|
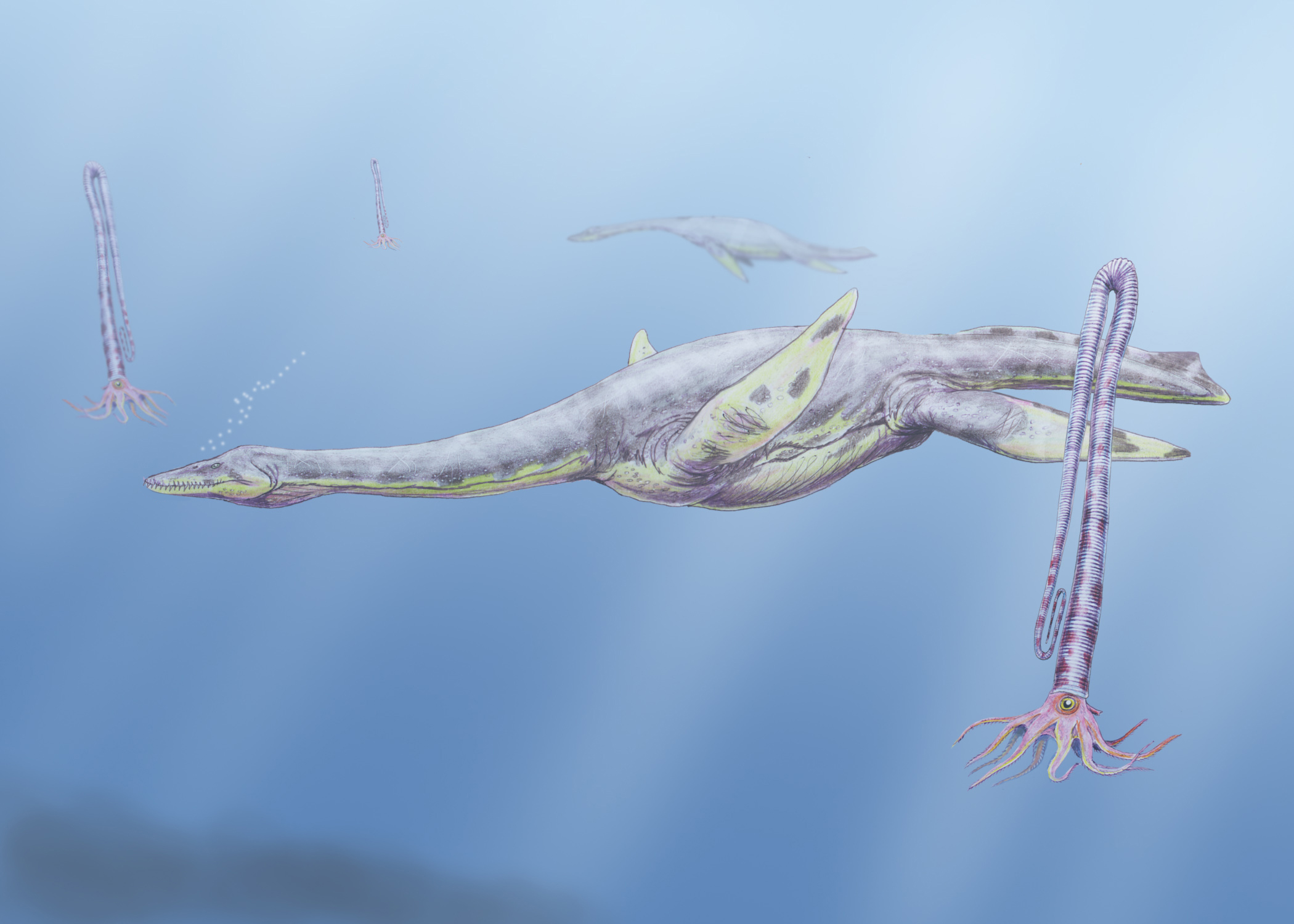
Hydrotherosaurus
''Hydrotherosaurus'' (meaning "water beast lizard") is an extinct genus of elasmosaurid plesiosaur from the Upper Cretaceous (Maastrichtian stage) Moreno Formation of Fresno County, California, USA. The only known species, ''H. alexandrae'', was named for its discoverer, Annie Montague Alexander, by Samuel Paul Welles. Description ''Hydrotherosaurus'' measured approximately in length. It has one of the longest necks relative to total length among elasmosaurids, with 60 vertebrae in total. It had a small head that measured about long, a streamlined body, and four large flippers that were specially designed to help the huge animal balance, move, and accelerate itself. See also * List of plesiosaur genera * Timeline of plesiosaur research This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles that flou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasmosaurids
Elasmosauridae is an extinct family of plesiosaurs, often called elasmosaurs. They had the longest necks of the plesiosaurs and existed from the Hauterivian to the Maastrichtian stages of the Cretaceous, and represented one of the two groups of plesiosaurs present at the end of the Cretaceous alongside Polycotylidae. Their diet mainly consisted of crustaceans and molluscs. Description The earliest elasmosaurids were mid-sized, about . In the Late Cretaceous, elasmosaurids grew as large as , such as ''Styxosaurus'', ''Albertonectes'', and ''Thalassomedon''. Their necks were the longest of all the plesiosaurs, with anywhere between 32 and 76 (''Albertonectes'') cervical vertebrae. They weighed up to several tons. Classification Early three-family classification Though Cope had originally recognized ''Elasmosaurus'' as a plesiosaur, in an 1869 paper he placed it, with '' Cimoliasaurus'' and '' Crymocetus'', in a new order of sauropterygian reptiles. He named the group Strept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasmosauridae
Elasmosauridae is an extinct family of plesiosaurs, often called elasmosaurs. They had the longest necks of the plesiosaurs and existed from the Hauterivian to the Maastrichtian stages of the Cretaceous, and represented one of the two groups of plesiosaurs present at the end of the Cretaceous alongside Polycotylidae. Their diet mainly consisted of crustaceans and molluscs. Description The earliest elasmosaurids were mid-sized, about . In the Late Cretaceous, elasmosaurids grew as large as , such as ''Styxosaurus'', '' Albertonectes'', and ''Thalassomedon''. Their necks were the longest of all the plesiosaurs, with anywhere between 32 and 76 (''Albertonectes'') cervical vertebrae. They weighed up to several tons. Classification Early three-family classification Though Cope had originally recognized ''Elasmosaurus'' as a plesiosaur, in an 1869 paper he placed it, with '' Cimoliasaurus'' and '' Crymocetus'', in a new order of sauropterygian reptiles. He named the group S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moreno Formation
The Moreno Formation is a Mesozoic geologic formation located in San Joaquin Valley (California).Dinosaur remains diagnostic to the genus level are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." Pp. 517-607. Paleofauna Ray-finned fish Dinosaurs Mosasaurs Plesiosaurs Turtles See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations ** List of stratigraphic units with few dinosaur genera This list of stratigraphic units with few non-avian dinosaur genera includes Mesozoic stratigraphic units of formation rank or higher that have produced dinosaur body fossils A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, i ... Footnotes References * Hilton, Richard P. 2003. Dinosaurs and Other Mesozoic Reptiles of California. Berkeley: University of California Press. 318 pp. * Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Plesiosaur Genera
This list of plesiosaurs is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the order Plesiosauria, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomen dubium''), or were not formally published (''nomen nudum''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered plesiosaurs. The list currently includes 201 genera. Scope and terminology There is no official, canonical list of plesiosaur genera but one of the most thorough attempts can be found on the Plesiosauria section of Mikko Haaramo's Phylogeny Archive; also pertinent is the Plesiosaur Genera section at Adam Stuart Smith's Plesiosaur Directory.See Smith, ''Plesiosaur Genera''. Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annie Montague Alexander
Annie Montague Alexander (29 December 1867 - 10 September 1950) was an explorer, naturalist, paleontological collector, and philanthropist. She founded the University of California Museum of Paleontology (UCMP) and the Museum of Vertebrate Zoology (MVZ). From its establishment in 1908 until she died in 1950 she financed the museum's collections and supported a series of paleontological expeditions throughout the western United States. Alexander herself took part in many of these expeditions, accumulating a significant collection of fossils and exotic game animals that she would later donate to the museum. Alexander is remembered by the University of California, Berkeley as one of the "builders of Berkeley" and as the benefactress of the museum. Early life Annie Montague Alexander was born December 29, 1867, in Honolulu during the Kingdom of Hawaii. She was the granddaughter of New England missionaries in Maui. Her father Samuel Thomas Alexander and her uncle Henry Perrine Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1943 In Paleontology
Dinosaurs Newly named dinosaurs Data are courtesy of George Olshevky's dinosaur genera list. Plesiosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian References {{portal, Paleontology [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiosaur
The Plesiosauria (; Greek: πλησίος, ''plesios'', meaning "near to" and ''sauros'', meaning "lizard") or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia. Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period, possibly in the Rhaetian stage, about 203 million years ago. They became especially common during the Jurassic Period, thriving until their disappearance due to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous Period, about 66 million years ago. They had a worldwide oceanic distribution, and some species at least partly inhabited freshwater environments. Plesiosaurs were among the first fossil reptiles discovered. In the beginning of the nineteenth century, scientists realised how distinctive their build was and they were named as a separate order in 1835. The first plesiosaurian genus, the eponymous '' Plesiosaurus'', was named in 1821. Since then, more than a hundred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Plesiosaur Research
This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles that flourished during the Mesozoic Era. The first scientifically documented plesiosaur fossils were discovered during the early 19th century by Mary Anning. Plesiosaurs were actually discovered and described before dinosaurs. They were also among the first animals to be featured in artistic reconstructions of the ancient world, and therefore among the earliest prehistoric creatures to attract the attention of the lay public. Plesiosaurs were originally thought to be a kind of primitive transitional form between marine life and terrestrial reptiles. However, now plesiosaurs are recognized as highly derived marine reptiles descended from terrestrial ancestors. Early researchers thought that plesiosaurs laid eggs like most reptiles. They commonly imagined p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Paul Welles
Samuel Paul Welles (November 9, 1907 – August 6, 1997) was an American palaeontologist. Welles was a research associate at the Museum of Palaeontology, University of California, Berkeley. He took part in excavations at the Placerias Quarry in 1930 and the '' Shonisaurus'' discoveries of 1954 and later, in what is now the Berlin-Ichthyosaur State Park. He accumulated an extensive collection of fossils of marine reptiles, amphibians, and fish, as well as describing the dinosaur ''Dilophosaurus ''Dilophosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of theropod dinosaurs that lived in what is now North America during the Early Jurassic, about 193 million years ago. Three skeletons were discovered in northern Arizona in 1940, and the two best preserv ...'' in 1954 and the elasmosaur '' Fresnosaurus'' in 1943. References American paleontologists 1907 births 1997 deaths University of California, Berkeley staff Scientists from California 20th-century American scientists {{Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', " chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from . The Maastrichtian was preceded by the Campanian and succeeded by the Danian (part of the Paleogene and Paleocene). The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event) occurred at the end of this age. In this mass extinction, many commonly recognized groups such as non-avian dinosaurs, plesiosaurs and mosasaurs, as well as many other lesser-known groups, died out. The cause of the extinction is most commonly linked to an asteroid about wide colliding with Earth, ending the Cretaceous. Stratigraphic definitions Definition The Maastrichtian was introduced into scientific literature by Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1849, after studying rock strata of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |