|
Hurricane Beatriz (1999)
The 1999 Pacific hurricane season was one of the least active Pacific hurricane seasons on record. The season officially began on May 15 in the Eastern Pacific, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; in both basins, it ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period during which most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. The first tropical cyclone of the season, Hurricane Adrian, developed on June 18, while the final storm of the season, Tropical Storm Irwin, dissipated on October 11. No storms developed in the Central Pacific during the season. However, two storms from the Eastern Pacific, Dora and Eugene, entered the basin, with the former entering as a hurricane. The season produced fourteen tropical cyclones and nine named storms, which was well below the average of sixteen named storms per season; this was largely due to a strong La Niña taking over much of the Pacific. However, the total of six hurrica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Dora (1999)
Hurricane Dora was one of few tropical cyclones to track across all three north Pacific basins and the first since Hurricane John in 1994. The fourth named storm, third hurricane, and second major hurricane of the 1999 Pacific hurricane season, Dora developed on August 6 from a tropical wave to the south of Mexico. Forming as a tropical depression, the system gradually strengthened and was upgraded to Tropical Storm Dora later that day. Thereafter Dora began heading in a steadily westward direction, before becoming a hurricane on August 8. Amid warm sea surface temperatures and low wind shear, the storm continued to intensify, eventually peaking as a 140 mph (220 km/h) Category 4 hurricane on August 12. Thereafter, Dora fluctuated significantly in intensity due to changes in water temperatures and wind shear, with the storm ranging from peak intensity as a Category 4 hurricane to a low-end Category 1 hurricane over a period of four days. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis is the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropical cyclogenesis occurs are distinctly different from those through which temperate cyclogenesis occurs. Tropical cyclogenesis involves the development of a warm-core cyclone, due to significant convection in a favorable atmospheric environment. Tropical cyclogenesis requires six main factors: sufficiently warm sea surface temperatures (at least ), atmospheric instability, high humidity in the lower to middle levels of the troposphere, enough Coriolis force to develop a low-pressure center, a pre-existing low-level focus or disturbance, and low vertical wind shear. Tropical cyclones tend to develop during the summer, but have been noted in nearly every month in most basins. Climate cycles such as ENSO and the Madden–Julian oscillation modulate the timing and frequency of tropical cyclone development. There is a limit on tropical cyclone i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Dateline
The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South and North Poles and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific Ocean, roughly following the 180° line of longitude and deviating to pass around some territories and island groups. Crossing the date line eastbound decreases the date by one day, while crossing the date line westbound increases the date. Geography Circumnavigating the globe People traveling westward around the world must set their clocks: *Back by one hour for every 15° of longitude crossed, and *Forward by 24 hours upon crossing the International Date Line. People traveling eastward must set their clocks: *Forward by one hour for every 15° of longitude crossed, and *Back by 24 hours upon crossing the International Date Line. Failing to do this would make their time inaccurate to the local time. The Arab geographer Abulfed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in a type of cloud known as a cumulonimbus. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce heavy rain and sometimes snow, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms produce little precipitation or no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow through the layer of the troposphere that they occupy, vertical wind shear sometimes causes a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pressure Area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible rain or storms), while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis force, Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In Meteorology#Dynamic meteorology, meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places: * The first is in the area on the east side of upper Trough (meteorology), troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough (meteorology), trough with la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of Baja California (). It has an area of (3.57% of the land mass of Mexico) and comprises the northern half of the Baja California Peninsula, north of the 28th parallel, plus oceanic Guadalupe Island. The mainland portion of the state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean; on the east by Sonora, the U.S. state of Arizona, and the Gulf of California; on the north by the U.S. state of California; and on the south by Baja California Sur. The state has an estimated population of 3,769,020 as of 2020, significantly higher than the sparsely populated Baja California Sur to the south, and similar to San Diego County, California, to its north. Over 75% of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landfall (meteorology)
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact of arriving there. Tropical cyclone A tropical cyclone is classified as making landfall when the center of the storm moves across the coast; in a relatively strong tropical cyclone, this is when the eye moves over land. This is where most of the damage occurs within a mature tropical cyclone, such as a typhoon or hurricane, as most of the damaging aspects of these systems are concentrated near the eyewall. Such effects include the peaking of the storm surge, the core of strong winds coming ashore, and heavy flooding rains. These coupled with high surf can cause major beach erosion. When a tropical cyclone makes landfall, the eye usually closes in upon itself due to negative environmental factors over land, such as friction with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1994 Pacific Hurricane Season
The 1994 Pacific hurricane season was the final season of the eastern north Pacific's consecutive active hurricane seasons that started in 1982. The season officially started on May 15, 1994, in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1, 1994, in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1994. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. The first tropical cyclone formed on June 18, while the last system dissipated on October 26. This season, twenty-two tropical cyclones formed in the north Pacific Ocean east of the dateline, with all but two becoming tropical storms or hurricanes. A total of 10 hurricanes occurred, including five major hurricanes. The above average activity in 1994 was attributed to the ongoing 1990–95 El Niño at the time. Of note in this season is an unusual spree of very intense storms; the season was the first on record to see three Category 5 hurricanes, later tied in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane John (1994)
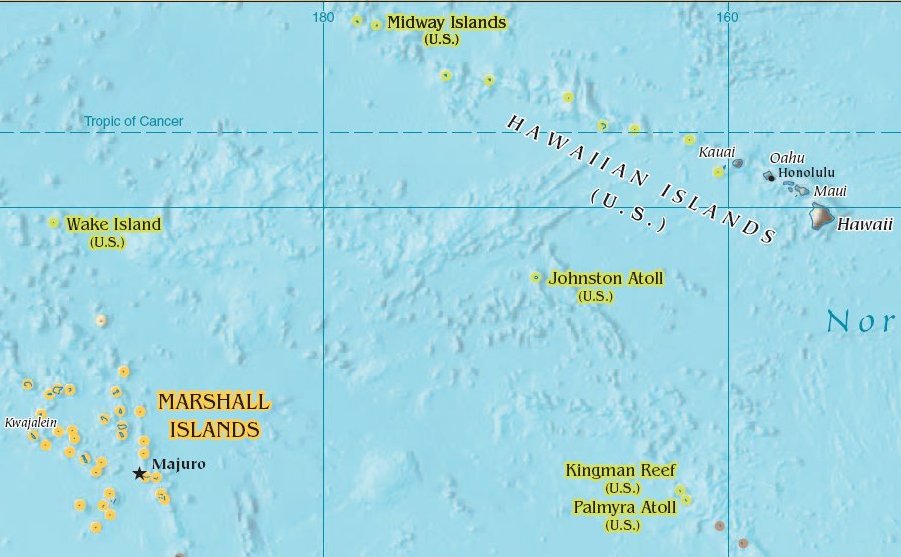
Hurricane John, also known as Typhoon John, was both the longest-lasting and the farthest-traveling tropical cyclone ever observed. John formed during the 1994 Pacific hurricane season, which had above-average activity due to the El Niño of 1994–1995, and peaked as a Category 5 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson scale, the highest categorization for hurricanes. Over the course of its existence, John followed a 7,165-mile (13,280-km) path from the eastern Pacific to the western Pacific and back to the central Pacific, lasting 31 days in total. Because it existed in both the eastern and western Pacific, John was one of a small number of tropical cyclones to be designated as both a hurricane and a typhoon. Despite lasting for a full month, John barely affected land at all, bringing only minimal effects to the Hawaiian Islands and the United States military base on Johnston Atoll. Its remnants later affected Alaska. Meteorological history The origins of Hurricane John w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaii (island)
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii ) is the List of islands of the United States by area, largest island in the United States, located in the U.S. state, state of Hawaii. It is the southeasternmost of the Hawaiian Islands, a chain of High island, volcanic islands in the Pacific Ocean, North Pacific Ocean. With an area of , it has 63% of the Hawaiian archipelago's combined landmass. However, it has only 13% of Hawaiʻi's population. The island of Hawaiʻi is the third largest island in Polynesia, behind the two main List of islands of New Zealand, islands of New Zealand. The island is often referred to as the Island of Hawaii or Hawaii Island to distinguish it from the state. It is also referred to as the Big Island. Administratively, the island is coextensive with Hawaii County, Hawaii, Hawaii County. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 200,629. The county seat and largest town is Hilo, Hawaii, Hilo. There are no Municipal corporation, incorporated cities i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnston Atoll
Johnston Atoll is an Unincorporated territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the United States, currently administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS). Johnston Atoll is a National Wildlife Refuge and part of the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument. It is closed to public entry, and limited access for management needs is only granted by Letter of Authorization from the United States Air Force and a Special Use Permit from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. For nearly 70 years, the isolated atoll was under the control of the United States Armed Forces, U.S. military. During that time, it was variously used as a naval refueling depot, an Johnston Island Air Force Base, airbase, a testing site for nuclear and biological weapons, a secret missile base, and a site for the storage and disposal of chemical weapons and Agent Orange. Those activities left the area environmentally contaminated, and monitoring continues. The island i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Date Line
The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South and North Poles and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific Ocean, roughly following the 180° line of longitude and deviating to pass around some territories and island groups. Crossing the date line eastbound decreases the date by one day, while crossing the date line westbound increases the date. Geography Circumnavigating the globe People traveling westward around the world must set their clocks: *Back by one hour for every 15° of longitude crossed, and *Forward by 24 hours upon crossing the International Date Line. People traveling eastward must set their clocks: *Forward by one hour for every 15° of longitude crossed, and *Back by 24 hours upon crossing the International Date Line. Failing to do this would make their time inaccurate to the local time. The Arab geographer Abulfed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |