 angstroms in diameter, typically transporting 3,000 to 6,000 fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HDL Cholesterol
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are typically composed of 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by one, two or three ApoA. HDL particles enlarge while circulating in the blood, aggregating more fat molecules) and transporting up to hundreds of fat molecules per particle. Overview Lipoproteins are divided into five subgroups, by density/size (an inverse relationship), which also correlates with function and incidence of cardiovascular events. Unlike the larger lipoprotein particles, which deliver fat molecules to cells, HDL particles remove fat molecules from cells. The lipids carried include cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides, amounts of each are variable. Increasing concentrations of HDL particles are associated with decreasing accumulation of atherosclerosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein
Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein large subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MTTP'' gene. MTP encodes the large subunit of the heterodimeric microsomal triglyceride transfer protein. Protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) completes the heterodimeric microsomal triaglyceride transfer protein, which has been shown to play a central role in lipoprotein assembly. Mutations in MTP can cause abetalipoproteinemia. Apolipoprotein B48 on chylomicra and Apolipoprotein B100 on LDL, IDL, and VLDL are important for MTP binding. Interactive pathway map Pharmacology Drugs that inhibit MTTP prevent the assembly of apo B-containing lipoproteins thus inhibiting the synthesis of chylomicrons and VLDL and leading to decrease in plasma levels of LDL-C. * Lomitapide (Juxtapid) was approved by the US FDA for adjunctive treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abetalipoproteinemia
Abetalipoproteinemia (also known as: Bassen-Kornzweig syndrome, microsomal triglyceride transfer protein deficiency disease, MTP deficiency, and betalipoprotein deficiency syndrome) is a disorder that interferes with the normal absorption of fat and fat-soluble vitamins from food. It is caused by a mutation in microsomal triglyceride transfer protein resulting in deficiencies in the apolipoproteins B-48 and B-100, which are used in the synthesis and exportation of chylomicrons and VLDL respectively. It is not to be confused with familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. It is a rare autosomal recessive disorder. Presentation Symptoms Often symptoms will arise that indicate the body is not absorbing or making the lipoproteins that it needs. These symptoms usually appear ''en masse''. These symptoms come as follows: * Failure to thrive (i.e. failure to grow in infancy) * Steatorrhea (i.e. fatty, pale stools) * Frothy stools * Foul smelling stools * Protruding abdomen * Intellectual dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SARA2
The Coat Protein Complex II, or COPII, is a group of proteins that facilitate the formation of vesicles to transport proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus or endoplasmic-reticulum–Golgi intermediate compartment. This process is termed anterograde transport, in contrast to the retrograde transport associated with the COPI complex. COPII is assembled in two parts: first an inner layer of Sar1, Sec23, and Sec24 forms; then the inner coat is surrounded by an outer lattice of Sec13 and Sec31. Function The COPII coat is responsible for the formation of vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). These vesicles transport cargo proteins to the Golgi apparatus (in yeast) or the endoplasmic-reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC, in mammals). Coat assembly is initiated when the cytosolic Ras GTPase Sar1 is activated by its guanine nucleotide exchange factor Sec12. Activated Sar1-GTP inserts itself into the ER membrane, binding preferentially to area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a group of eight fat soluble compounds that include four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. Vitamin E deficiency, which is rare and usually due to an underlying problem with digesting dietary fat rather than from a diet low in vitamin E, can cause nerve problems. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant which may help protect cell membranes from reactive oxygen species. Worldwide, government organizations recommend adults consume in the range of 3 to 15 mg per day. As of 2016, consumption was below recommendations according to a worldwide summary of more than one hundred studies that reported a median dietary intake of 6.2 mg per day for alpha-tocopherol. Population studies suggested that people who consumed foods with more vitamin E, or who chose on their own to consume a vitamin E dietary supplement, had lower incidence of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, dementia, and other diseases. However, placebo-controlled clinical trials using alpha-tocopherol as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |