|
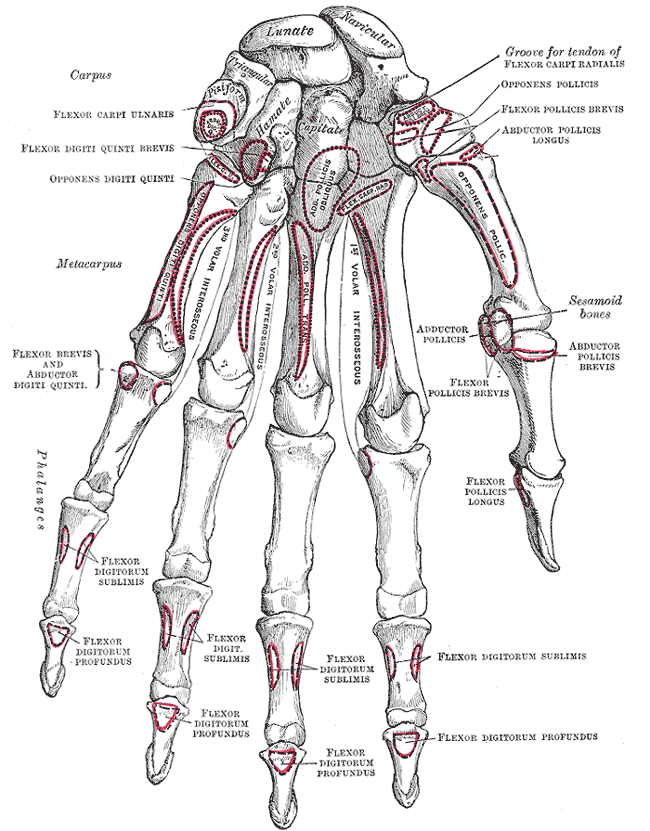
Humerus Bone
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity of humerus, upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body of humerus, body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prism (geometry), prismatic below. The lower extremity of humerus, lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes (trochlea of the humerus, trochlea & capitulum of the humerus, capitulum), and 3 fossae (radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its Surgical neck of the humerus, surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Bone
The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities and they are crucial for skeletal mobility. They grow primarily by elongation of the diaphysis, with an epiphysis at each end of the growing bone. The ends of epiphyses are covered with hyaline cartilage ("articular cartilage"). The longitudinal growth of long bones is a result of endochondral ossification at the epiphyseal plate. Bone growth in length is stimulated by the production of growth hormone (GH), a secretion of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The long bone category includes the femora, tibiae, and fibulae of the legs; the humeri, radii, and ulnae of the arms; metacarpals and metatarsals of the hands and feet, the phalanges of the fingers and toes, and the clavicles or collar bones. The long bones of the human leg compris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Neck Of The Humerus
The surgical neck of the humerus is a bony constriction at the proximal end of shaft of humerus. It is situated distal to the greater tubercle and lesser tubercle, and proximal to the deltoid tuberosity. Clinical significance The surgical neck is much more frequently fractured than the anatomical neck of the humerus. This type of fracture takes place when the humerus is forced in one direction while the joint capsule and the rotator cuff muscles remain intact. A fracture in this area is most likely to cause damage to the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery. Damage to the axillary nerve affects function of the teres minor and deltoid Deltoid (delta-shaped) can refer to: * The deltoid muscle, a muscle in the shoulder * Kite (geometry), also known as a deltoid, a type of quadrilateral * A deltoid curve, a three-cusped hypocycloid * A leaf shape * The deltoid tuberosity, a part of ... muscles, resulting in loss of abduction of arm (from 15-90 degrees), wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraspinatus Muscle
In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'', see infobox. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspinatus is to externally rotate the humerus and stabilize the shoulder joint. Structure It attaches medially to the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and laterally to the middle facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The muscle arises by fleshy fibers from the medial two-thirds of the infraspinatous fossa, and by tendinous fibers from the ridges on its surface; it also arises from the infraspinatous fascia which covers it, and separates it from the teres major and teres minor. The fibers converge to a tendon, which glides over the lateral border of the spine of the scapula and passing across the posterior part of the capsule of the shoulder-joint, is inserted into the middle impression on the greater tubercle of the humerus. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraspinatus Muscle
The supraspinatus (plural ''supraspinati'') is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotator cuff muscles and also abducts the arm at the shoulder. The spine of the scapula separates the supraspinatus muscle from the infraspinatus muscle, which originates below the spine. Structure The supraspinatus muscle arises from the supraspinous fossa, a shallow depression in the body of the scapula above its spine. The supraspinatus muscle tendon passes laterally beneath the cover of the acromion. Research in 1996 showed that the postero-lateral origin was more lateral than classically described. The supraspinatus tendon is inserted into the superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The distal attachments of the three rotator cuff muscles that insert into the greater tubercle of the humerus can be abbreviated as SIT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Humeral Circumflex Artery
The posterior humeral circumflex artery (posterior circumflex artery, posterior circumflex humeral artery) arises from the third part of axillary artery at the lower border of the subscapularis, and runs posteriorly with the axillary nerve through the quadrangular space. It winds around the surgical neck of the humerus and is distributed to the deltoid muscle and shoulder-joint, anastomosing with the anterior humeral circumflex and deep artery of the arm. It supplies the teres major, teres minor, deltoid Deltoid (delta-shaped) can refer to: * The deltoid muscle, a muscle in the shoulder * Kite (geometry), also known as a deltoid, a type of quadrilateral * A deltoid curve, a three-cusped hypocycloid * A leaf shape * The deltoid tuberosity, a part of ..., and (long head only) triceps muscles. Additional images File:Gray810.png, Suprascapular and axillary nerves of right side, seen from behind. File:Slide4SSS.JPG, Posterior humeral circumflex artery See also * Anterior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axillary Nerve
The axillary nerve or the circumflex nerve is a nerve of the human body, that originates from the brachial plexus ( upper trunk, posterior division, posterior cord) at the level of the axilla (armpit) and carries nerve fibers from C5 and C6. The axillary nerve travels through the quadrangular space with the posterior circumflex humeral artery and vein to innervate the deltoid and teres minor. Structure The nerve lies at first behind the axillary artery, and in front of the subscapularis, and passes downward to the lower border of that muscle. It then winds from anterior to posterior around the neck of the humerus, in company with the posterior humeral circumflex artery, through the quadrangular space (bounded above by the teres minor, below by the teres major, medially by the long head of the triceps brachii, and laterally by the surgical neck of the humerus), and divides into an anterior, a posterior, and a collateral branch to the long head of the triceps brachii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. plural foramina, or foramens ) is an open hole that is present in extant or extinct s. Foramina inside the body of animals typically allow nerves, arteries, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray's Anatomy
''Gray's Anatomy'' is a reference book of human anatomy written by Henry Gray, illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter, and first published in London in 1858. It has gone through multiple revised editions and the current edition, the 42nd (October 2020), remains a standard reference, often considered "the doctors' bible". Earlier editions were called ''Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical'', ''Anatomy of the Human Body'' and ''Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied'', but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, ''Gray's Anatomy''. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject. Publication history Origins The English anatomist Henry Gray was born in 1827. He studied the development of the endocrine glands and spleen and in 1853 was appointed Lecturer on Anatomy at St George's Hospital Medical School in London. In 1855, he approached his colleague Henry Vandyke Carter with his idea to produce an inexpensive a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
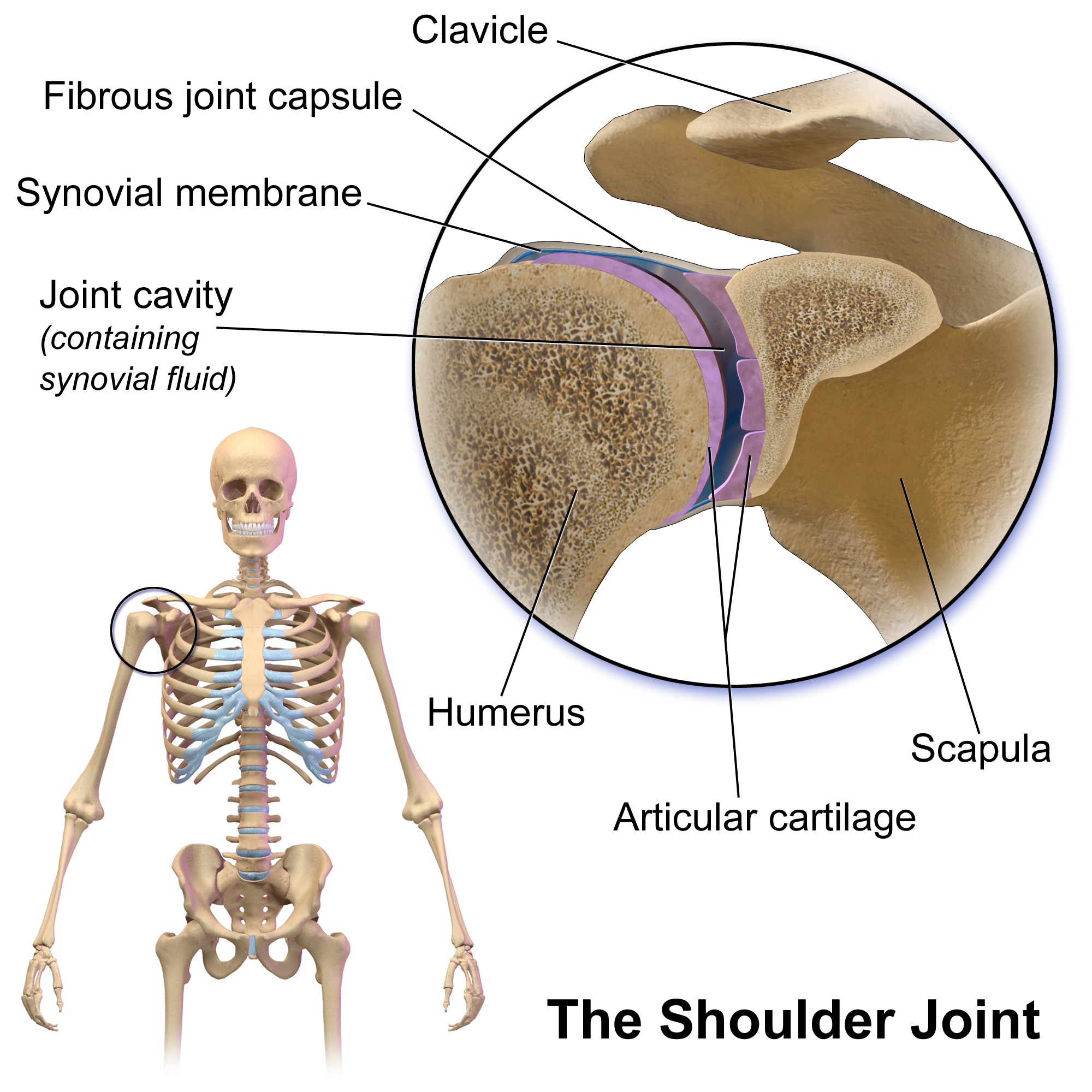
Glenohumeral Joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body. Structure The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. The socket of the glenoid fossa of the scapula is itself quite shallow, but it is made deeper by the addition of the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilaginous fibre attached to the circumference of the cavity. This ring is continuous with the tendon of the biceps brachii above. Spaces Significant joint spaces are: * The normal glenohumeral space is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenoid Cavity
The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a bone part of the shoulder. The word ''glenoid'' is pronounced or (both are common) and is from el, gléne, "socket", reflecting the shoulder joint's ball-and-socket form. It is a shallow, pyriform articular surface, which is located on the lateral angle of the scapula. It is directed laterally and forward and articulates with the head of the humerus; it is broader below than above and its vertical diameter is the longest. This cavity forms the glenohumeral joint along with the humerus. This type of joint is classified as a synovial, ball and socket joint. The humerus is held in place within the glenoid cavity by means of the long head of the biceps tendon. This tendon originates on the superior margin of the glenoid cavity and loops over the shoulder, bracing humerus against the cavity. The rotator cuff also reinforces this joint more specifically with the supraspinatus tendon to hold the head of the humerus i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |