|
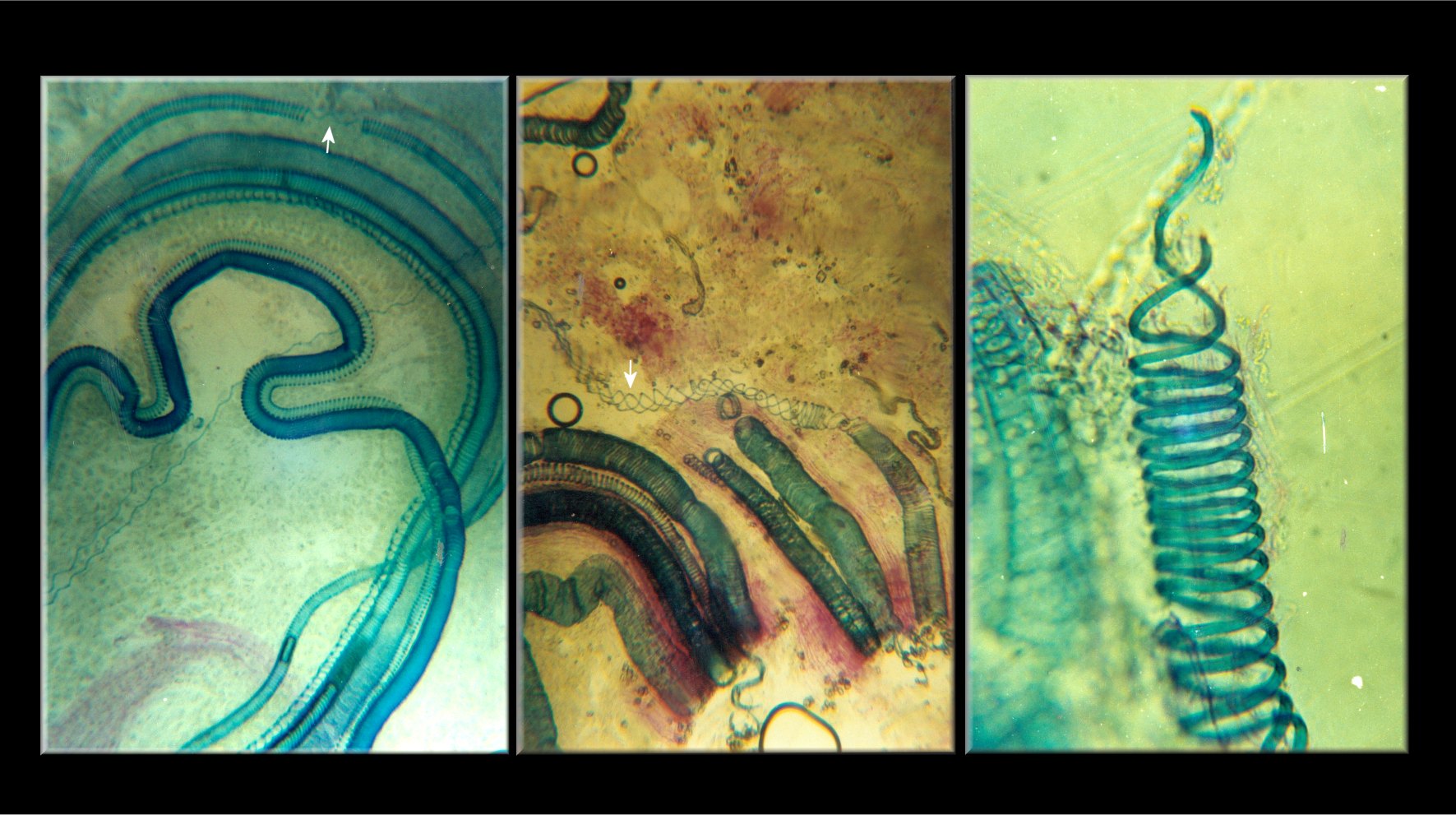
Hydropunctaria
''Hydropunctaria'' is a genus of saxicolous (rock-dwelling), crustose lichens in the family Verrucariaceae. The genus includes both aquatic and amphibious species, with members that colonise either marine or freshwater habitats. The type species, '' Hydropunctaria maura'', was formerly classified in the large genus ''Verrucaria''. It is a widely distributed species common to littoral zones. Including the type species, five ''Hydropunctaria'' lichens are considered marine species: ''H. adriatica'', ''H. amphibia'', ''H. aractina'', ''H. orae'', and ''H. oceanica''. Taxonomy ''Hydropunctaria'' was circumscribed in 2009 by Christine Keller, Cécile Gueidan, and Holger Thüs, with '' Hydropunctaria maura'' assigned as the type species. Description The thallus of ''Hydropunctaria'' is crustose, with a form ranging from continuous (more or less unbroken) to rimose or areolate. In some species the texture of the thallus is somewhat gelatinous. Documented thallu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydropunctaria Maura 77786203
''Hydropunctaria'' is a genus of saxicolous (rock-dwelling), crustose lichens in the family Verrucariaceae. The genus includes both aquatic and amphibious species, with members that colonise either marine or freshwater habitats. The type species, '' Hydropunctaria maura'', was formerly classified in the large genus ''Verrucaria''. It is a widely distributed species common to littoral zones. Including the type species, five ''Hydropunctaria'' lichens are considered marine species: ''H. adriatica'', ''H. amphibia'', ''H. aractina'', ''H. orae'', and ''H. oceanica''. Taxonomy ''Hydropunctaria'' was circumscribed in 2009 by Christine Keller, Cécile Gueidan, and Holger Thüs, with '' Hydropunctaria maura'' assigned as the type species. Description The thallus of ''Hydropunctaria'' is crustose, with a form ranging from continuous (more or less unbroken) to rimose or areolate. In some species the texture of the thallus is somewhat gelatinous. Documented thallu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydropunctaria Maura
''Hydropunctaria maura'' (still often called by the older name ''Verrucaria maura'') is a species of saxicolous (rock-dwelling), crustose lichen belonging to the family Verrucariaceae. A perennial species that does not experience seasonal variations, it is the type species of the genus ''Hydropunctaria''. The medulla is a black basal layer that forms columns (Latin: ''punctae'') to the upper surface and isolates the algae into pockets near the upper surface. The black band formed by ''H. maura'' can often be seen at a distance as a marker of the high water point. Ecology ''Hydropunctaria maura'' is commonly found on hard rocks in the intertidal zone. Compared to terrestrial lichens, the species is typically located in areas of direct sunlight, suggests that it may have specific adaptations against damage from the sun. It is considered an upper littoral (supralittoral) lichen, compared to other, lower littoral lichens such as ''Wahlenbergiella mucosa'', distinguished by e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verrucariaceae
The Verrucariaceae are a family of mostly lichenised fungi in the order Verrucariales. The lichen-forming species, which comprise the vast majority of the family, have a wide variety of thallus forms, and include crustose (crust-like), foliose (bushy), and squamulose (scaly) representatives. Several characteristics of the spore-bearing structures, the ascomata, define the family, including their perithecioid form–more or less spherical or flask-shaped, with a single opening and otherwise completely enclosed by a wall. Squamulose members of the Verrucariaceae with simple ascospores (lacking partitions called septa), and without algae in the spore-bearing region are known as lichens; there are more than 80 of these species. The family has several dozen lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) examples, including a few genera that contain solely lichenicolous members. An unusually diverse variety of photobiont partners have been recorded, mostly green algae, but also brown algae and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verrucaria
''Verrucaria'' is a genus of lichenized (lichen-forming) fungi in the family Verrucariaceae. Taxonomy The genus was circumscribed by German botanist Heinrich Adolph Schrader in 1794, with '' Verrucaria rupestris'' assigned as the type species. In his brief diagnosis of the genus, Schrader mentioned the more or less spherical (''subglobose''), closed ascomata, and the crustose thallus. The genus name is derived from the Latin word ''verruca'' (meaning "wart") and the suffix ''-aria'' (meaning "belonging to" or "possession"). Ecology As of 2015, there were 16 ''Verrucaria'' species classified as marine species: '' V. adguttata'', '' V. allantoidea'', '' V. ceuthocarpa'', '' V. corallensi'', '' V. ditmarsica'', '' V. erichsenii'', '' V. halizoa'', '' V. halochlora'', '' V. microsporoides'', '' V. paulula'', '' V. psychrophila'', '' V. sandstedei'', '' V. serpuloides'', '' V. sessilis'', '' V. subdiscreta'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Pigment
Biological pigments, also known simply as pigments or biochromes, are substances produced by living organisms that have a color resulting from selective color absorption. Biological pigments include plant pigments and flower pigments. Many biological structures, such as skin, eyes, feathers, fur and hair contain pigments such as melanin in specialized cells called chromatophores. In some species, pigments accrue over very long periods during an individual's lifespan. Pigment color differs from structural color in that it is the same for all viewing angles, whereas structural color is the result of selective reflection or iridescence, usually because of multilayer structures. For example, butterfly wings typically contain structural color, although many butterflies have cells that contain pigment as well. Biological pigments See conjugated systems for electron bond chemistry that causes these molecules to have pigment. * Heme/porphyrin-based: chlorophyll, bilirubin, hemocy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla (lichenology)
The medulla is a horizontal layer within a lichen thallus. It is a loosely arranged layer of interlaced hyphae below the upper cortex and photobiont A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Galloway, D.J. (1992). Flora of Australia - ''Lichen Glossary'' The medulla generally has a cottony appearance. It is the widest layer of a heteromerous lichen thallus. References Fungal morphology and anatomy Lichenology {{lichen-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plectenchyma
Plectenchyma (from Greek πλέκω ''pleko'' 'I weave' and ἔγχυμα ''enchyma'' 'infusion', i.e., 'a woven tissue') is the general term employed to designate all types of fungal tissues. The two most common types of tissues are prosenchyma and pseudoparenchyma. The hyphae A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or ... specifically become fused together. Notes Fungal morphology and anatomy {{mycology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parenchyma
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. In zoology it is the name for the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms. Etymology The term ''parenchyma'' is New Latin from the word παρέγχυμα ''parenchyma'' meaning 'visceral flesh', and from παρεγχεῖν ''parenchyma'' meaning 'to pour in' from παρα- ''para-'' 'beside' + ἐν ''en-'' 'in' + χεῖν ''chyma'' 'to pour'. Originally, Erasistratus and other anatomists used it to refer to certain human tissues. Later, it was also applied to plant tissues by Nehemiah Grew. Structure The parenchyma is the ''functional'' parts of an organ (anatomy), organ, or of a structure such as a tumour in the body. This is in contrast to the Stroma (animal tissue), stroma, which refers to the ''structural'' tissue of organs or of structures, namely, the connective tissues. Brain The brain parenchyma refers to the functional tissue in the brain that is made up of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Plants
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plants). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophytes) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones. Historically, vascular plants were known as "higher plants", as it was believed that they were further evolved than other plants due to being more complex organisms. However, this is an antiquated remnant of the obsolete scala naturae, and the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cécile Gueidan
Cécile Gueidan is a mycologist and lichenologist who applies morphological and molecular biological methods to the origin and taxonomy of fungi that live in lichen symbioses and within rocks. Early life and education Gueidan began working on lichens during her Maitrise (1998) and DEA (1999) qualifications from Université Louis Pasteur and National Museum of Natural History, France. This included practical fieldwork experience with Claude Roux. She then studied molecular methods for lichen taxonomy at Duke University, USA and applied them to pyrenocarpous and Verrucariaceae lichens. Through combining morphological and molecular characters, she was able to refine the taxonomy of these groups. She was awarded her doctorate for this research in 2007. Career Her research focuses on the evolution and taxonomy of lichenised fungi and other ascomycete fungi. After gaining her doctorate, Gueidan carried out research at the Westerdijk Institute in the Netherlands on relationships be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortex (botany)
In botany, a cortex is an outer layer of a stem or root in a vascular plant, lying below the epidermis but outside of the vascular bundles. The cortex is composed mostly of large thin-walled parenchyma cells of the ground tissue system and shows little to no structural differentiation. The outer cortical cells often acquire irregularly thickened cell walls, and are called collenchyma cells. Plants Stems and branches In the three dimensional structure of herbaceous stems, the epidermis, cortex and vascular cambium form concentric cylinders around the inner cylindrical core of pith. Some of the outer cortical cells may contain chloroplasts, giving them a green color. They can therefore produce simple carbohydrates through photosynthesis. In woody plants, the cortex is located between the periderm (bark) and the vascular tissue (phloem, in particular). It is responsible for the transportation of materials into the central cylinder of the root through diffusion and may als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomata
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic—about the size of flecks of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |