|
Humeri
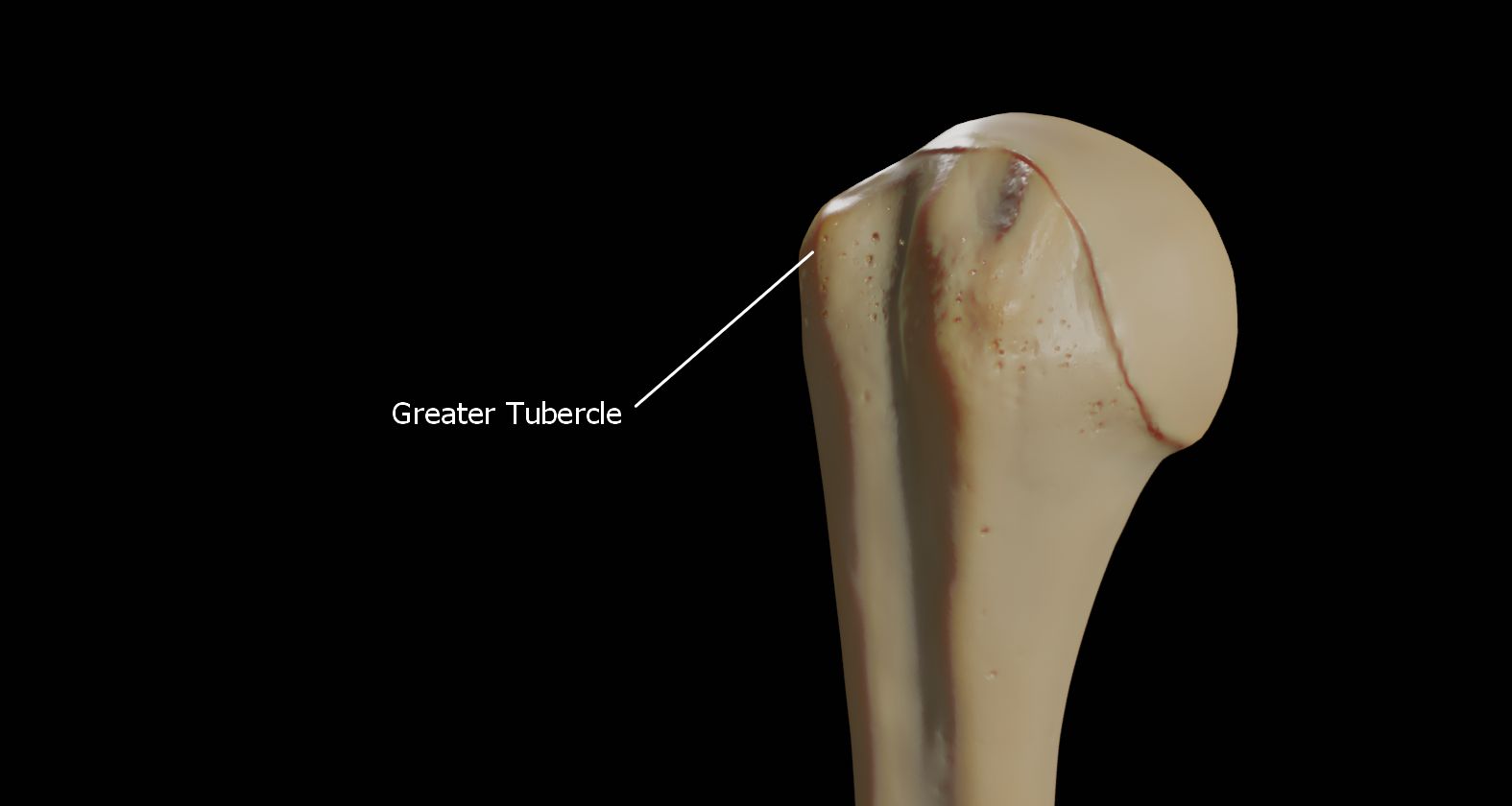
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes ( trochlea & capitulum), and 3 fossae (radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from la, humerus, umerus meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic ''ams'' shoulder and Greek ''ōmos''. Structure Upper extremity The upper or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Extremity Of Humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes (trochlea & capitulum), and 3 fossae (radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from la, humerus, umerus meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic ''ams'' shoulder and Greek ''ōmos''. Structure Upper extremity The upper or pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Of The Humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes (trochlea & capitulum), and 3 fossae (radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from la, humerus, umerus meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic ''ams'' shoulder and Greek ''ōmos''. Structure Upper extremity The upper or pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Extremity Of Humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity of humerus, upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body of humerus, body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prism (geometry), prismatic below. The lower extremity of humerus, lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes (trochlea of the humerus, trochlea & capitulum of the humerus, capitulum), and 3 fossae (radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its Surgical neck of the humerus, surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Of Humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes ( trochlea & capitulum), and 3 fossae (radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from la, humerus, umerus meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic ''ams'' shoulder and Greek ''ōmos''. Structure Upper extremity The upper o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitulum Of The Humerus
In human anatomy of the arm, the capitulum of the humerus is a smooth, rounded eminence on the lateral portion of the distal articular surface of the humerus. It articulates with the cupshaped depression on the head of the radius, and is limited to the front and lower part of the bone. In non-human tetrapods, the name capitellum is generally used, with "capitulum" limited to the anteroventral articular facet of the rib (in archosauromorphs). Lepidosauromorpha Lepidosaurs show a distinct capitellum and trochlea on the centre of the ventral (anterior in upright taxa) surface of the humerus at the distal end. Archosauromorpha In non-avian archosaurs, including crocodiles, the capitellum and the trochlea are no longer bordered by distinct etc.- and entepicondyles respectively, and the distal humerus consists two gently expanded condyles, one lateral and one medial, separated by a shallow groove and a supinator process. Romer (1976) homologizes the capitellum in Archosauromorphs w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
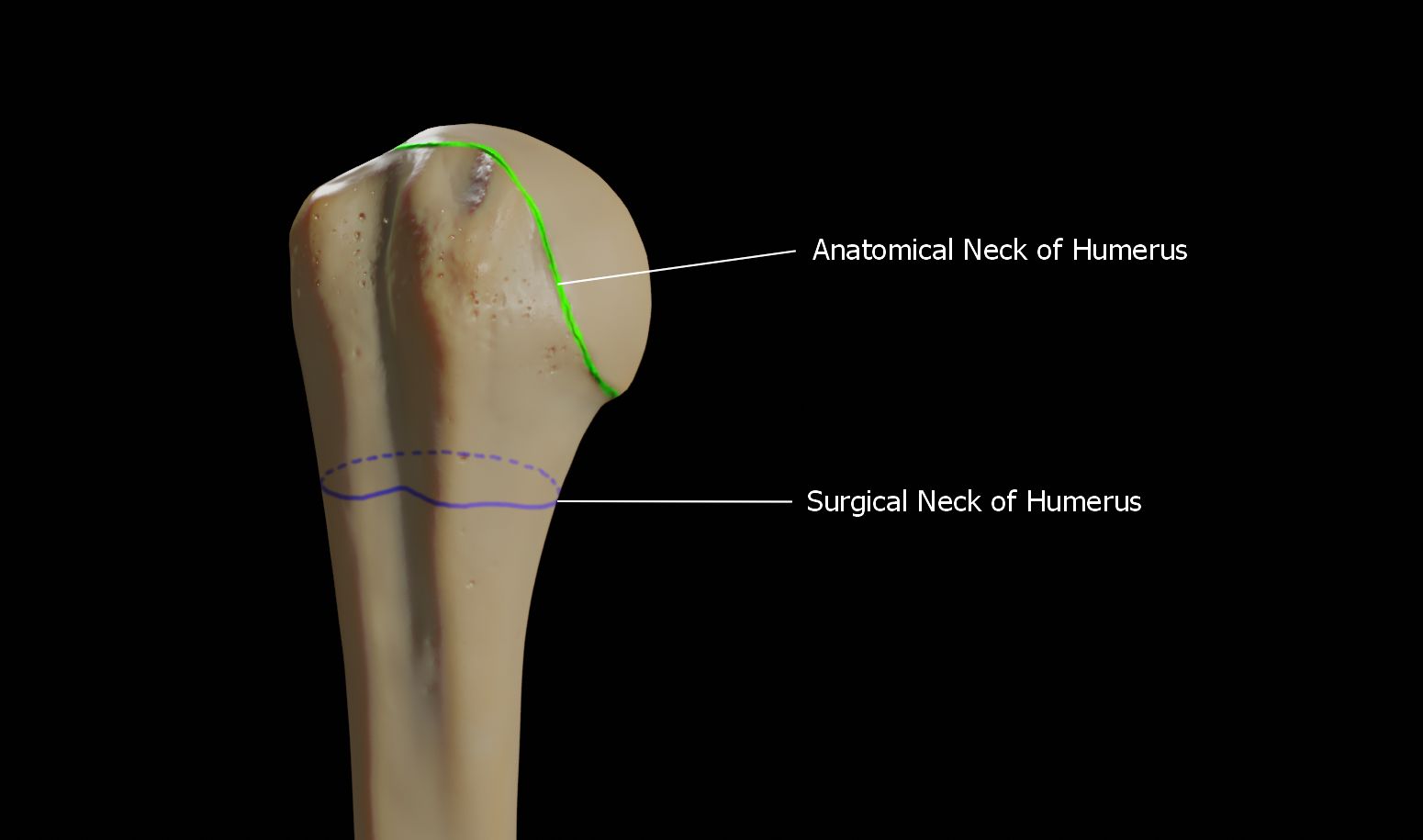
Surgical Neck Of The Humerus
The surgical neck of the humerus is a bony constriction at the proximal end of shaft of humerus. It is situated distal to the greater tubercle and lesser tubercle, and proximal to the deltoid tuberosity. Clinical significance The surgical neck is much more frequently fractured than the anatomical neck of the humerus. This type of fracture takes place when the humerus is forced in one direction while the joint capsule and the rotator cuff muscles remain intact. A fracture in this area is most likely to cause damage to the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery. Damage to the axillary nerve affects function of the teres minor and deltoid muscles, resulting in loss of abduction of arm (from 15-90 degrees), weak flexion, extension, and rotation of shoulder as well as loss of sensation of the skin over a small part of the lateral shoulder. Additional images File:Neck-of-Humerus.jpg, The difference between anatomical neck and surgical neck of the humerus File:Illus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder
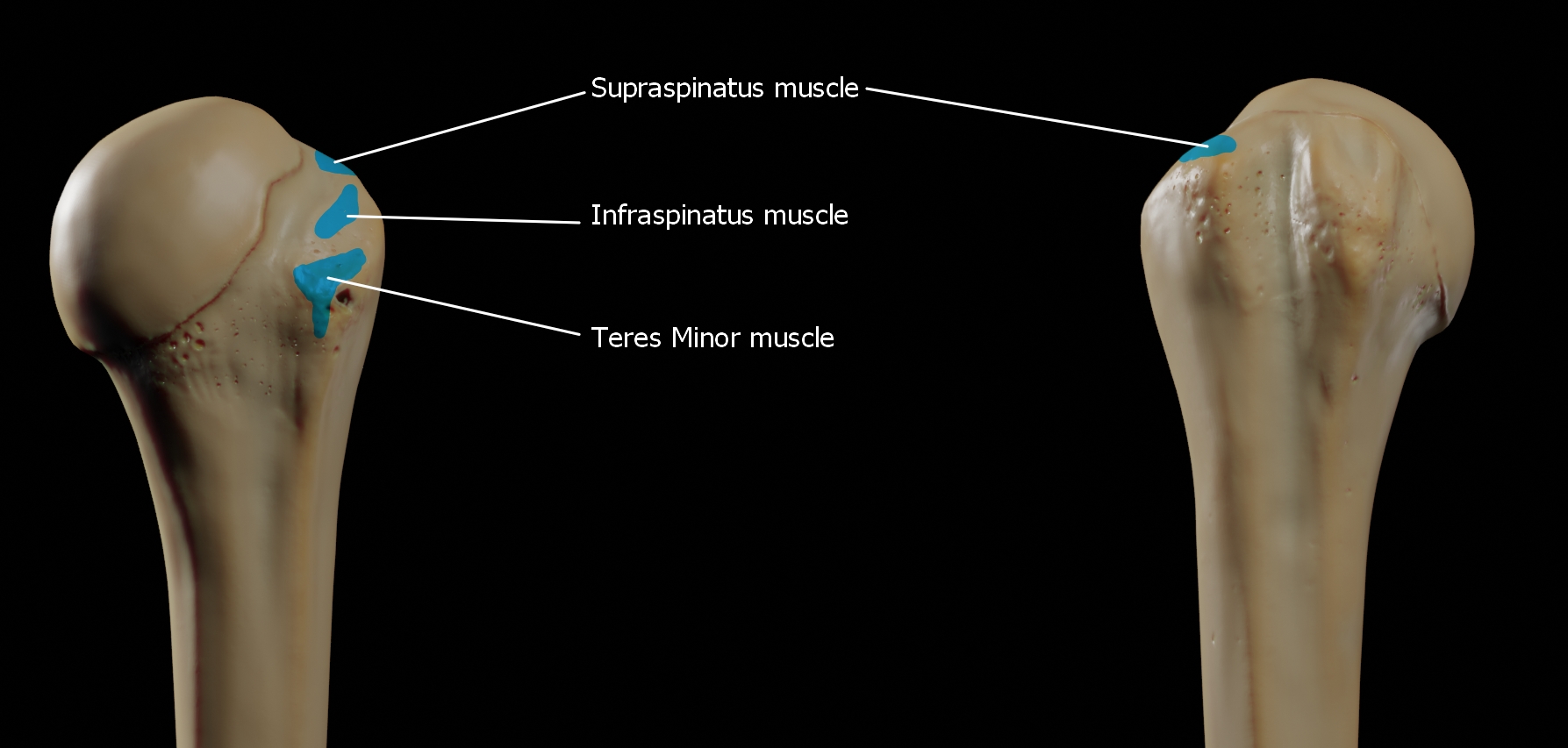
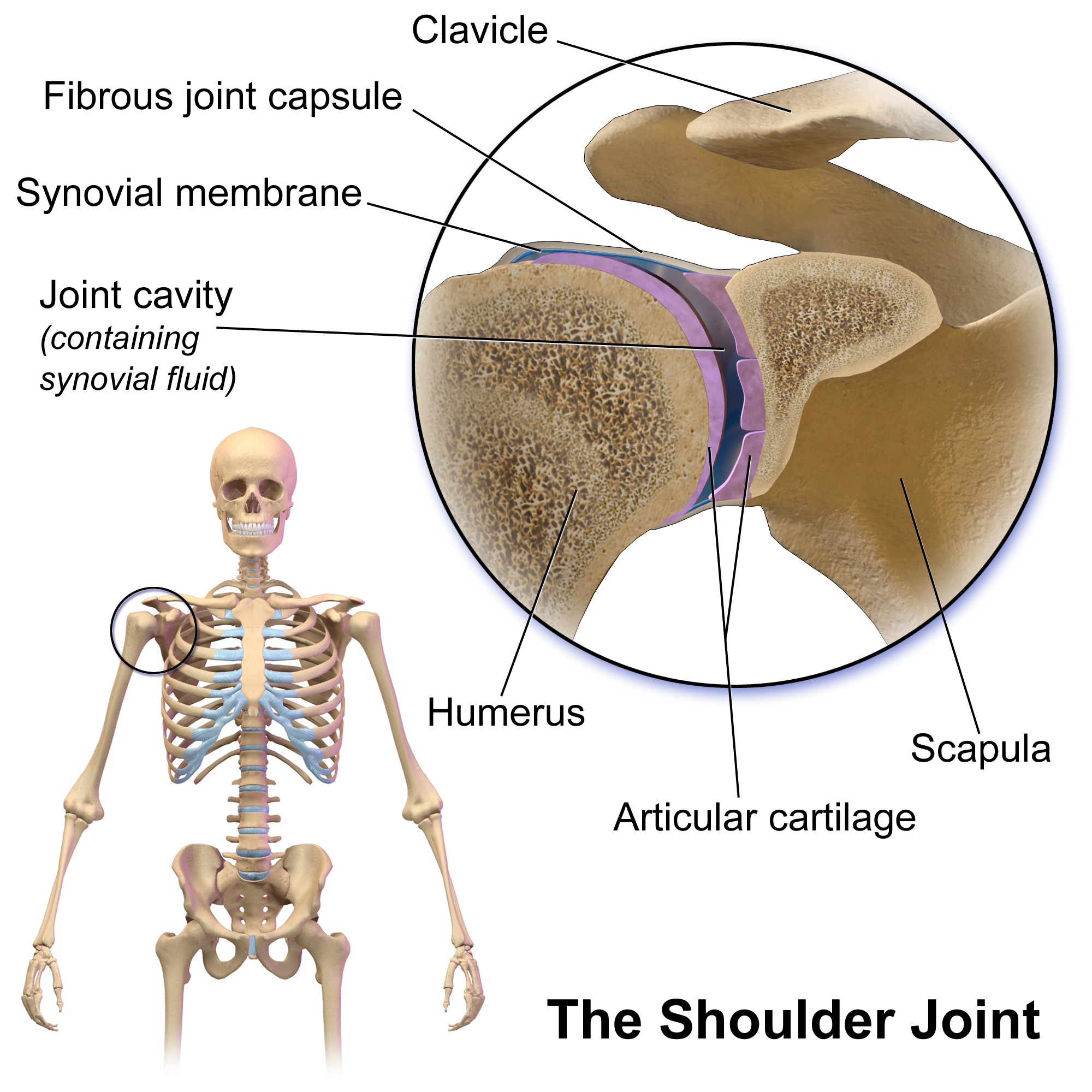
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is the major joint of the shoulder, but can more broadly include the acromioclavicular joint. In human anatomy, the shoulder joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula, and the head sits in the glenoid cavity. The shoulder is the group of structures in the region of the joint. The shoulder joint is the main joint of the shoulder. It is a ball and socket joint that allows the arm to rotate in a circular fashion or to hinge out and up away from the body. The joint capsule is a soft tissue envelope that encircles the glenohumeral joint and attaches to the scapula, humerus, and head of the biceps. It is lined by a thin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronoid Fossa
Superior to the anterior portion of the Trochlea of humerus, trochlea is a small depression, the coronoid fossa, which receives the coronoid process of the ulna during flexion of the forearm. It is directly adjacent to the radial fossa of the humerus. Additional images File:Human arm bones diagram.svg, Human arm bones diagram File:Elbow joint - deep dissection (anterior view, human cadaver).jpg, Elbow joint. Deep dissection. Anterior view. File:Slide2xzxzxz.JPG, Elbow joint. Deep dissection. Anterior view. References External links * Humerus {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Fossa
The radial fossa is a slight depression found on the humerus above the front part of the capitulum. It receives the anterior border of the head of the radius when the forearm is flexed. Structure The joint capsule of the elbow attaches to the humerus The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a roun ... just proximal to the radial fossa. Additional images File:Human arm bones diagram.svg, Human arm bones diagram File:Elbow joint - deep dissection (anterior view, human cadaver).jpg, Elbow joint. Deep dissection. Anterior view. File:Slide2xzxzxz.JPG, Elbow joint. Deep dissection. Anterior view. References External links * Humerus {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochlea Of The Humerus
In the human arm, the humeral trochlea is the medial portion of the articular surface of the elbow joint which articulates with the trochlear notch on the ulna in the forearm. Structure In humans and apes it is trochleariform (or trochleiform), as opposed to cylindrical in most monkeys and conical in some prosimians. It presents a deep depression between two well-marked borders; it is convex from before backward, concave from side to side, and occupies the anterior, lower, and posterior parts of the extremity. The trochlea has the capitulum located on its lateral side and the medial epicondyle on its medial. It is directly inferior to the coronoid fossa anteriorly and to the olecranon fossa posteriorly. In humans, these two fossae, the most prominent in the humerus, are occasionally transformed into a hole, the supratrochlear foramen, which is regularly present in, for example, dogs. Carrying angle When viewed from in front or behind, the trochlea looks roughly cylindrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Bone
The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, Short bone, short, Flat bone, flat, Irregular bone, irregular and Sesamoid bone, sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities and they are crucial for skeletal mobility. They grow primarily by elongation of the diaphysis, with an epiphysis at each end of the growing bone. The ends of epiphyses are covered with hyaline cartilage ("articular cartilage"). The longitudinal growth of long bones is a result of endochondral ossification at the epiphyseal plate. Bone growth in length is stimulated by the production of growth hormone (GH), a secretion of the Anterior pituitary, anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The long bone category includes the femora, tibiae, and fibulae of the legs; the humerus, humeri, Radius (bone), radii, and ulnae of the arms; metacarpals and metatarsals of the hands and feet, the Phalanx bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenohumeral Joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body. Structure The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. The socket of the glenoid fossa of the scapula is itself quite shallow, but it is made deeper by the addition of the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilaginous fibre attached to the circumference of the cavity. This ring is continuous with the tendon of the biceps brachii above. Spaces Significant joint spaces are: * The normal glenohumeral space is 4– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |