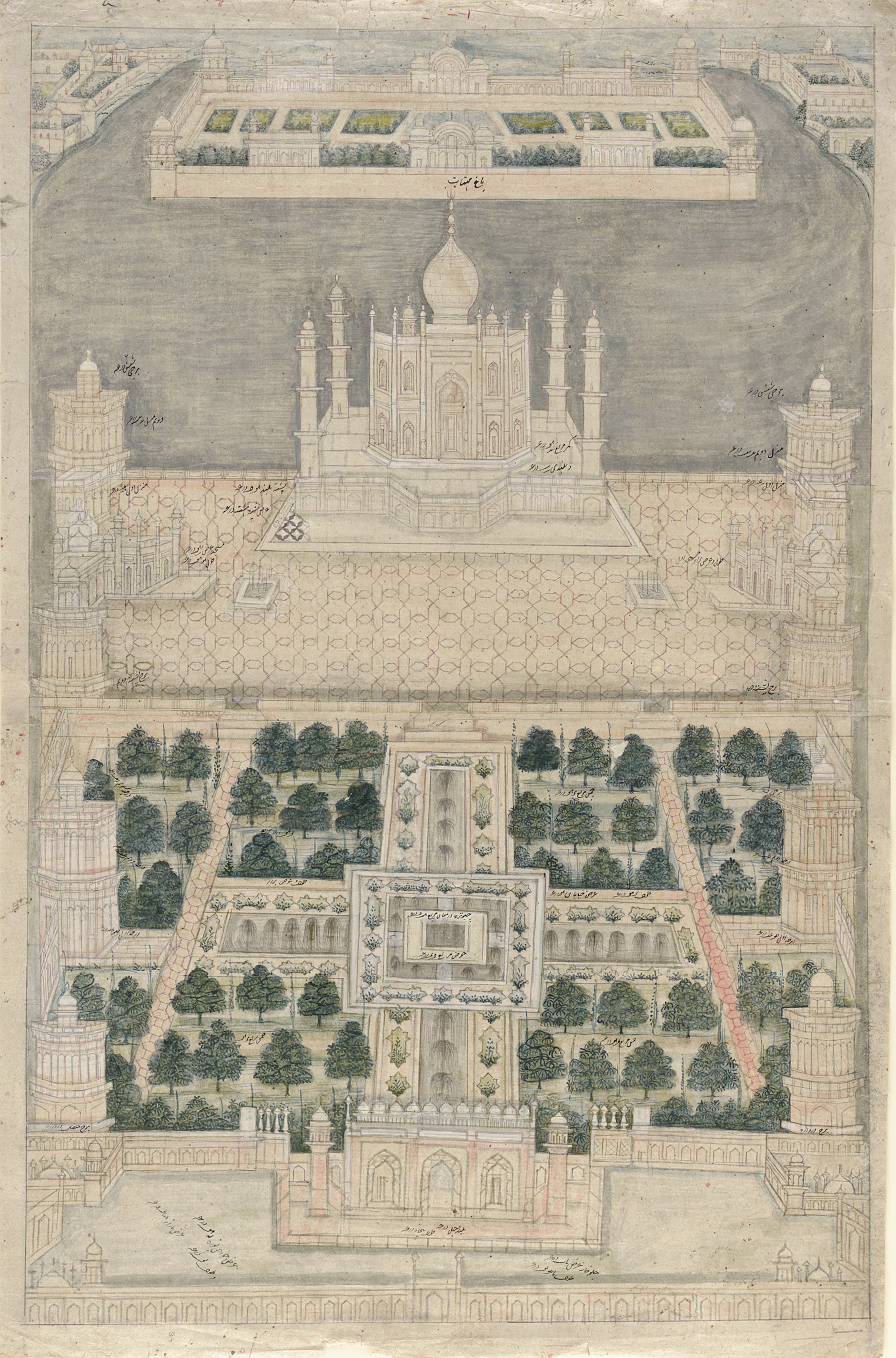
|
Humanyun Mosque
Humayun Mosque is situated in the village of Kachhpura in Agra on the left bank of River Yamuna. History Though this mosque has not been mentioned in texts related to Mughal period, it is the only monument in Agra that can undoubtedly be attributed to the reign of Humayun. According to the inscriptions on this monument, the mosque was constructed in 1530, when Humayun ascended the throne. Architecture The facade of the mosque bears five arches, the central of which is a high iwan. A dome tops the central nave, and is supported on kite-shaped pendentives and net squinches. There are double-aisled wings on either side of the central nave. The building is made of brick and lime, and covered with stucco work. See also * Moti Masjid, Agra * Gyarah Sidi * Mehtab Bagh Mehtab Bagh () is a charbagh complex in Agra, North India. It lies north of the Taj Mahal complex and the Agra Fort on the opposite side of the Yamuna River, in the flood plains. The garden complex, square in shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agra
Agra (, ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital New Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is the fourth-most populous city in Uttar Pradesh and List of cities in India by population, twenty-third most populous city in India. Agra's notable historical period began during Sikandar Lodi's reign, but the golden age of the city began with the Mughals. Agra was the foremost city of the Indian subcontinent and the capital of the Mughal Empire under Mughal emperors Babur, Humayun, Akbar, Jahangir and Shah Jahan. Under Mughal rule, Agra became a centre for learning, arts, commerce, and religion, and saw the construction of the Agra Fort, Sikandra, Agra, Sikandra and Agra's most prized monument, the Taj Mahal, built by Shah Jahan as a mausoleum for his favourite empress. With the decline of the Mughal empire in the late 18th century, the ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Yamuna
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Lower Himalaya in Uttarakhand, it travels a total length of and has a drainage system of , 40.2% of the entire Ganges Basin. It merges with the Ganges at Triveni Sangam, Allahabad, which is a site of the Kumbh Mela, a Hindu festival held every 12 years. Like the Ganges, the Yamuna is highly venerated in Hinduism and worshipped as the goddess Yamuna. In Hinduism she is the daughter of the sun god, Surya, and the sister of Yama, the god of death, and so is also known as Yami. According to popular legends, bathing in its sacred waters frees one from the torments of death. It crosses several states: Haryana and Uttar Pradesh, passing by Uttarakhand and later Delhi, and meeting its tributaries on the way, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iwan
An iwan ( fa, ایوان , ar, إيوان , also spelled ivan) is a rectangular hall or space, usually vaulted, walled on three sides, with one end entirely open. The formal gateway to the iwan is called , a Persian term for a portal projecting from the facade of a building, usually decorated with calligraphy bands, glazed tilework, and geometric designs. Since the definition allows for some interpretation, the overall forms and characteristics can vary greatly in terms of scale, material, or decoration. Iwans are most commonly associated with Islamic architecture; however, the form is Iranian in origin and was invented much earlier and fully developed in Mesopotamia around the third century CE, during the Parthian period of Persia. Etymology ''Iwan'' is a Persian word which was subsequently borrowed into other languages such as Arabic and Turkish. Its etymology is unclear. A theory by scholars like Ernst Herzfeld and W. B. Henning proposed that the root of this term is Old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moti Masjid, Agra
The Moti Masjid () is a 17th-century congregational mosque located within the Agra Fort UNESCO World Heritage Site. Built by Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan, the mosque is made entirely of white marble. History ] The Agra Fort's modern appearance is largely owed to Shah Jahan, who dismantled several structures within the Agra Fort to add his own in marble. The Moti Masjid was one such structure. The mosque was constructed in the period 1646-1653, which was notably later than all of his other Agra Fort contributions (these were commenced in 1627, his first regnal year, and completed in 1638). The mosque's completion in 1653 was five years after the Mughal residence had shifted to Shahjahanabad. When Shah Jahan visited the mosque upon its completion, he was so impressed with the structure that he returned two years later to show two of his sons. Architecture The mosque complex, built on a high plinth, is a walled enclosure situated to the north of the fort's courtyard. It lies on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyarah Sidi
Gyarah Sidi (''Literally: Eleven steps'') are the remains of the astrological observatory of the Mughal Emperor Humayun. The ruins are situated at a stone's throw from Babur’s Mehtab Bagh, in a field on the banks of the Yamuna river in Agra. History Gyarah Sidi or Eleven Steps refers to the steps overlooking the hemispherical cavities in the ground from which astronomical readings could be taken. Though nowhere close to their size, Humayun's observatory is an interesting, diminutive precursor to the massive Jantar Mantars at Jaipur and Delhi built nearly 200 years later. Humayun and astronomy Humayun was absorbed in astrology and astronomy, manifesting his passion in the most eccentric way. The business at court was not conducted according to exigencies of matter on hand but deferred to the planets: *Sunday and Tuesday for government - As the sun regulates sovereignty and Mars is the patron of soldiers. *Saturday and Thursday were devoted to matters of religion. He even w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehtab Bagh
Mehtab Bagh () is a charbagh complex in Agra, North India. It lies north of the Taj Mahal complex and the Agra Fort on the opposite side of the Yamuna River, in the flood plains. The garden complex, square in shape, measures about and is perfectly aligned with the Taj Mahal on the opposite bank. During the rainy season, the ground becomes partially flooded. History The Mehtab Bagh garden was the last of eleven Mughal-built gardens along the Yamuna opposite the Taj Mahal and the Agra Fort. The garden was built by Emperor Babur (d. 1530). It is also noted that Emperor Shah Jahan had identified a site from the crescent-shaped, grass-covered floodplain across the Yamuna River as an ideal location for viewing the Taj Mahal. It was then created as "a moonlit pleasure garden called Mehtab Bagh." White plaster walkways, airy pavilions, pools and fountains were also created as part of the garden, with fruit trees and Narcissus (plant), narcissus. The garden was designed as an integral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jama Masjid, Agra
The Jama Mosque is a 17th-century congregational mosque located in the historic core of Agra, Uttar Pradesh. It was built by Jahanara Begum, ''Padshah Begum'' (First Lady) of the Mughal Empire, during the reign of her father, Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan. It is one of the largest mosques in India. Today it is still in use, serving as the principal mosque for the city of Agra. It stands opposite to the Agra Fort, and overlooks the Agra Fort Railway Station. History The Jama Masjid was commissioned by Jahanara Begum, after receiving permission from Shah Jahan. Its construction began in 1643 and was completed in 1648, coming at a cost of five lakh rupees. The mosque was part of several imperial reconstruction projects undertaken to improve Agra, the then-capital of the Mughal Empire. There was a spacious, octagonal Tripolia Chowk which existed between the Jama Masjid and the Delhi gate of the Agra Fort. This Tropolia was destroyed in order to create the Agra Fort Railway Statio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Mosques
Mughal or Moghul may refer to: Related to the Mughal Empire * Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries * Mughal dynasty * Mughal emperors * Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia * Mughal architecture * Mughlai cuisine * Mughal painting Other uses * Moghulistan in Central Asia ** Moghol people * Moghul, Iran, a village * Mirza Mughal (1817–1857), a Mughal prince * Fiyaz Mughal, founder of Tell MAMA Tell MAMA (Measuring Anti-Muslim Attacks) is a national project which records and measures anti-Muslim incidents in the United Kingdom. It is modelled on the Jewish Community Security Trust (CST) and like the CST it also provides support for v ... See also * Mogul (other) * Mughal-e-Azam (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosques In Agra
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, including outdoor courtyards. The first mosques were simple places of prayer for Muslims, and may have been open spaces rather than buildings. In the first stage of Islamic architecture, 650-750 CE, early mosques comprised open and closed covered spaces enclosed by walls, often with minarets from which calls to prayer were issued. Mosque buildings typically contain an ornamental niche ('' mihrab'') set into the wall that indicates the direction of Mecca (''qiblah''), ablution facilities. The pulpit ('' minbar''), from which the Friday (jumu'ah) sermon (''khutba'') is delivered, was in earlier times characteristic of the central city mosque, but has since become common in smaller mosques. Mosques typically have segregated spaces for men a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)