|
Hydnellum Peckii
''Hydnellum peckii'' is a fungus in the genus '' Hydnellum'' of the family Bankeraceae. It is a hydnoid species, producing spores on the surface of vertical spines or tooth-like projections that hang from the undersurface of the fruit bodies. It is found in North America, Europe, and was recently discovered in Iran (2008) and Korea (2010). ''Hydnellum peckii'' is a mycorrhizal species, and forms mutually beneficial relationships with a variety of coniferous trees, growing on the ground singly, scattered, or in fused masses. The fruit bodies typically have a funnel-shaped cap with a white edge, although the shape can be highly variable. Young, moist fruit bodies can "bleed" bright red guttation droplets that contain a pigment known to have anticoagulant properties similar to heparin. The unusual appearance of the young fruit bodies has earned the species several descriptive common names, including strawberries and cream, the bleeding Hydnellum, the bleeding tooth fungus, the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard James Banker
Howard James Banker (April 19, 1866 – November 13, 1940) was an American mycology, mycologist. He received his PhD from Columbia University in 1908. Banker was an associate editor of the journal ''Mycologia'' starting from its establishment in 1909, until it became the official publication of the Mycological Society of America in 1933. He published several papers in the journal, including a revision of the North American Hydnaceae, which discussed 62 species in 10 genera. Banker died at his home in Huntington, New York, in 1940. The genus ''Bankera'' is named after him. Selected publications *Banker JH. 1902. A Historical Review of the Proposed Genera of the Hydnaceae. ''Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club'', Vol. 29, No. 7, pp. 436–448 *_________. 1909. A New Fungus of the Swamp Cedar. ''Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club'', Vol. 36, No. 6, pp. 341–343 *_________. 1912. Type Studies in the Hydnaceae II. The Genus ''Steccherinum''. ''Mycologia'', Vol. 4, No. 6, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
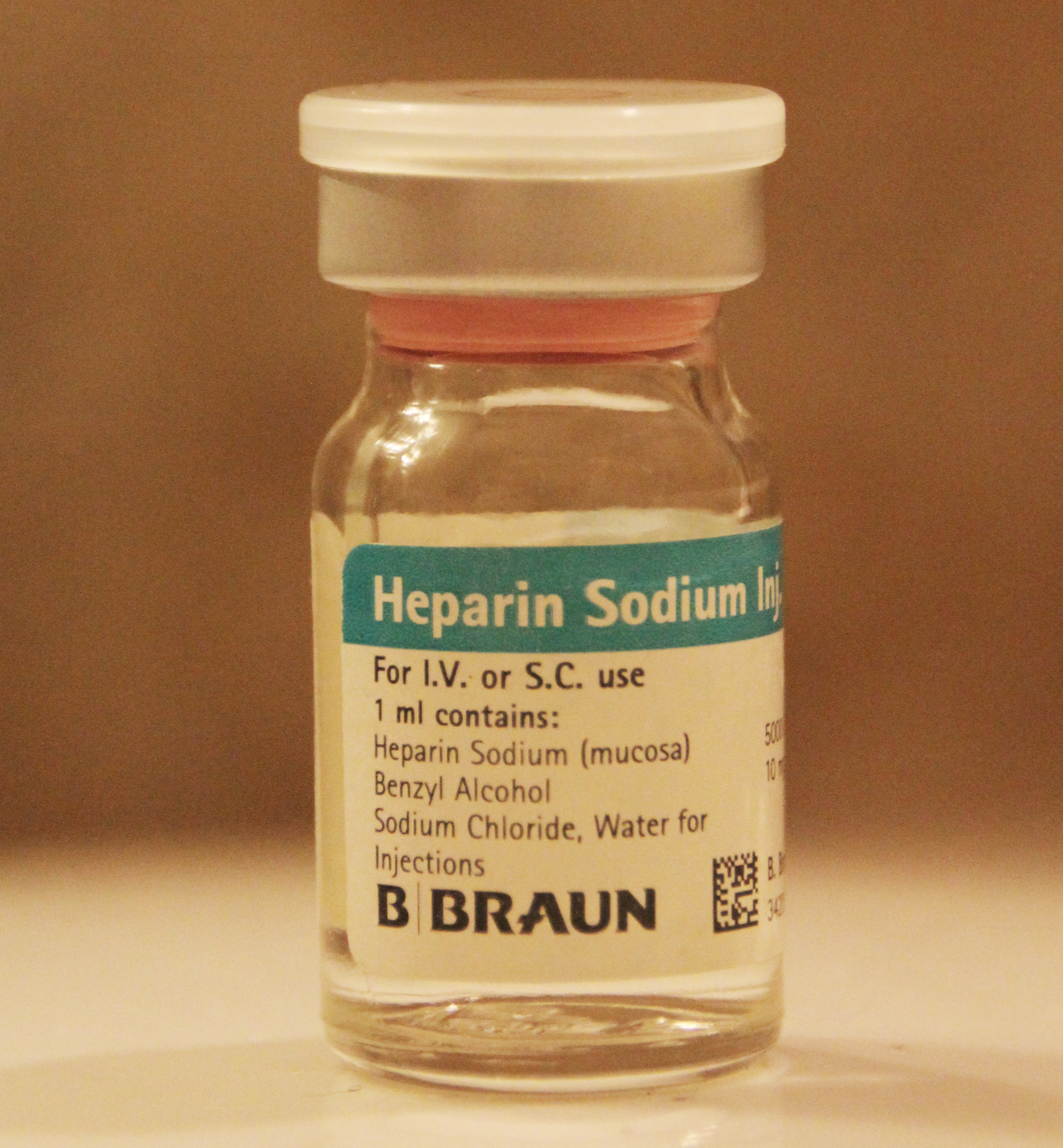
Heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatment of heart attacks and unstable angina. It is given intravenously or by injection under the skin. Other uses for its anticoagulant properties include inside blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines. Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and low blood platelets. Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function. Heparin is contraindicated for suspected cases of vaccine-induced pro-thrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) secondary to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, as heparin may further increase the risk of bleeding in an anti-PF4/heparin complex autoimmune manner, in favor of alternative anticoagulant medications (such as arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Blue
Methyl blue is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C37H27N3Na2O9S3. It is used as a stain in histology, and stains collagen blue in tissue sections. It can be used in some differential staining techniques such as Mallory's connective tissue stain and Gömöri trichrome stain, and can be used to mediate electron transfer in microbial fuel cells. Fungal cell walls are also stained by methyl blue. Methyl blue is also available in mixture with water blue, under name Aniline Blue WS, Aniline blue, China blue, or Soluble blue; and in a solution of phenol, glycerol, and lactic acid under the name Lactophenol cotton blue (LPCB), which is used for microscopic visualization of fungi. Chemistry Methyl blue ( 4-[Bis[4-[(sulfophenyl)aminohenyl">is[4-[(sulfophenyl)amino.html" ;"title="4-[Bis[4-[(sulfophenyl)amino">4-[Bis[4-[(sulfophenyl)aminohenylethylene]-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylidene]amino]-benzenesulfonic acid disodium salt) is distinctly different to methylene blue ([7- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melzer's Reagent
Melzer's reagent (also known as Melzer's iodine reagent, Melzer's solution or informally as Melzer's) is a chemical reagent used by mycologists to assist with the identification of fungi, and by phytopathologists for fungi that are plant pathogens. Composition Melzer's reagent is an aqueous solution of chloral hydrate, potassium iodide, and iodine. Depending on the formulation, it consists of approximately 2.50-3.75% potassium iodide and 0.75–1.25% iodine, with the remainder of the solution being 50% water and 50% chloral hydrate. Melzer's is toxic to humans if ingested due to the presence of iodine and chloral hydrate. Due to the legal status of chloral hydrate, Melzer's reagent is difficult to obtain in the United States. In response to difficulties obtaining chloral hydrate, scientists at Rutgers formulated Visikol (compatible with Lugol's iodine) as a replacement. In 2019, research showed that Visikol behaves differently to Melzer’s reagent in several key situations, notin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Tests In Mushroom Identification
Chemical tests in mushroom identification are methods that aid in determining the variety of some fungi. The most useful tests are Melzer's reagent and potassium hydroxide. Ammonia Household ammonia can be used. A couple of drops are placed on the flesh. For example, '' Boletus spadiceus'' gives a fleeting blue to blue-green reaction. Iron salts Iron salts are used commonly in ''Russula'' and Bolete identification. It is best to dissolve the salts in water (typically a 10% solution) and then apply to the flesh, but it is sometimes possible to apply the dry salts directly to see a color change. For example, the white flesh of ''Boletus chrysenteron'' stains lemon-yellow or olive. Three results are expected with the iron salts tests: no change indicates a negative reaction; a color change to olive, green or blackish green; or a color change to reddish-pink. Meixner test for amatoxins The Meixner test (also known as the Wieland test) uses concentrated hydrochloric acid and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek 'violet-coloured'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. It is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-first most abundant element. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloid (mycology)
In mycology a tissue or feature is said to be amyloid if it has a positive amyloid reaction when subjected to a crude chemical test using iodine as an ingredient of either Melzer's reagent or Lugol's solution, producing a blue to blue-black staining. The term "amyloid" is derived from the Latin ''amyloideus'' ("starch-like"). It refers to the fact that starch gives a similar reaction, also called an amyloid reaction. The test can be on microscopic features, such as spore walls or hyphal walls, or the apical apparatus or entire ascus wall of an ascus, or be a macroscopic reaction on tissue where a drop of the reagent is applied. Negative reactions, called inamyloid or nonamyloid, are for structures that remain pale yellow-brown or clear. A reaction producing a deep reddish to reddish-brown staining is either termed a dextrinoid reaction (pseudoamyloid is a synonym) or a hemiamyloid reaction. Melzer's reagent reactions Hemiamyloidity Hemiamyloidity in mycology refers to a special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry which intersect at a center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal axes'', or simply axes of the ellipsoid. If the three axes have different lengths, the figure is a triaxial ellipsoid (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zonate
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trama (mycology)
In mycology, the term trama is used in two ways. In the broad sense, it is the inner, fleshy portion of a mushroom's basidiocarp, or fruit body. It is distinct from the outer layer of tissue, known as the pileipellis or cuticle, and from the spore-bearing tissue layer known as the hymenium. In essence, the trama is the tissue that is commonly referred to as the "flesh" of mushrooms and similar fungi.Largent D, Johnson D, Watling R. 1977. ''How to Identify Mushrooms to Genus III: Microscopic Features''. Arcata, CA: Mad River Press. . pp. 60–70. The second use is more specific, and refers to the "hymenophoral trama" that supports the hymenium. It is similarly interior, connective tissue, but it is more specifically the central layer of hyphae running from the underside of the mushroom cap to the lamella or gill, upon which the hymenium rests. Various types have been classified by their structure, including trametoid, cantharelloid, boletoid, and agaricoid, with agaricoid the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (biology)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia leva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Henry Snell
Walter Henry "Doc" Snell (May 19, 1889 – July 23, 1980) was a pinch-hitter/catcher in Major League Baseball who played briefly for the Boston Red Sox during the season. Following this brief baseball career he became a successful mycologist who worked primarily at Brown University for the next 60 years. Baseball career Snell was a college three-sport athlete turned scientist. Besides baseball, he played football and basketball at Brockton High School, graduating in 1907. He then attended Phillips Andover Academy for two years, graduating in 1909, before enrolling at Brown University. At Brown, Snell was both a scholar and an athlete, as a Phi Beta Kappa in academics and a catcher for four years on the varsity baseball team under coach Harry Pattee. In 1913, he was signed by the Philadelphia Athletics owner Connie Mack, but broke his hand in a game at Brown and was dealt to the Red Sox. In a six-game career, Snell was a .250 hitter (3-for-12) with one run and one sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |