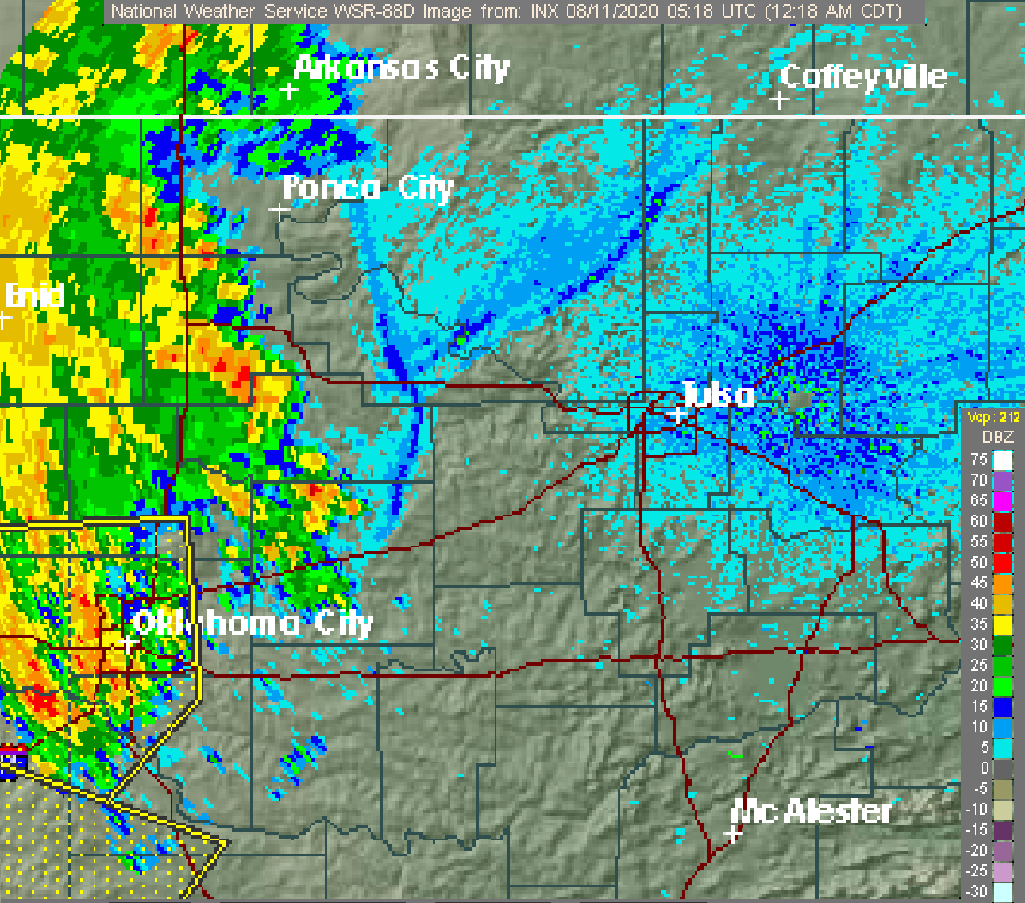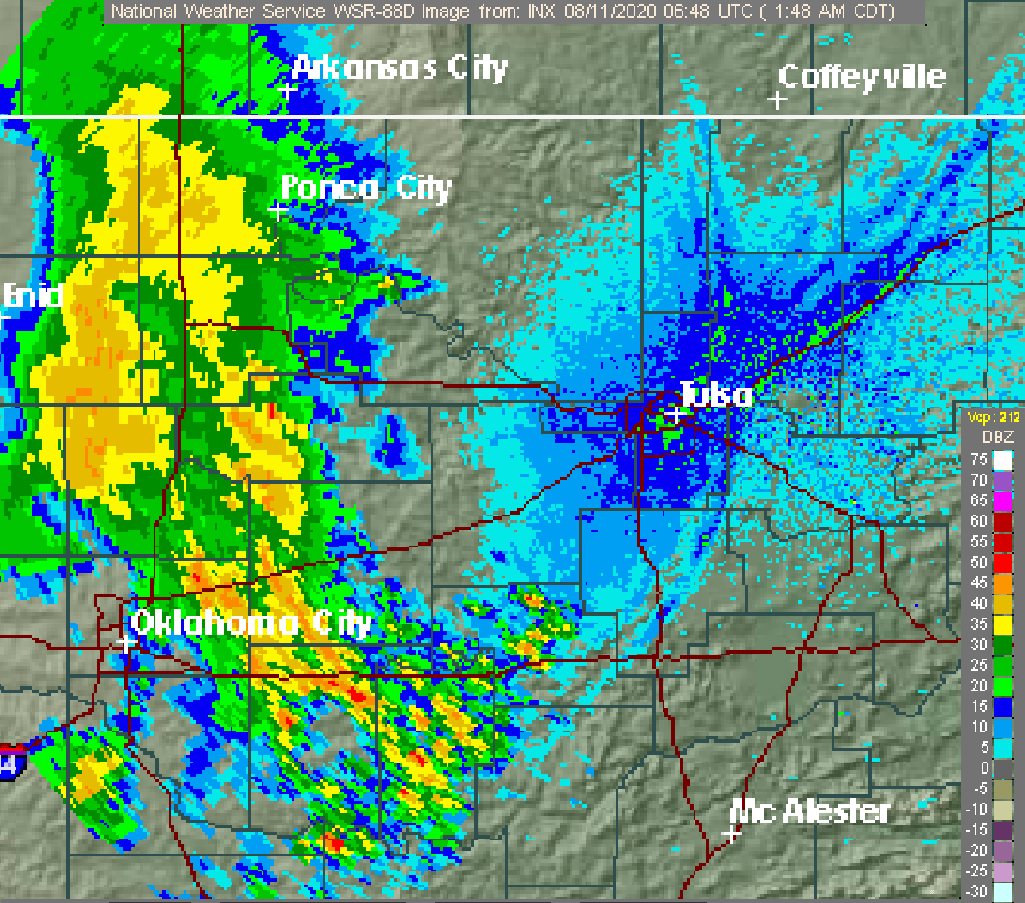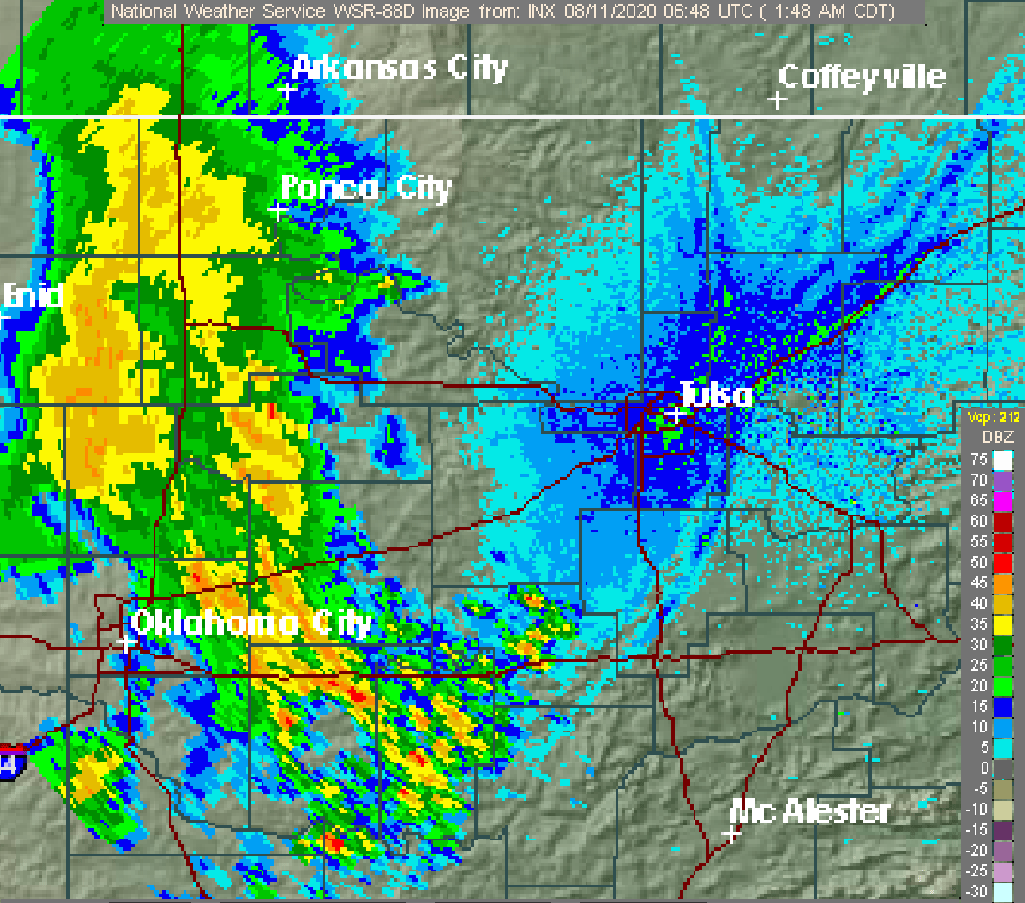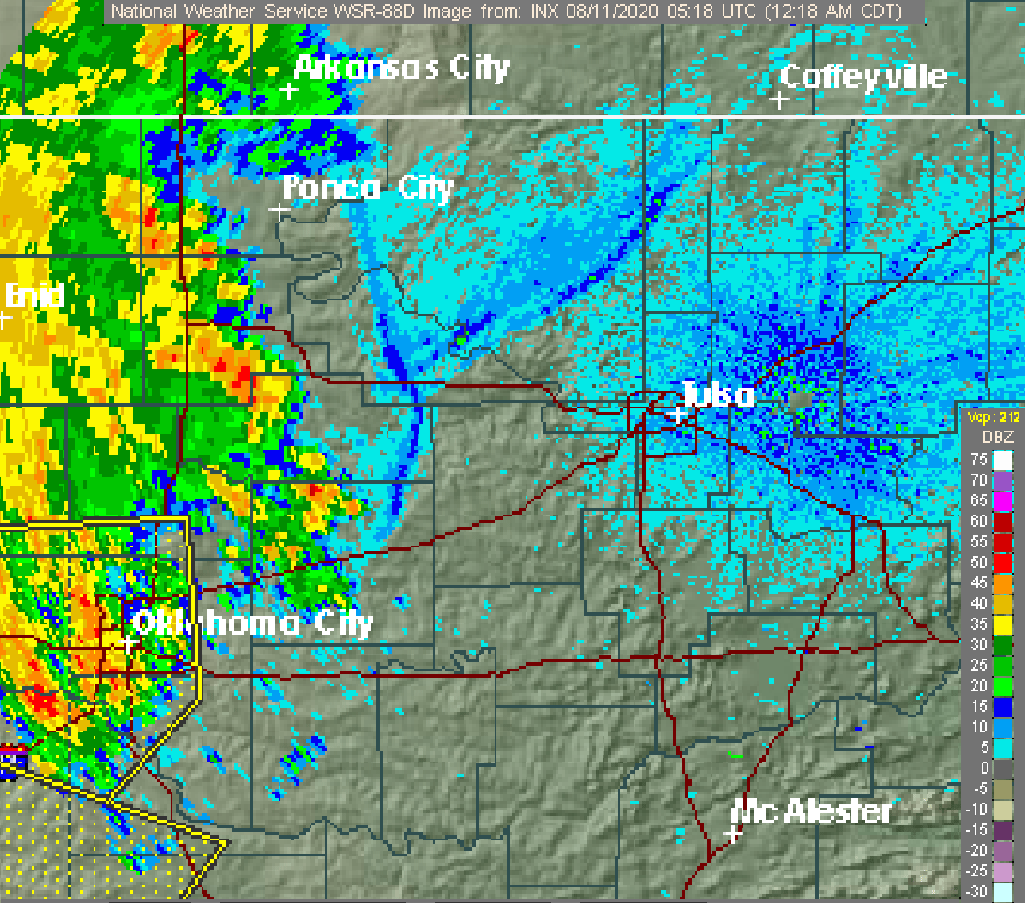
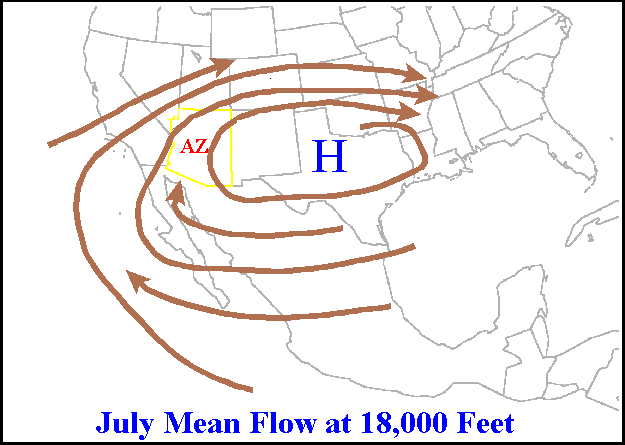
|
Hurricane Arlene (1987)
Hurricane Arlene was a long-lived tropical cyclone that moved eastward in an erratic fashion in the northern Atlantic Ocean in mid-August 1987. The first named storm of the 1987 Atlantic hurricane season, Arlene formed out of an area of low pressure associated with a decaying frontal system along the North Carolina coastline, Arlene tracked in a general eastward direction across the Atlantic Ocean, taking an erratic track with several curves. On August 13, the storm brushed Bermuda as a weak tropical storm before continuing out to sea. On August 20, the storm briefly stalled before becoming a hurricane two days later. Early on August 24, the storm transitioned into an extratropical cyclone over the far north Atlantic before curving southeast and dissipating near the Iberian Peninsula on August 26. In Bermuda, Arlene produced winds up to and waves up to ; however, little damage resulted from the storm. Offshore, a blind man was undertaking a challenge to becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing of ocean space. The Bahama Islands were inhabited by the Lucayans, a branch of the Arawakan-speaking Taíno, for many centuries. Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands, making his first landfall in the "New World" in 1492 when he landed on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/ National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th parallel north in the northeast Pacific Ocean and the 31st parallel north in the northern Atlantic Ocean. The agency, which is co-located with the Miami branch of the National Weather Service, is situated on the campus of Florida International University in Westchester, Florida. The NHC's Tropical Analysis and Forecast Branch (TAFB) routinely issues marine forecasts, in the form of graphics and high seas forecasts year round, with the Ocean Prediction Center having backup responsibility for this unit. The Technology and Science Branch (TSB) provides technical support for the center, which includes new infusions of technology from abroad. The Chief, Aerial Reconnaissance Coordination, All Hurricanes (CARCAH) unit tasks planes, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696 psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azores
) , motto= ( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace") , anthem=( en, "Anthem of the Azores") , image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg , map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union , map_caption=Location of the Azores within the European Union , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , established_title=Settlement , established_date=1432 , established_title3=Autonomous status , established_date3=30 April 1976 , official_languages= Portuguese , demonym= ( en, Azorean) , capital_type=Capitals , capital = Ponta Delgada (executive) Angra do Heroísmo (judicial)Horta (legislative) , largest_city = Ponta Delgada , government_type= Autonomous Region , leader_title1=Representative of the Republic , leader_name1=Pedro Manuel dos Reis Alves Catarino , leader_title2= President of the Legislative Assembly , leader_name2= Luís Garcia , leader_title3= President of the Regional Government , le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Pressure Area
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interplays between the relatively larger-scale dynamics of an entire planet's atmospheric circulation. The strongest high-pressure areas result from masses of cold air which spread out from polar regions into cool neighboring regions. These highs weaken once they extend out over warmer bodies of water. Weaker—but more frequently occurring—are high-pressure areas caused by atmospheric subsidence: Air becomes cool enough to precipitate out its water vapor, and large masses of cooler, drier air descend from above. Within high-pressure areas, winds flow from where the pressure is highest, at the center of the area, toward the periphery where the pressure is lower. However, if the planet is rotating, the straight direction of the air flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
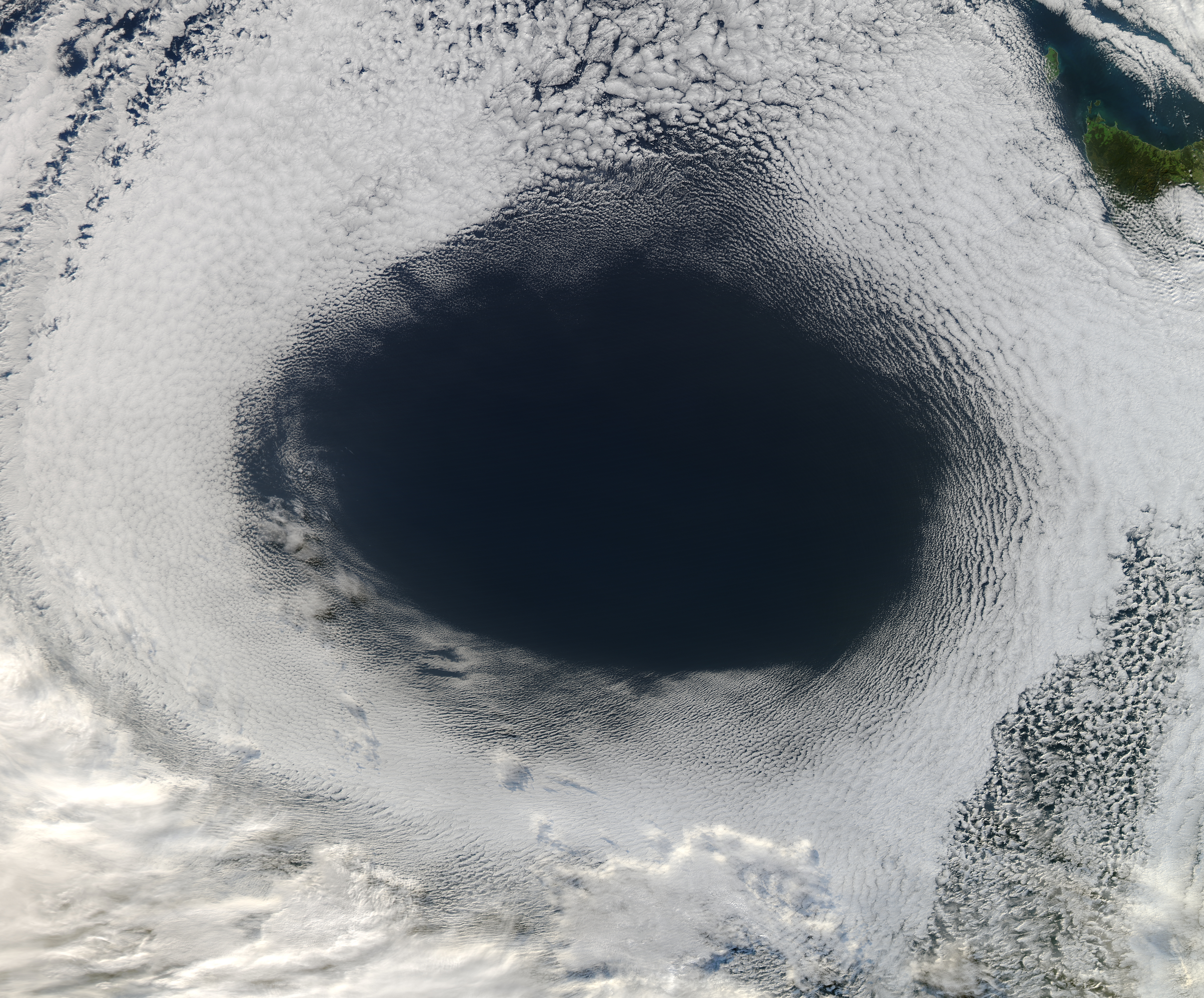
Eye (cyclone)
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weather and highest winds occur. The cyclone's lowest barometric pressure occurs in the eye and can be as much as 15 percent lower than the pressure outside the storm. In strong tropical cyclones, the eye is characterized by light winds and clear skies, surrounded on all sides by a towering, symmetric eyewall. In weaker tropical cyclones, the eye is less well defined and can be covered by the central dense overcast, an area of high, thick clouds that show up brightly on satellite imagery. Weaker or disorganized storms may also feature an eyewall that does not completely encircle the eye or have an eye that features heavy rain. In all storms, however, the eye is the location of the storm's minimum barometric pressure—where the atmospheri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outflow (meteorology)
Outflow, in meteorology, is air that flows outwards from a storm system. It is associated with ridging, or anticyclonic flow. In the low levels of the troposphere, outflow radiates from thunderstorms in the form of a wedge of rain-cooled air, which is visible as a thin rope-like cloud on weather satellite imagery or a fine line on weather radar imagery. For observers on the ground, a thunderstorm outflow boundary often approaches in otherwise clear skies as a low, thick cloud that brings with it a gust front. Low-level outflow boundaries can disrupt the center of small tropical cyclones. However, outflow aloft is essential for the strengthening of a tropical cyclone. If this outflow is restricted or undercut, the tropical cyclone weakens. If two tropical cyclones are in close proximity, the upper-level outflow from the upwind system can limit the development of the other system. Thunderstorms For thunderstorms, outflow tends to indicate the development of a system. Large qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shortwave (meteorology)
A shortwave or shortwave trough is an embedded kink in the trough / ridge pattern. Its length scale is much smaller than that of and is embedded within longwaves, which are responsible for the largest scale (synoptic scale) weather systems. Shortwaves may be contained within or found ahead of longwaves and range from the mesoscale to the synoptic scale. Shortwaves are most frequently caused by either a cold pool or an upper level front. Shortwaves are commonly referred to as a vorticity maximum. Corresponding weather and effects Shortwaves are often associated with warm air advection (WAA) or cold air advection (CAA), which influence temperature. Due to the way they move the air around them and the way air moves away from them, shortwaves produce positive curvature vorticity and positive shear vorticity, respectively. Ahead of a shortwave there is large-scale lift due to divergence from positive vorticity advection (PVA). This lift often causes precipitation. In a capped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Arlene (1987)
Hurricane Arlene was a long-lived tropical cyclone that moved eastward in an erratic fashion in the northern Atlantic Ocean in mid-August 1987. The first named storm of the 1987 Atlantic hurricane season, Arlene formed out of an area of low pressure associated with a decaying frontal system along the North Carolina coastline, Arlene tracked in a general eastward direction across the Atlantic Ocean, taking an erratic track with several curves. On August 13, the storm brushed Bermuda as a weak tropical storm before continuing out to sea. On August 20, the storm briefly stalled before becoming a hurricane two days later. Early on August 24, the storm transitioned into an extratropical cyclone over the far north Atlantic before curving southeast and dissipating near the Iberian Peninsula on August 26. In Bermuda, Arlene produced winds up to and waves up to ; however, little damage resulted from the storm. Offshore, a blind man was undertaking a challenge to becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconnaissance Mission
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities. Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops (skirmishers, long-range reconnaissance patrol, U.S. Army Rangers, cavalry scouts, or military intelligence specialists), ships or submarines, crewed or uncrewed reconnaissance aircraft, satellites, or by setting up observation posts. Espionage is usually considered to be different from reconnaissance, as it is performed by non-uniformed personnel operating behind enemy lines. Often called recce (British, Canadian and Australian English) or recon (American English), the word for this activity has at its root the associated verb ''reconnoitre'' or ''reconnoiter''. Etymology The word from the Middle French ''reconoissance''. Overview Reconnaissance conducted by ground forces includes special reconnaissance, armored reconnaissance, amphibious recon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ridge (meteorology)
A ridge or barometric ridge is a term in meteorology describing an elongated area of relatively high atmospheric pressure compared to the surrounding environment, without being a closed circulation. It is associated with an area of maximum anticyclonic curvature of wind flow. The ridge originates in the center of an anticyclone and sandwiched between two low-pressure areas, and the locus of the maximum curvature is called the ''ridge line''. This phenomenon is the opposite of a trough. Description Ridges can be represented in two ways: * On surface weather maps, the pressure isobars form contours where the maximum pressure is found along the axis of the ridge. * In upper-air maps, geopotential height isohypses form similar contours where the maximum defines the ridge. Related weather Given the direction of the winds around an anticyclonic circulation and the fact that weather systems move from west to east: *ahead of an upper-ridge, the airflow that comes from the polar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |