|
Humboldt Penguin
The Humboldt penguin (''Spheniscus humboldti'') is a medium-sized penguin. It resides in South America, its range mainly contains most of coastal Peru. Its nearest relatives are the African penguin, the Magellanic penguin and the Galápagos penguin. The Humboldt penguin and the cold water current it swims in both are named after the explorer Alexander von Humboldt. The species is listed as vulnerable by the IUCN with no population recovery plan in place. The current population is composed of 32,000 mature individuals and is going down. It is a migrant species. Humboldt penguins nest on islands and rocky coasts, burrowing holes in guano and sometimes using scrapes or caves. In South America the Humboldt penguin is found only along the Pacific coast, and the range of the Humboldt penguin overlaps that of the Magellanic penguin on the central Chilean coast. It is vagrant in Ecuador and Colombia. The Humboldt penguin has been known to live in mixed species colonies with the Magell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islas Ballestas
The Ballestas Islands (Spanish: ''Islas Ballestas'') are a group of small islands near the town of Paracas within the Paracas District of the Pisco Province in the Ica Region, on the south coast of Peru. Geography Composed largely of rock formations and covering an estimated area of 0.12 km², these islands are an important sanctuary for marine fauna like the guanay guano bird, the blue-footed booby and the tendril. Other notable species include Humboldt penguins and two varieties of seals (fur seals and sea lions), amongst other mammals. Access These islands are accessible from the resort town of Paracas (near Pisco) by tour boat which typically lasts 2 hours. During the visits it is not uncommon for the sea lions to approach the tourist boats and make spectacles for the visiting tourists. Lonely Planet’s Discover Peru: Top sights, authentic experiences. 1786575191 Lonely Planet - 2017 "Protruding out of the Pacific Ocean, the Islas Ballestas are home to an astonishin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broodiness
Broodiness is the action or behavioral tendency to sit on a clutch of eggs to incubate them, often requiring the non-expression of many other behaviors including feeding and drinking.Homedes Ranquini, J. y Haro-García, F. Zoogenética. 1ra. edición, 1958, (La Habana, 1967 Ed. Revolucionaria) Being broody has been defined as "Being in a state of readiness to brood eggs that is characterized by cessation of laying and by marked changes in behavior and physiology". . Broodiness is usually associated with female birds, although males of some bird species become broody and some non-avian animals also show broodiness. In wild birds In wild birds, egg incubation is a normal and essential phase in the process of reproduction, and in many families of birds, e.g. pigeons, the eggs are incubated by both male and female parents. Broodiness in males In all species of phalaropes, the males become broody rather than the female. The females leave the nest after finishing laying to let the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg Incubation
Egg incubation is the process by which an egg, of oviparous (egg-laying) animals, develops an embryo within the egg, after the egg's formation and ovipositional release. Egg incubation is done under favorable environmental conditions, possibly by brooding and hatching the egg. Multiple and various factors are vital to the incubation of various species of animal. In many species of reptile for example, no fixed temperature is necessary, but the actual temperature determines the sex ratio of the offspring. In birds in contrast, the sex of offspring is genetically determined, but in many species a constant and particular temperature is necessary for successful incubation. Especially in poultry, the act of sitting on eggs to incubate them is called brooding. The action or behavioral tendency to sit on a clutch of eggs is also called broodiness, and most egg-laying breeds of poultry have had this behavior selectively bred out of them to increase production. Avian incubation A wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan De Azúcar National Park
Pan de Azúcar National Park is a national park of Chile. The park straddles the border between the Antofagasta Region and the Atacama Region. Its name, ''Parque Nacional Pan de Azúcar'', means "sugar loaf national park". Geography The park is located 30 km north of Chañaral and 180 km north of Copiapó. It was founded in 1985 and has an extension of 437.54 km² (including 1.1 km² of insular terrain). It is importance derives from the relative diversity of species. Isla Pan de Azúcar Isla Pan de Azúcar is located 24 km farther. Humboldt penguins breed on this island. The island can be reached by boat from the mainland but passengers are not allowed to leave the boat. Caleta Pan de Azúcar Caleta Pan de Azúcar (Pan de Azúcar Cove) is a small fishing settlement which now caters to tourism. Formerly, copper was worked here and freighted by boat. Divers can still explore parts of the wharf and the loading crane below the water. From here the look-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foraging
Foraging is searching for wild food resources. It affects an animal's Fitness (biology), fitness because it plays an important role in an animal's ability to survive and reproduce. Optimal foraging theory, Foraging theory is a branch of behavioral ecology that studies the foraging behavior of animals in response to the environment where the animal lives. Behavioral ecologists use economic models and categories to understand foraging; many of these models are a type of optimal model. Thus foraging theory is discussed in terms of optimizing a payoff from a foraging decision. The payoff for many of these models is the amount of energy an animal receives per unit time, more specifically, the highest ratio of energetic gain to cost while foraging. Foraging theory predicts that the decisions that maximize energy per unit time and thus deliver the highest payoff will be selected for and persist. Key words used to describe foraging behavior include ''resources'', the elements necessary fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver-sided Weedfish
''Cristiceps argyropleura'', the silver-sided weedfish, is a species of clinid found around southern Australia at depths from where it is predominantly found in kelp Kelps are large brown algae seaweeds that make up the order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genera. Despite its appearance, kelp is not a plant - it is a heterokont, a completely unrelated group of organisms. Kelp grows in "underwat ... beds. This species can reach a length of TL. References argyropleura Fish described in 1865 {{Clinidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araucanian Herring
The Araucanian herring (''Strangomera bentincki'' or ''Clupea bentincki'') is a fish species in the family Clupeidae. It is an epipelagic fish, silvery below and dark blue above, which schools in coastal waters off the west coast of South America. It ranges along the Chilean coast from Valparaiso south to Talcahuano. It schools at depths from 0 to 70 meters in nearshore areas. There it filter feeds on smaller plankton such as diatoms. It reaches sexual maturity when it is about 10 centimetres long, and is a pelagic spawner, spawning between June and November. It grows to a maximum standard length of 15 cm. Fisheries The Araucanian herring is a commercial species, largely used for fishmeal. Based on the FAO fishery statistics, it was the 12th most important capture fish species in 2009. All reported landings are from Chile. References Literature * * * Whitehead PJP, Nelson GJ and Wongratana T (1988) FAO species catalogue, volume 7''Clupeoid Fishes of the World (Suborder C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchovy
An anchovy is a small, common forage fish of the family Engraulidae. Most species are found in marine waters, but several will enter brackish water, and some in South America are restricted to fresh water. More than 140 species are placed in 17 genera; they are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans, and in the Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. Anchovies are usually classified as oily fish. Genera Characteristics Anchovies are small, green fish with blue reflections due to a silver-colored longitudinal stripe that runs from the base of the caudal (tail) fin. They range from in adult length, and their body shapes are variable with more slender fish in northern populations. The snout is blunt with tiny, sharp teeth in both jaws. The snout contains a unique rostral organ, believed to be electro-sensory in nature, although its exact function is unknown. The mouth is larger than that of herrings and silversides, two fish which anchovies closely resemble in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Saury
The Atlantic saury (''Scomberesox saurus'') is a fish of the family Scomberesocidae found in the North Atlantic Ocean from the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, Canada south to Bermuda and North Carolina in the western Atlantic and from Iceland to Morocco in the eastern Atlantic, it is also found in the Mediterranean Sea, the Adriatic Sea and the Aegean Sea. Description The Atlantic saury is an elongated slender fish with very long, beak-like jaws with minute teeth. The fish grow to about in length, with a maximum length of . They have a row of finlets behind their dorsal and anal fins. They are similar in appearance to garfish but differ in having much smaller teeth. Atlantic sauries live near the surface, and will often jump above the surface. Distribution and habitat The Atlantic saury is native to the northern Atlantic Ocean, being present off the coast of North America, from the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to North Carolina and Bermuda, and off the coast of Western Europe. It has occasion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, whereas in the Nautiloidea, the external shell remains. About 800 living species of cephalopods have been ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
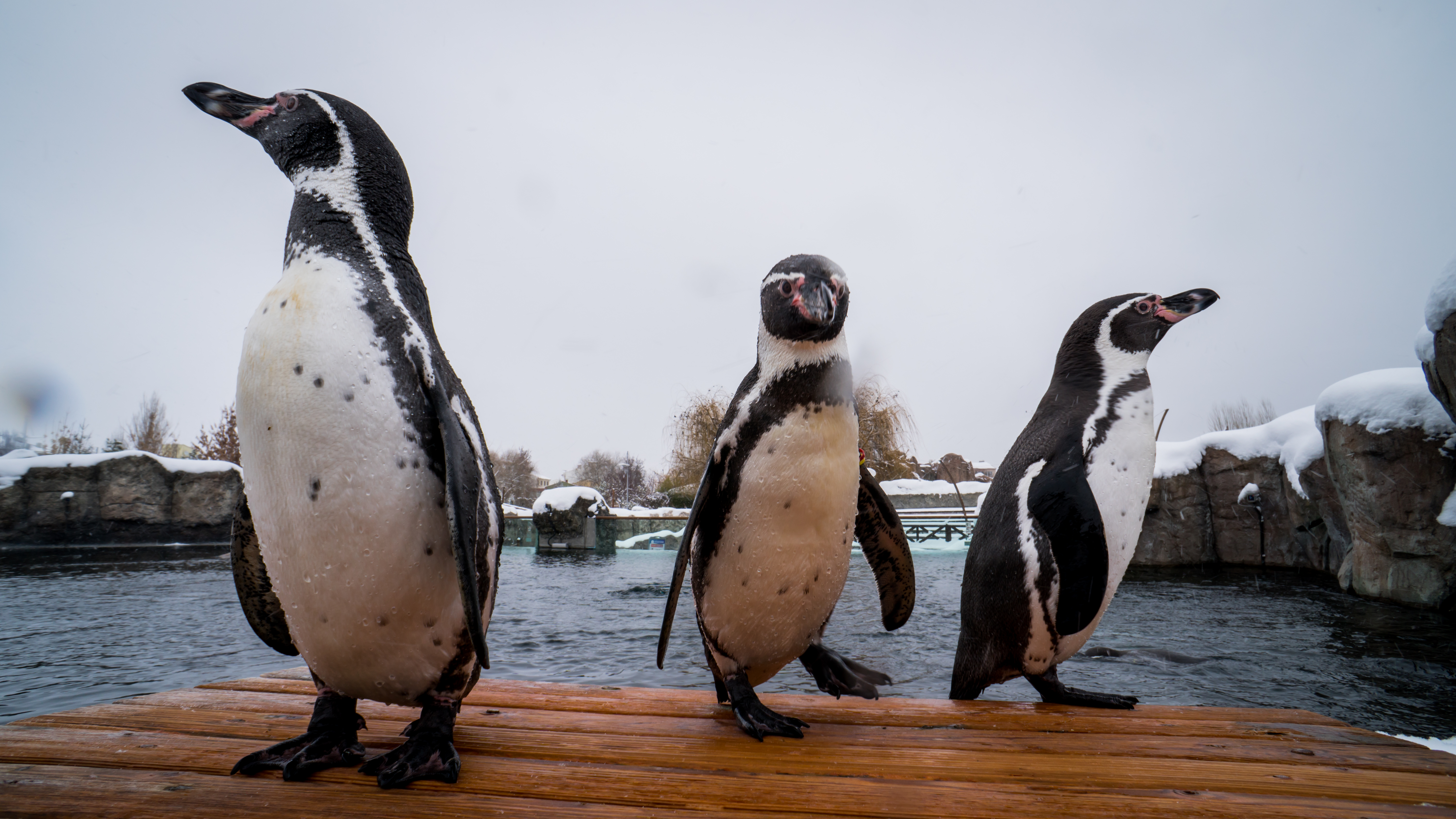

.jpg)





.jpg)