|
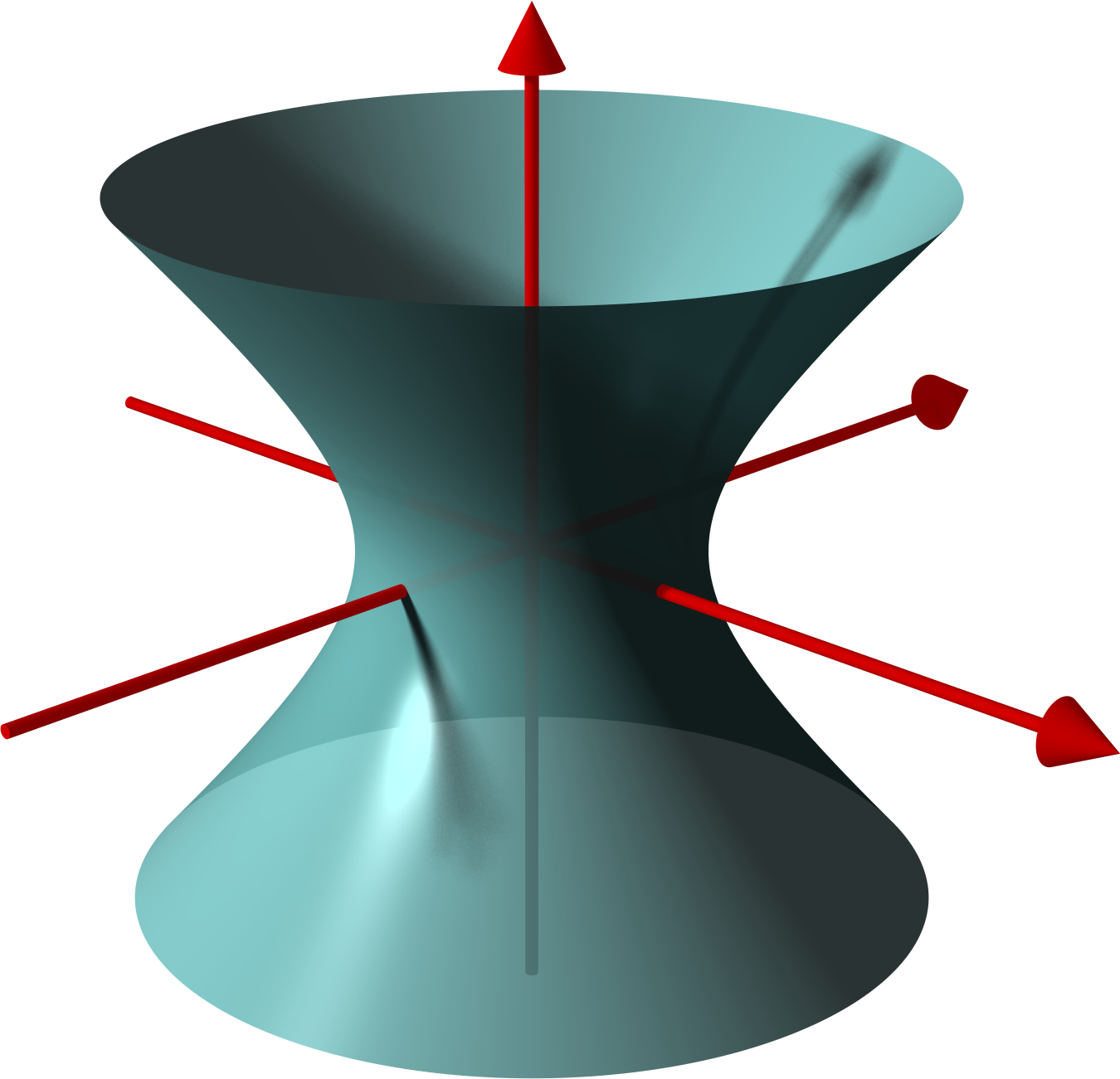
Hyperboloid2
In geometry, a hyperboloid of revolution, sometimes called a circular hyperboloid, is the surface (mathematics), surface generated by rotating a hyperbola around one of its Hyperbola#Nomenclature and features, principal axes. A hyperboloid is the surface obtained from a hyperboloid of revolution by deforming it by means of directional scaling (geometry) , scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. A hyperboloid is a quadric surface, that is, a surface (mathematics), surface defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, a hyperboloid is characterized by not being a conical surface , cone or a cylinder, having a central symmetry, center of symmetry, and intersecting many plane (geometry), planes into hyperbolas. A hyperboloid has three pairwise perpendicular rotational symmetry, axes of symmetry, and three pairwise perpendicular reflection symmetry, planes of symmetry. Given a hyperboloid, one can choose a Cartesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbola
In mathematics, a hyperbola (; pl. hyperbolas or hyperbolae ; adj. hyperbolic ) is a type of smooth curve lying in a plane, defined by its geometric properties or by equations for which it is the solution set. A hyperbola has two pieces, called connected components or branches, that are mirror images of each other and resemble two infinite bows. The hyperbola is one of the three kinds of conic section, formed by the intersection of a plane and a double cone. (The other conic sections are the parabola and the ellipse. A circle is a special case of an ellipse.) If the plane intersects both halves of the double cone but does not pass through the apex of the cones, then the conic is a hyperbola. Hyperbolas arise in many ways: * as the curve representing the reciprocal function y(x) = 1/x in the Cartesian plane, * as the path followed by the shadow of the tip of a sundial, * as the shape of an open orbit (as distinct from a closed elliptical orbit), such as the orbit of a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperboloid2
In geometry, a hyperboloid of revolution, sometimes called a circular hyperboloid, is the surface (mathematics), surface generated by rotating a hyperbola around one of its Hyperbola#Nomenclature and features, principal axes. A hyperboloid is the surface obtained from a hyperboloid of revolution by deforming it by means of directional scaling (geometry) , scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. A hyperboloid is a quadric surface, that is, a surface (mathematics), surface defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, a hyperboloid is characterized by not being a conical surface , cone or a cylinder, having a central symmetry, center of symmetry, and intersecting many plane (geometry), planes into hyperbolas. A hyperboloid has three pairwise perpendicular rotational symmetry, axes of symmetry, and three pairwise perpendicular reflection symmetry, planes of symmetry. Given a hyperboloid, one can choose a Cartesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbola
In mathematics, a hyperbola (; pl. hyperbolas or hyperbolae ; adj. hyperbolic ) is a type of smooth curve lying in a plane, defined by its geometric properties or by equations for which it is the solution set. A hyperbola has two pieces, called connected components or branches, that are mirror images of each other and resemble two infinite bows. The hyperbola is one of the three kinds of conic section, formed by the intersection of a plane and a double cone. (The other conic sections are the parabola and the ellipse. A circle is a special case of an ellipse.) If the plane intersects both halves of the double cone but does not pass through the apex of the cones, then the conic is a hyperbola. Hyperbolas arise in many ways: * as the curve representing the reciprocal function y(x) = 1/x in the Cartesian plane, * as the path followed by the shadow of the tip of a sundial, * as the shape of an open orbit (as distinct from a closed elliptical orbit), such as the orbit of a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Curvature
In differential geometry, the Gaussian curvature or Gauss curvature of a surface at a point is the product of the principal curvatures, and , at the given point: K = \kappa_1 \kappa_2. The Gaussian radius of curvature is the reciprocal of . For example, a sphere of radius has Gaussian curvature everywhere, and a flat plane and a cylinder have Gaussian curvature zero everywhere. The Gaussian curvature can also be negative, as in the case of a hyperboloid or the inside of a torus. Gaussian curvature is an ''intrinsic'' measure of curvature, depending only on distances that are measured “within” or along the surface, not on the way it is isometrically embedding, embedded in Euclidean space. This is the content of the ''Theorema egregium''. Gaussian curvature is named after Carl Friedrich Gauss, who published the ''Theorema egregium'' in 1827. Informal definition At any point on a surface, we can find a Normal (geometry), normal vector that is at right angles to the sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection Symmetry
In mathematics, reflection symmetry, line symmetry, mirror symmetry, or mirror-image symmetry is symmetry with respect to a reflection. That is, a figure which does not change upon undergoing a reflection has reflectional symmetry. In 2D there is a line/axis of symmetry, in 3D a plane of symmetry. An object or figure which is indistinguishable from its transformed image is called mirror symmetric. In conclusion, a line of symmetry splits the shape in half and those halves should be identical. Symmetric function In formal terms, a mathematical object is symmetric with respect to a given operation such as reflection, rotation or translation, if, when applied to the object, this operation preserves some property of the object. The set of operations that preserve a given property of the object form a group. Two objects are symmetric to each other with respect to a given group of operations if one is obtained from the other by some of the operations (and vice versa). The symm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartesian Coordinate System
A Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference coordinate line is called a ''coordinate axis'' or just ''axis'' (plural ''axes'') of the system, and the point where they meet is its ''origin'', at ordered pair . The coordinates can also be defined as the positions of the perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axes, expressed as signed distances from the origin. One can use the same principle to specify the position of any point in three-dimensional space by three Cartesian coordinates, its signed distances to three mutually perpendicular planes (or, equivalently, by its perpendicular projection onto three mutually perpendicular lines). In general, ''n'' Cartesian coordinates (an element of real ''n''-space) specify the point in an ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptotic
In analytic geometry, an asymptote () of a curve is a line such that the distance between the curve and the line approaches zero as one or both of the ''x'' or ''y'' coordinates tends to infinity. In projective geometry and related contexts, an asymptote of a curve is a line which is tangent to the curve at a point at infinity. The word asymptote is derived from the Greek ἀσύμπτωτος (''asumptōtos'') which means "not falling together", from ἀ priv. + σύν "together" + πτωτ-ός "fallen". The term was introduced by Apollonius of Perga in his work on conic sections, but in contrast to its modern meaning, he used it to mean any line that does not intersect the given curve. There are three kinds of asymptotes: ''horizontal'', ''vertical'' and ''oblique''. For curves given by the graph of a function , horizontal asymptotes are horizontal lines that the graph of the function approaches as ''x'' tends to Vertical asymptotes are vertical lines near which the fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Up To
Two Mathematical object, mathematical objects ''a'' and ''b'' are called equal up to an equivalence relation ''R'' * if ''a'' and ''b'' are related by ''R'', that is, * if ''aRb'' holds, that is, * if the equivalence classes of ''a'' and ''b'' with respect to ''R'' are equal. This figure of speech is mostly used in connection with expressions derived from equality, such as uniqueness or count. For example, ''x'' is unique up to ''R'' means that all objects ''x'' under consideration are in the same equivalence class with respect to the relation ''R''. Moreover, the equivalence relation ''R'' is often designated rather implicitly by a generating condition or transformation. For example, the statement "an integer's prime factorization is unique up to ordering" is a concise way to say that any two lists of prime factors of a given integer are equivalent with respect to the relation ''R'' that relates two lists if one can be obtained by reordering (permutation) from the other. As anot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connected Set
In topology and related branches of mathematics, a connected space is a topological space that cannot be represented as the union of two or more disjoint non-empty open subsets. Connectedness is one of the principal topological properties that are used to distinguish topological spaces. A subset of a topological space X is a if it is a connected space when viewed as a subspace of X. Some related but stronger conditions are path connected, simply connected, and n-connected. Another related notion is ''locally connected'', which neither implies nor follows from connectedness. Formal definition A topological space X is said to be if it is the union of two disjoint non-empty open sets. Otherwise, X is said to be connected. A subset of a topological space is said to be connected if it is connected under its subspace topology. Some authors exclude the empty set (with its unique topology) as a connected space, but this article does not follow that practice. For a topologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
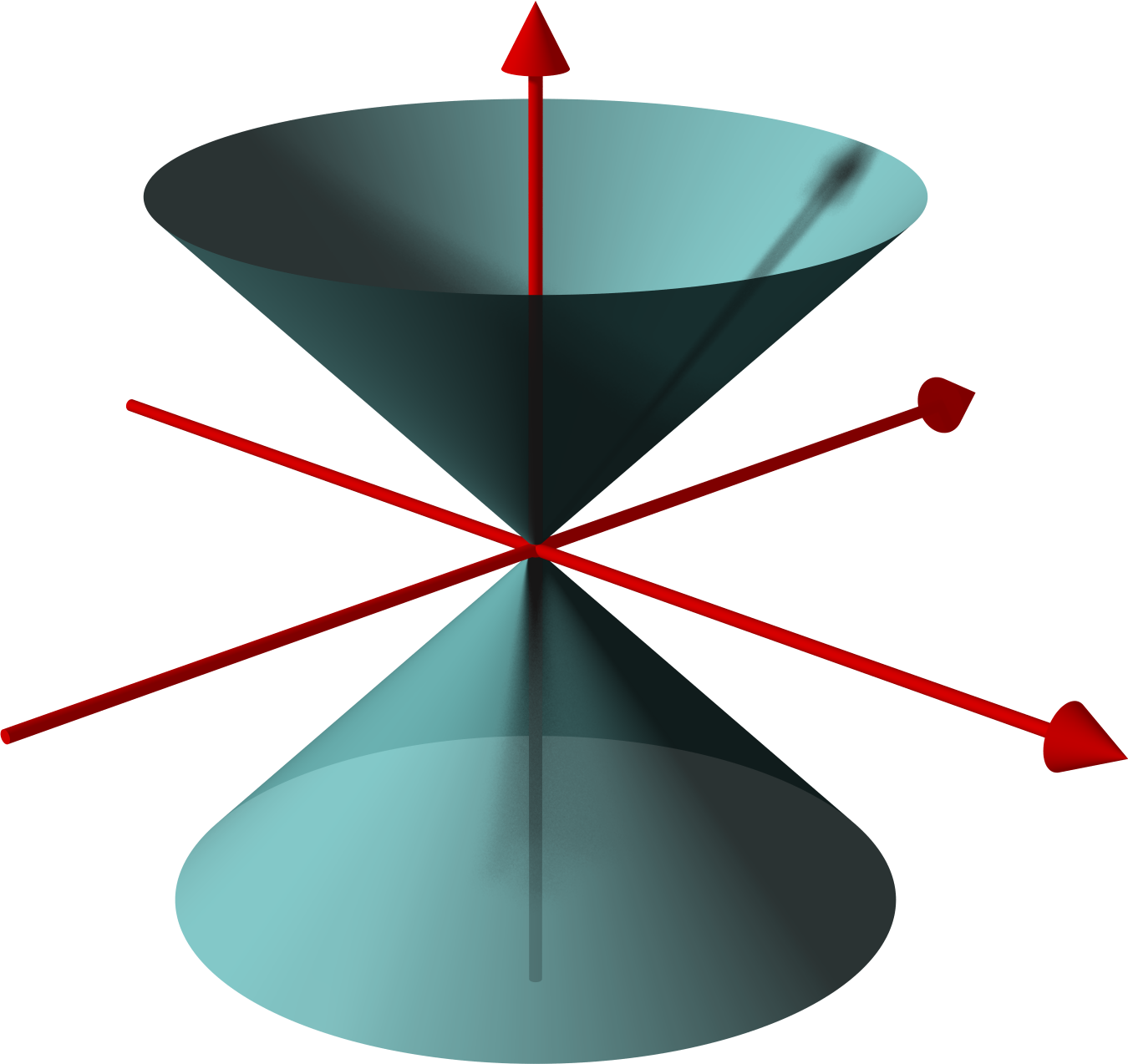
Hyperbolic Paraboloid
In geometry, a paraboloid is a quadric surface that has exactly one axis of symmetry and no center of symmetry. The term "paraboloid" is derived from parabola, which refers to a conic section that has a similar property of symmetry. Every plane section of a paraboloid by a plane parallel to the axis of symmetry is a parabola. The paraboloid is hyperbolic if every other plane section is either a hyperbola, or two crossing lines (in the case of a section by a tangent plane). The paraboloid is elliptic if every other nonempty plane section is either an ellipse, or a single point (in the case of a section by a tangent plane). A paraboloid is either elliptic or hyperbolic. Equivalently, a paraboloid may be defined as a quadric surface that is not a cylinder, and has an implicit equation whose part of degree two may be factored over the complex numbers into two different linear factors. The paraboloid is hyperbolic if the factors are real; elliptic if the factors are complex conjugate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangent Plane
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points on the curve. More precisely, a straight line is said to be a tangent of a curve at a point if the line passes through the point on the curve and has slope , where ''f'' is the derivative of ''f''. A similar definition applies to space curves and curves in ''n''-dimensional Euclidean space. As it passes through the point where the tangent line and the curve meet, called the point of tangency, the tangent line is "going in the same direction" as the curve, and is thus the best straight-line approximation to the curve at that point. The tangent line to a point on a differentiable curve can also be thought of as a '' tangent line approximation'', the graph of the affine function that best approximates the original function at the given point. Similarly, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular
In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90 degrees or π/2 radians). The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the ''perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. It can be defined between two lines (or two line segments), between a line and a plane, and between two planes. Perpendicularity is one particular instance of the more general mathematical concept of '' orthogonality''; perpendicularity is the orthogonality of classical geometric objects. Thus, in advanced mathematics, the word "perpendicular" is sometimes used to describe much more complicated geometric orthogonality conditions, such as that between a surface and its '' normal vector''. Definitions A line is said to be perpendicular to another line if the two lines intersect at a right angle. Explicitly, a first line is perpendicular to a second line if (1) the two lines meet; and (2) at the point of intersection the straight angle on one side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |