|
Hurricane Joan
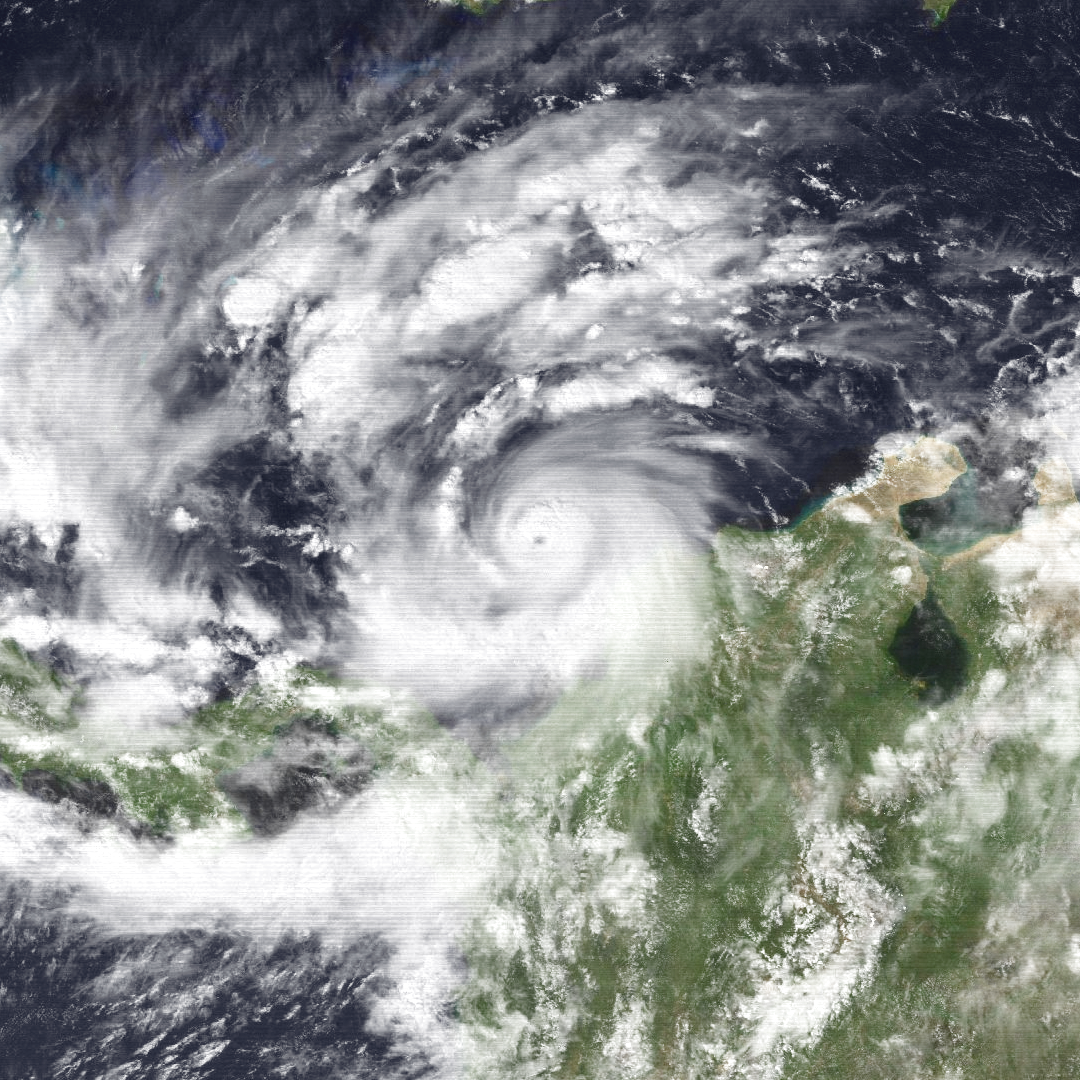
Hurricane Joan was a long lived and powerful tropical cyclone that caused death and destruction in over a dozen countries in the Caribbean and Central America. Moving on a due west course for nearly two weeks in October 1988, Hurricane Joan caused widespread flooding and over 200 deaths after moving into Central America. Widespread suffering and economic crises were exacerbated by Joan, primarily across Nicaragua, as heavy rains and high winds impacted those near the hurricane's path. After crossing Central America into the Pacific, the cyclone was renamed Tropical Storm Miriam, with the system's dissipation occurring southwest of Mexico. Joan–Miriam was the final hurricane of the 1988 Atlantic hurricane season and the final named storm of the Pacific hurricane season. Meteorological history At the time, Joan was one of the latest tropical cyclones to form in the central Atlantic in any season. It formed from an area of convection in the Intertropical Convergence Zone that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, and Maritime boundary, maritime border with Ecuador to the south of Cocos Island. It has a population of around five million in a land area of . An estimated 333,980 people live in the capital and largest city, San José, Costa Rica, San José, with around two million people in the surrounding metropolitan area. The sovereign state is a Unitary state, unitary Presidential system, presidential Constitution of Costa Rica, constitutional republic. It has a long-standing and stable democracy and a highly educated workforce. The country spends roughly 6.9% of its budget (2016) on education, compared to a global average of 4.4%. Its economy, once heavily dependent on agricultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joan 1988-10-18 1800Z
Joan may refer to: People and fictional characters *Joan (given name), including a list of women, men and fictional characters *:Joan of Arc, a French military heroine *Joan (surname) Weather events *Tropical Storm Joan (other), multiple tropical cyclones are named Joan Music * ''Joan'' (album), a 1967 album by Joan Baez *"Joan", a song by The Art Bears from their 1978 album ''Hopes and Fears'' *"Joan", a song by Lene Lovich from her 1980 album ''Flex'' *"Joan", a song by Erasure from their 1991 album ''Chorus'' *"Joan", a song by The Innocence Mission from their 1991 album ''Umbrella'' *"Joan", a song by God Is My Co-Pilot from their 1992 album ''I Am Not This Body'' Other uses *Jōan (era), a Japanese era name * ''Joan'' (play), 2015 one-woman play written by Lucy J. Skillbeck *Joan Township, Ontario, a geographic township See also *''Jo-an'' tea house, National Treasure in Inuyama, Aichi Prefecture, Japan * *Jane (other) *Jean (other) *Jeanne (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Irene-Olivia
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm, storm system characterized by a Low-pressure area, low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, Beaufort scale, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by #Nomenclature and intensity classifications, different names, including hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A Atlantic hurricane, hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms". "Tropical" refers to the geographical origin of these systems, which form al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1933 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1933 Atlantic hurricane season set the record for the most named or nameable storms formed within a single season, 20, which stood until the 2005 season, during which there were 28 storms. It also produced the highest Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE) on record in the Atlantic basin, with a total of 259. The season ran through the summer and the first half of fall in 1933, with activity as early as May and as late as November. A tropical cyclone was active for all but 13 days from June 28 to October 7. Because technologies such as Earth observation satellites were not available until the 1960s, historical data on tropical cyclones from the early 20th century is often incomplete. Tropical cyclones that did not approach populated areas or shipping lanes, especially if they were relatively weak and of short duration, may have remained undetected. Compensating for the lack of comprehensive observation and the limited technological ability to monitor all trop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th parallel north in the northeast Pacific Ocean and the 31st parallel north in the northern Atlantic Ocean. The agency, which is co-located with the Miami branch of the National Weather Service, is situated on the campus of Florida International University in Westchester, Florida. The NHC's Tropical Analysis and Forecast Branch (TAFB) routinely issues marine forecasts, in the form of graphics and high seas forecasts year round, with the Ocean Prediction Center having backup responsibility for this unit. The Technology and Science Branch (TSB) provides technical support for the center, which includes new infusions of technology from abroad. The Chief, Aerial Reconnaissance Coordination, All Hurricanes (CARCAH) unit tasks planes, for r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction with a change in altitude. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with a change in lateral position for a given altitude. Wind shear is a microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by thunderstorms, fronts, areas of locally higher low-level winds referred to as low-level jets, near mountains, radiation inversions that occur due to clear skies and calm winds, buildings, wind turbines, and sailboats. Wind shear has significant effects on the control of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Nicaragua
Lake Nicaragua or Cocibolca or Granada ( es, Lago de Nicaragua, , or ) is a freshwater lake in Nicaragua. Of tectonic origin and with an area of , it is the largest lake in Central America, the 19th largest lake in the world (by area) and the tenth largest in the Americas, slightly smaller than Lake Titicaca. With an elevation of above sea level, the lake reaches a depth of . It is intermittently joined by the Tipitapa River to Lake Managua. The lake drains to the Caribbean Sea via the San Juan River, historically making the lakeside city of Granada an Atlantic port, although Granada (as well as the entire lake) is closer to the Pacific Ocean geographically. The Pacific is near enough to be seen from the mountains of Ometepe (an island in the lake). The lake has a history of Caribbean pirates who assaulted Granada on three occasions. Before construction of the Panama Canal, a stagecoach line owned by Cornelius Vanderbilt's Accessory Transit Company connected the lake with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bluefields, Nicaragua
Bluefields is the capital of the South Caribbean Autonomous Region in Nicaragua. It was also the capital of the former Kingdom of Mosquitia, and later the Zelaya Department, which was divided into North and South Caribbean Coast Autonomous Regions. It is located on Bluefields Bay at the mouth of the Bluefields River in the municipality of the same name. It was named after Abraham Blauvelt, a Dutch- Jewish pirate, privateer, and explorer of Central America and the western Caribbean. It has a population of 55,575 (2021 estimate) and its inhabitants are mostly Afro-descendant Creoles, Miskitu, Mestizo, as well as smaller communities of Garinagu,Chinese, Mayangna, and Rama. Bluefields is the chief Caribbean port, from which hardwood, seafood, shrimp and lobster are exported. Bluefields was a rendezvous for European buccaneers in the 16th and 17th century and became capital of the English protectorate of the Kingdom of Mosquitia in 1678. During United States interventions (1912� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Ivan
Hurricane Ivan was a large, long-lived, Cape Verde hurricane that caused widespread damage in the Caribbean and United States. The cyclone was the ninth named storm, the sixth hurricane and the fourth major hurricane of the active 2004 Atlantic hurricane season. Ivan formed in early September, and reached Category 5 strength on the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale (SSHS). Ivan caused catastrophic damage in Grenada as a strong Category 3 storm, heavy damage in Jamaica as a strong Category 4 storm, and then severe damage in Grand Cayman, Cayman Islands, and the western tip of Cuba as a Category 5 hurricane. After peaking in strength, the hurricane moved north-northwest across the Gulf of Mexico to strike Pensacola/ Milton, Florida and Alabama as a strong Category 3 storm, causing significant damage. Ivan dropped heavy rain on the Southeastern United States as it progressed northeastward and eastward through the Eastern United States, becoming an extratropical cyclone on Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Category 4 Hurricane
Category, plural categories, may refer to: Philosophy and general uses *Categorization, categories in cognitive science, information science and generally *Category of being * ''Categories'' (Aristotle) *Category (Kant) *Categories (Peirce) *Category (Vaisheshika) *Stoic categories *Category mistake Mathematics * Category (mathematics), a structure consisting of objects and arrows * Category (topology), in the context of Baire spaces * Lusternik–Schnirelmann category, sometimes called ''LS-category'' or simply ''category'' * Categorical data In statistics, a categorical variable (also called qualitative variable) is a variable that can take on one of a limited, and usually fixed, number of possible values, assigning each individual or other unit of observation to a particular group or ..., in statistics Linguistics *Lexical category, a part of speech such as ''noun'', ''preposition'', etc. *Syntactic category, a similar concept which can also include phrasal categories * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Deepening
In meteorology, rapid intensification is a situation where a tropical cyclone intensifies dramatically in a short period of time. The United States National Hurricane Center defines rapid intensification as an increase in the maximum sustained winds of a tropical cyclone of at least in a 24-hour period. Necessary conditions External In order for rapid intensification to occur, several conditions must be in place. Water temperatures must be extremely warm (near or above ), and water of this temperature must be sufficiently deep such that waves do not churn deeper cooler waters up to the surface. Wind shear must be low; when wind shear is high, the convection and circulation in the cyclone will be disrupted. Dry air can also limit the strengthening of tropical cyclones. Internal Usually, an anticyclone in the upper layers of the troposphere above the storm must also be present for extremely low surface pressures to develop. This is because air must be converging towards the low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |