|
Human Trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing. The trachea begins to form in the second month of embryo development, becoming longer and more fixed in its position over time. It is epithelium lined with column-shaped cells that have hair-like extensions called cilia, with scattered goblet cells that produce protective mucins. The trachea can be affected by inflammation or infection, usually as a result of a viral illness affecting other part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheal Branches Of Inferior Thyroid Artery
The inferior thyroid artery is an artery in the neck. It arises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and longus colli muscle. It then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and also behind the sympathetic trunk, the middle cervical ganglion resting upon the vessel. Reaching the lower border of the thyroid gland it divides into two branches, which supply the postero-inferior parts of the gland, and Circulatory anastomosis, anastomose with the superior thyroid artery, and with the corresponding artery of the opposite side. Structure The branches of the inferior thyroid artery are the inferior laryngeal, the oesophageal, the tracheal, the ascending cervical and the pharyngeal arteries. The inferior laryngeal artery climbs the trachea to the back part of the larynx under cover of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. It is accompanied by the recurrent nerve, and supplies the muscles and mucous membrane of this p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pair of mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic'' – the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheole
Tracheole (trā'kē-ōl') is a fine respiratory tube of the trachea of an insect or a spider, part of the respiratory system. Tracheoles are about 1 µm in diameter, and they convey oxygen to cells while providing a means for carbon dioxide to escape. Tracheoles branch from the larger tracheae (which can be several mm in diameter) much like capillaries branch from arteries, or twigs from branches of a tree. This increases the surface area for gas exchange in the insect. Areas of intense metabolic activity, such as the digestive tract and flight muscles, have very dense aggregations of tracheoles. Though usually closely associated with cells, tracheoles physically penetrate only the flight muscle cells which have the highest oxygen demands. Unlike the larger tracheae which are derived of ectodermal The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiracle (arthropods)
A spiracle or stigma is the opening in the exoskeletons of insects and some spiders to allow air to enter the trachea. In the respiratory system of insects, the tracheal tubes primarily deliver oxygen directly into the animals' tissues. The spiracles can be opened and closed in an efficient manner to reduce water loss. This is done by contracting closer muscles surrounding the spiracle. In order to open, the muscle relaxes. The closer muscle is controlled by the central nervous system, but can also react to localized chemical stimuli. Several aquatic insects have similar or alternative closing methods to prevent water from entering the trachea. The timing and duration of spiracle closures can affect the respiratory rates of the organism. Spiracles may also be surrounded by hairs to minimize bulk air movement around the opening, and thus minimize water loss. Although all insects have spiracles, only some spiders have them, such as orb weavers and wolf spiders. Ancestrally, spiders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory System Of Insects
An insect's respiratory system is the system with which it introduces respiratory gases to its interior and performs gas exchange. Air enters the respiratory systems of insects through a series of external openings called spiracles. These external openings, which act as muscular valves in some insects, lead to the internal respiratory system, a densely networked array of tubes called tracheae. This network of transverse and longitudinal tracheae equalizes pressure throughout the system. It is responsible for delivering sufficient oxygen (O2) to all cells of the body and for removing carbon dioxide (CO2) that is produced as a waste product of cellular respiration. The respiratory system of insects (and many other arthropods) is separate from the circulatory system. Structure of the spiracle Insects have spiracles on their exoskeletons to allow air to enter the trachea. In insects, the tracheal tubes primarily deliver oxygen directly into the insects' tissues. The spiracles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms and cnidarians. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 50 μm (0.002 in) rotifers to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the invertebrates paraphyletic, so the term has little meaning in taxonomy. Etymology The word "invertebrate" comes from the Latin word ''vertebra'', whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Patients are generally anesthetized beforehand. Examples include tracheal intubation, and the balloon tamponade with a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube (a tube into the gastrointestinal tract). Examples * Catheterization * Nasogastric intubation * Tracheal intubation Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic catheter, tube into the vertebrate trachea, trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer ce ... References Airway management Emergency medical procedures Medical equipment Routes of administration {{surgery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheal Tube
A tracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the trachea for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent airway and to ensure the adequate exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Many different types of tracheal tubes are available, suited for different specific applications: * An endotracheal tube is a specific type of tracheal tube that is nearly always inserted through the mouth (orotracheal) or nose (nasotracheal). * A tracheostomy tube is another type of tracheal tube; this curved metal or plastic tube may be inserted into a tracheostomy stoma (following a tracheotomy) to maintain a patent lumen. * A tracheal button is a rigid plastic cannula about 1 inch in length that can be placed into the tracheostomy after removal of a tracheostomy tube to maintain patency of the lumen. History Portex Medical (England and France) produced the first cuff-less plastic 'Ivory' endotracheal tubes. Ivan Magill later added a cuff (these were glued on by hand to mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
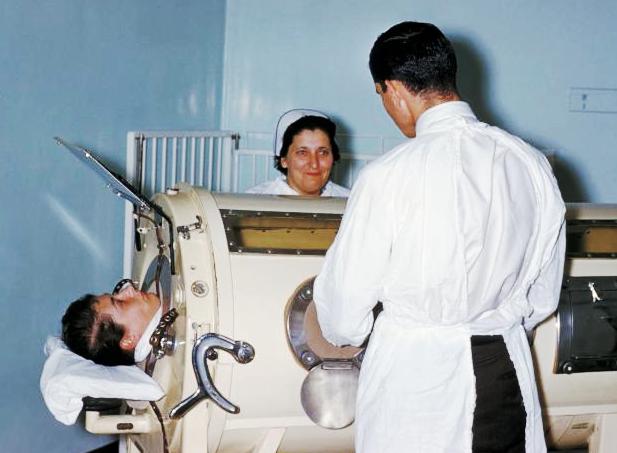
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheostomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the Vertebrate trachea, trachea (windpipe). The resulting Stoma (medicine), stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheal tube or tracheostomy tube to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth. Etymology and terminology The etymology of the word ''tracheotomy'' comes from two Greek language, Greek words: the root (linguistics), root ''tom-'' (from Ancient Greek, Greek τομή ''tomḗ'') meaning "to cut", and the word ''trachea'' (from Greek τραχεία ''tracheía''). The word ''tracheostomy'', including the root ''stom-'' (from Greek στόμα ''stóma'') meaning "mouth," refers to the making of a semi-permanent or permanent opening, and to the opening itself. Some sources offer differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croup
Croup, also known as laryngotracheobronchitis, is a type of respiratory infection that is usually caused by a virus. The infection leads to swelling inside the trachea, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classic symptoms of "barking/brassy" cough, inspiratory stridor and a hoarse voice. Fever and runny nose may also be present. These symptoms may be mild, moderate, or severe. Often it starts or is worse at night and normally lasts one to two days. Croup can be caused by a number of viruses including parainfluenza and influenza virus. Rarely is it due to a bacterial infection. Croup is typically diagnosed based on signs and symptoms after potentially more severe causes, such as epiglottitis or an airway foreign body, have been ruled out. Further investigations, such as blood tests, X-rays and cultures, are usually not needed. Many cases of croup are preventable by immunization for influenza and diphtheria. Most cases of croup are mild and the child can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |