|
Hutchinson's Sign
Hutchinson's sign is a clinical sign which may refer to: *Hutchinson's pupil, an unresponsive and enlarged pupil on the side of an intracranial mass * Vesicles on the tip of the nose, or vesicles on the side of the nose, precedes the development of ophthalmic herpes zoster. This occurs because the nasociliary branch of the trigeminal nerve innervates both the cornea and the lateral dorsum of the nose as well as the tip of the nose. This sign is named after Sir Jonathan Hutchinson. * Melanonychia with pigmentation of the proximal nail fold.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . This is an important sign of subungual melanoma although is not an infallible predictor. Periungual hyperpigmentation occurs in at least one nonmelanoma skin cancer, Bowen's disease of the nail unit. This is a nail fold pigmentation which then widens progressively to produce a triangular pigmented macule with associated nail dystrophy. Hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Sign
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggering gait, and arcus senilis and arcus juvenilis of the eyes. Indicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hutchinson's Pupil
Hutchinson's pupil is a clinical sign in which the pupil on the side of an intracranial mass lesion is dilated and unreactive to light, due to compression of the oculomotor nerve The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of ... on that side. The sign is named after Sir Jonathan Hutchinson. These can be due to concussion injury to the brain and is associated with subdural haemorrhage and unconsciousness. The parasympathetic fibers to the pupil are responsible for pupillary constriction. The fibers pass through the periphery of the oculomotor nerve, and hence are the first to be affected in case of compression of the nerve. In Stage 1, the parasympathetic fibers on the side of injury are irritated, leading to constriction of pupil on that side. In stage 2, the parasympathetic fibers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpes Zoster
Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. Two to four days before the rash occurs there may be tingling or local pain in the area. Otherwise, there are typically few symptoms though some people may have fever or headache, or feel tired. The rash usually heals within two to four weeks; however, some people develop ongoing nerve pain which can last for months or years, a condition called postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). In those with poor immune function the rash may occur widely. If the rash involves the eye, vision loss may occur. Shingles is caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) that also causes chickenpox. In the case of chickenpox, also called varicella, the initial infection with the virus typically occurs during childhood or adolescence. Once the chickenpox has resolved, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasociliary Nerve
The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve, itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It is intermediate in size between the other two branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and lacrimal nerve. Structure The nasociliary nerve enters the orbit via the superior orbital fissure, between the two heads of the lateral rectus muscle and between the superior and inferior rami of the oculomotor nerve. It passes across the optic nerve (CN II) and runs obliquely beneath the superior rectus muscle and superior oblique muscle to the medial wall of the orbital cavity. It passes through the anterior ethmoidal opening as the anterior ethmoidal nerve and enters the cranial cavity just below the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It supplies branches to the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and finally emerges between the inferior border of the nasal bone and the side nasal cartilages as the external nasal branch. Branches * posterior ethmoidal nerve * ante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigeminal Nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve ( lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name ("trigeminal", ) derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V), the maxillary nerve (V), and the mandibular nerve (V). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions. Adding to the complexity of this nerve is that autonomic nerve fibers as well as special sensory fibers (taste) are contained within it. The motor division of the trigeminal nerve derives from the basal plate of the embryonic pons, and the sensory division originates in the cranial neural crest. Sensory information from the face and body is proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres. The cornea can be reshaped by surgical procedures such as LASIK. While the cornea contributes most of the eye's focusing power, its focus is fixed. Accommodation (the refocusing of light to better view near objects) is accomplished by changing the geometry of the lens. Medical terms related to the cornea often start with the prefix "'' kerat-''" from the Greek word κέρας, ''horn''. Structure The cornea has unmyelinated nerve endings sensitive to touch, temperature and chemicals; a touch of the cornea causes an involuntary reflex to close the eyelid. Because transparency is of prime importance, the healthy cornea does not have or need blood vessels with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan Hutchinson
Sir Jonathan Hutchinson (23 July 1828 – 23 June 1913), was an English surgeon, ophthalmologist, dermatologist, venereologist, and pathologist. Life He was born in Selby, Yorkshire, of Quaker parents and educated in the local school. Then he was apprenticed for five years to Caleb Williams, an apothecary and surgeon in York. He entered St Bartholomew's Hospital in London, and became a member of the Royal College of Surgeons in 1850 (and a fellow in 1862), and rapidly gained reputation as a skillful operator and a scientific inquirer. While a student, Hutchinson chose a career in surgery from 1854 on, under the influence and help of his mentor, Sir James Paget (1814–99). In 1851, he studied ophthalmology at Moorfields and practised it at London Ophthalmic Hospital. Other hospitals where he practised in the following years were the Lock Hospital, the City of London Chest Hospital, the London Hospital, the Metropolitan Hospitals, and the Blackfriars Hospital for Diseases of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanonychia
Melanonychia is a black or brown pigmentation of the normal nail plate, and may be present as a normal finding on many digits in Afro-Caribbeans, as a result of trauma, systemic disease, or medications, or as a postinflammatory event from such localized events as lichen planus or fixed drug eruption.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. .Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . There are two types, longitudinal and transverse melanonychia. Longitudinal melanonychia may be a sign of subungual melanoma (acral lentiginous melanoma),Baran, Robert, et al. 2008. ''Baran & Dawber's Diseases of the Nails and Their Management''. Oxford: Blackwell, p. 516. although there are other diagnoses such as chronic paronychia, onychomycosis, subungual hematoma, pyogenic granuloma, glomus tumour, subungual verruca, mucous cyst, subungual fibroma, k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanoma
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In women, they most commonly occur on the legs, while in men, they most commonly occur on the back. About 25% of melanomas develop from moles. Changes in a mole that can indicate melanoma include an increase in size, irregular edges, change in color, itchiness, or skin breakdown. The primary cause of melanoma is ultraviolet light (UV) exposure in those with low levels of the skin pigment melanin. The UV light may be from the sun or other sources, such as tanning devices. Those with many moles, a history of affected family members, and poor immune function are at greater risk. A number of rare genetic conditions, such as xeroderma pigmentosum, also increase the risk. Diagnosis is by biopsy and analysis of any skin lesion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hutchinson's Triad
Hutchinson's triad is named after Sir Jonathan Hutchinson (1828–1913). It is a common pattern of presentation for congenital syphilis, and consists of three phenomena: interstitial keratitis, malformed teeth (Hutchinson incisors and mulberry molars), and eighth nerve A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e ... deafness. There may also be a deformity on the nose known as saddle nose deformity. References Infectious diseases Pediatrics Syphilis Medical triads {{Pediatrics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Syphilis
Congenital syphilis is syphilis present ''in utero'' and at birth, and occurs when a child is born to a mother with syphilis. Untreated early syphilis infections results in a high risk of poor pregnancy outcomes, including saddle nose, lower extremity abnormalities, miscarriages, premature births, stillbirths, or death in newborns. Some infants with congenital syphilis have symptoms at birth, but many develop symptoms later. Symptoms may include rash, fever, an enlarged liver and spleen, and skeletal abnormalities. Newborns will typically not develop a primary syphilitic chancre but may present with signs of secondary syphilis (i.e. generalized body rash). Often these babies will develop syphilitic rhinitis ("snuffles"), the mucus from which is laden with the ''T. pallidum'' bacterium, and therefore highly infectious. If a baby with congenital syphilis is not treated early, damage to the bones, teeth, eyes, ears, and brain can occur. Classification Early This is a subset of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
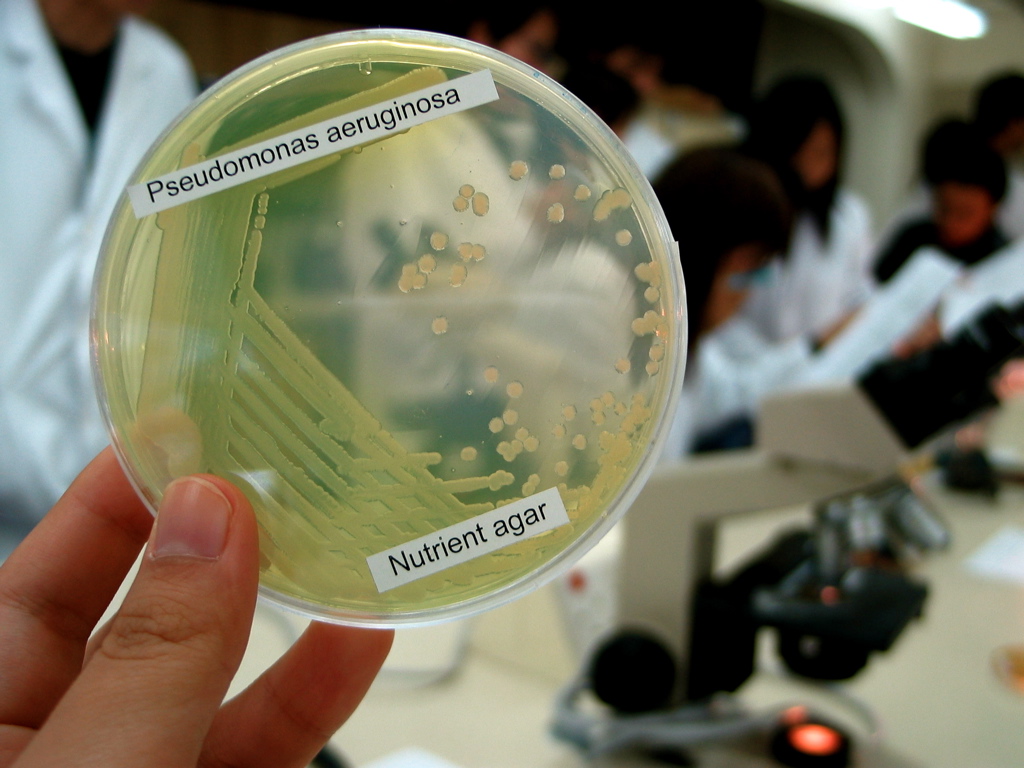
Green Nail Sign
Green nail syndrome is an infection that can develop in individuals whose hands are frequently submerged in water resulting in discolouration of the nails from shades of green to black. It may also occur as transverse green stripes that are ascribed to intermittent episodes of infection. It is usually caused by the bacteria '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and is linked to hands being constantly moist or exposed to chemicals, or in individuals who have damaged or traumatised nails. There are several activities and nail injuries or conditions that are linked to higher risk of contracting the condition. Symptoms and signs Green nail syndrome (chloronychia or Goldman-Fox syndrome) is characterised by discolouration of the infected nail, inflammation of the skin around the nail known as paronychia, and an odour resembling fruit. The colour may range from light or blueish green or yellow-green to darker green or black. Nails may be separated from the nail bed ( onycholysis) and may have g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |