|
Human Sexual Response Cycle
The human sexual response cycle is a four-stage model of physiological responses to sexual stimulation, which, in order of their occurrence, are the excitement, plateau, orgasmic, and resolution phases. This physiological response model was first formulated by William H. Masters and Virginia E. Johnson, in their 1966 book ''Human Sexual Response''.Masters & Johnson ''Human Sexual Response'', Bantam, 1981 ; 1st ed. 1966 Since that time, other models regarding human sexual response have been formulated by several scholars who have criticized certain inaccuracies in the human sexual response cycle model. Excitement phase The excitement phase (also known as the arousal phase or initial excitement phase) is the first stage of the human sexual response cycle, which occurs as a result of physical or mental erotic stimuli, such as kissing, making out, fantasizing or viewing erotic images, that leads to sexual arousal. During this stage, the body prepares for sexual intercourse, init ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiological Response
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggering gait, and arcus senilis and arcus juvenilis of the eyes. Indication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigastrium
In anatomy, the epigastrium (or epigastric region) is the upper central region of the abdomen. It is located between the costal margins and the subcostal plane. Pain may be referred to the epigastrium from damage to structures derived from the foregut. Structure The epigastrium is one of the nine regions of the abdomen, along with the right and left hypochondria, right and left lateral regions (lumbar areas or flanks), right and left inguinal regions (or fossae), and the umbilical and pubic regions. It is located between the costal margins and the subcostal plane. During breathing, the diaphragm contracts and flattens, displacing the viscera and producing an outward movement of the upper abdominal wall (epigastric region). It is a convergence of the diaphragm and the abdominals, so that "when both sets of muscles (diaphragm and abdominals) tense, the epigastrium pushes forward". Therefore, the epigastric region is not a muscle nor is it an organ, but it is a zone of activity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Frustration
Sexual frustration is a sense of dissatisfaction stemming from a discrepancy between a person's desired and achieved sexual activity. It may result from physical, mental, emotional, social, and religious or spiritual barriers. It may also derive from not being satisfied during sex, which may be due to issues such as anorgasmia, anaphrodisia, premature ejaculation, delayed ejaculation, erectile dysfunction, or an incompatibility or discrepancy (or self-sensed feeling of discrepancy) in libido. It may also relate to broader existential frustration. Sexual frustration can result from an individual's lacking one or more of the organs needed for achieving sexual release. This may occur when a male is born without a penis or has it removed, or when a female's clitoris is removed for cultural or medical reasons. Historical methods of dealing with sexual frustration have included fasting and the taking of libido suppressants such as anaphrodisiacs (food supplements) or antaphrodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Lubrication
Vaginal lubrication is a naturally produced fluid that lubricates a vagina. Vaginal lubrication is always present, but production increases significantly near ovulation and during sexual arousal in anticipation of sexual intercourse. Vaginal dryness is the condition in which this lubrication is insufficient, and sometimes artificial lubricants are used to augment it. Without sufficient lubrication, sexual intercourse can be painful. The vaginal lining has no glands, and therefore the vagina must rely on other methods of lubrication. Plasma from vaginal walls due to vascular engorgement is considered to be the chief lubrication source, and the Bartholin's glands, located slightly below and to the left and right of the introitus (vaginal opening), also secrete mucus to augment vaginal-wall secretions. Near ovulation, cervical mucus provides additional lubrication. Vaginal discharge Composition Vaginal fluid is slightly acidic and can become more acidic with certain sexua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasocongestion
Vasocongestion, vascular congestion or vascular engorgement is the swelling of bodily tissues caused by increased vascular blood flow and a localized increase in blood pressure. Typical causes of vasocongestion in humans includes menstruation, sexual arousal, REM sleep, strong emotions, illnesses, deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and allergic reactions. Illnesses Menstrual cramps are one of the most common side effects of vasocongestion in adult females. Although pain and discomfort varies among individuals, vasocongestion is an essential part of the shedding of the lining of the uterus. Abnormal vasocongestion during the menstrual cycle can lead to irregular bleeding, severe and debilitating cramps and anemia caused by increased menstrual flow. The temporary vasocongestion of the cheeks of the face is called blushing. It may be caused by the emotions of anger or embarrassment. The illness of rosacea is a chronic vasocongestion condition of the face that primarily affects the cheeks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
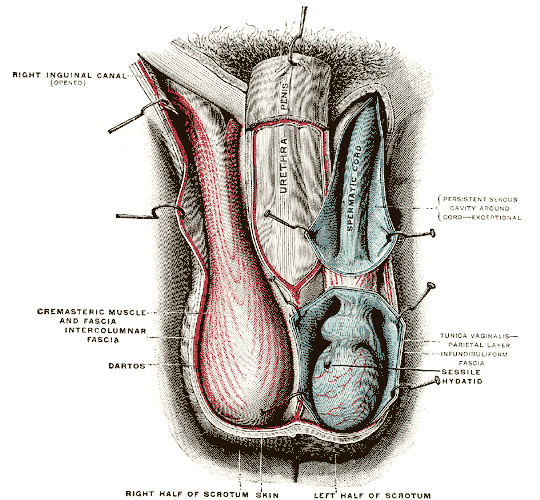
Scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and pampiniform plexus. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. In humans and some other mammals the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperatures. One testis is typically lower than the other to avoid compression in the event of an impact. The scrotum is bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. Topical or locally injected anesthesia is generally used to reduce pain and physiologic stress. It is usually elective, performed as preventive healthcare, a religious rite, or cultural practice. It is also an option for cases of phimosis, other pathologies that do not resolve with other treatments, and chronic urinary tract infections (UTIs). The procedure is contraindicated in cases of certain genital structure abnormalities or poor general health. Circumcision is associated with reduced rates of sexually transmitted infections and urinary tract infections. This includes decreasing the incidence of cancer-causing forms of human papillomavirus (HPV) and significantly reducing HIV transmission among heterosexual men within high ris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineum
The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male, or between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), including the perineal body and surrounding structures. There is some variability in how the boundaries are defined. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone. The word perineum entered English from late Latin via Greek περίναιος ~ περίνεος ''perinaios, perineos'', itself from περίνεος, περίνεοι 'male genitals' and earlier περίς ''perís'' 'penis' through influence from πηρίς ''pērís'' 'scrotum'. The term was originally understood as a purely male body-part with the perineal raphe seen as a continuation of the scrotal septum since masculinization causes the development of a large anogenital distance in men, in comparison to the correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone, whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and comparing it to ellipsoids of known sizes. Another method is to use calip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
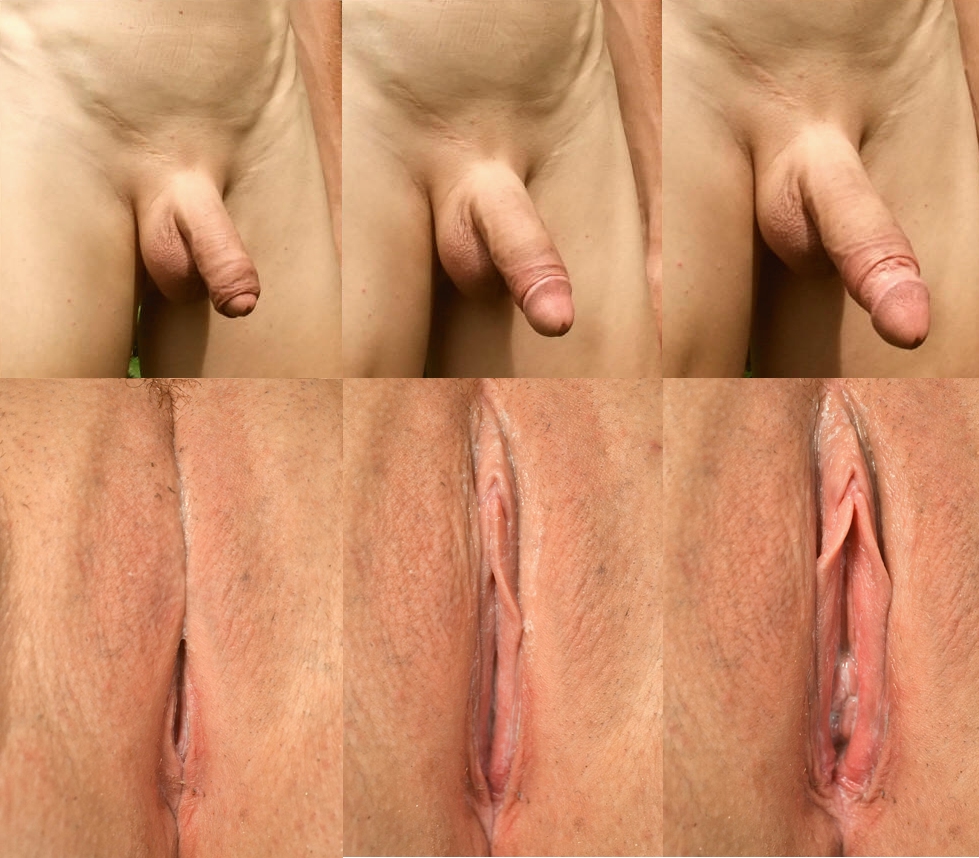
Erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, and endocrine factors, and is often associated with sexual arousal or sexual attraction, although erections can also be spontaneous. The shape, angle, and direction of an erection varies considerably between humans. Physiologically, an erection is required for a male to effect vaginal penetration or sexual intercourse and is triggered by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, causing the levels of nitric oxide (a vasodilator) to rise in the trabecular arteries and smooth muscle of the penis. The arteries dilate causing the corpora cavernosa of the penis (and to a lesser extent the corpus spongiosum) to fill with blood; simultaneously the ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles compress the veins of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
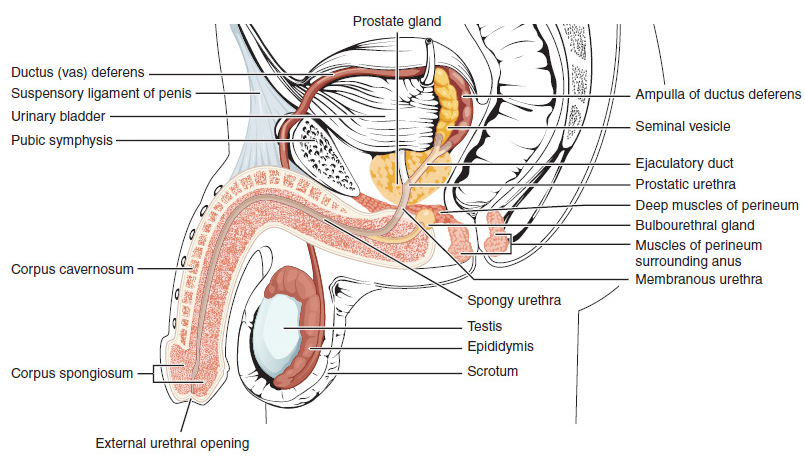
Human Penis
The human penis is an external male intromittent organ that additionally serves as the urinary duct. The main parts are the root (radix); the body (corpus); and the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin and the foreskin (prepuce) covering the glans penis. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue: two corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The human male urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct, and then through the penis. The urethra traverses the corpus spongiosum, and its opening, the meatus (), lies on the tip of the glans penis. It is a passage both for urination and ejaculation of semen (''see'' male reproductive system.) Most of the penis develops from the same embryonic tissue as the clitoris in females. The skin around the penis and the urethra share the same embryonic origin as the labia minora in females. An erection is the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orgasm
Orgasm (from Greek , ; "excitement, swelling") or sexual climax is the sudden discharge of accumulated sexual excitement during the sexual response cycle, resulting in rhythmic, involuntary muscular contractions in the pelvic region characterized by sexual pleasure.Se133–135 for orgasm information, anpage 76for G-spot and vaginal nerve ending information. Experienced by males and females, orgasms are controlled by the involuntary or autonomic nervous system. They are usually associated with involuntary actions, including muscular spasms in multiple areas of the body, a general euphoric sensation and, frequently, body movements and vocalizations. The period after orgasm (known as the refractory period) is typically a relaxing experience, attributed to the release of the neurohormones oxytocin and prolactin as well as endorphins (or "endogenous morphine"). Human orgasms usually result from physical sexual stimulation of the penis in males (typically accompanying ejac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |