|
Huaso
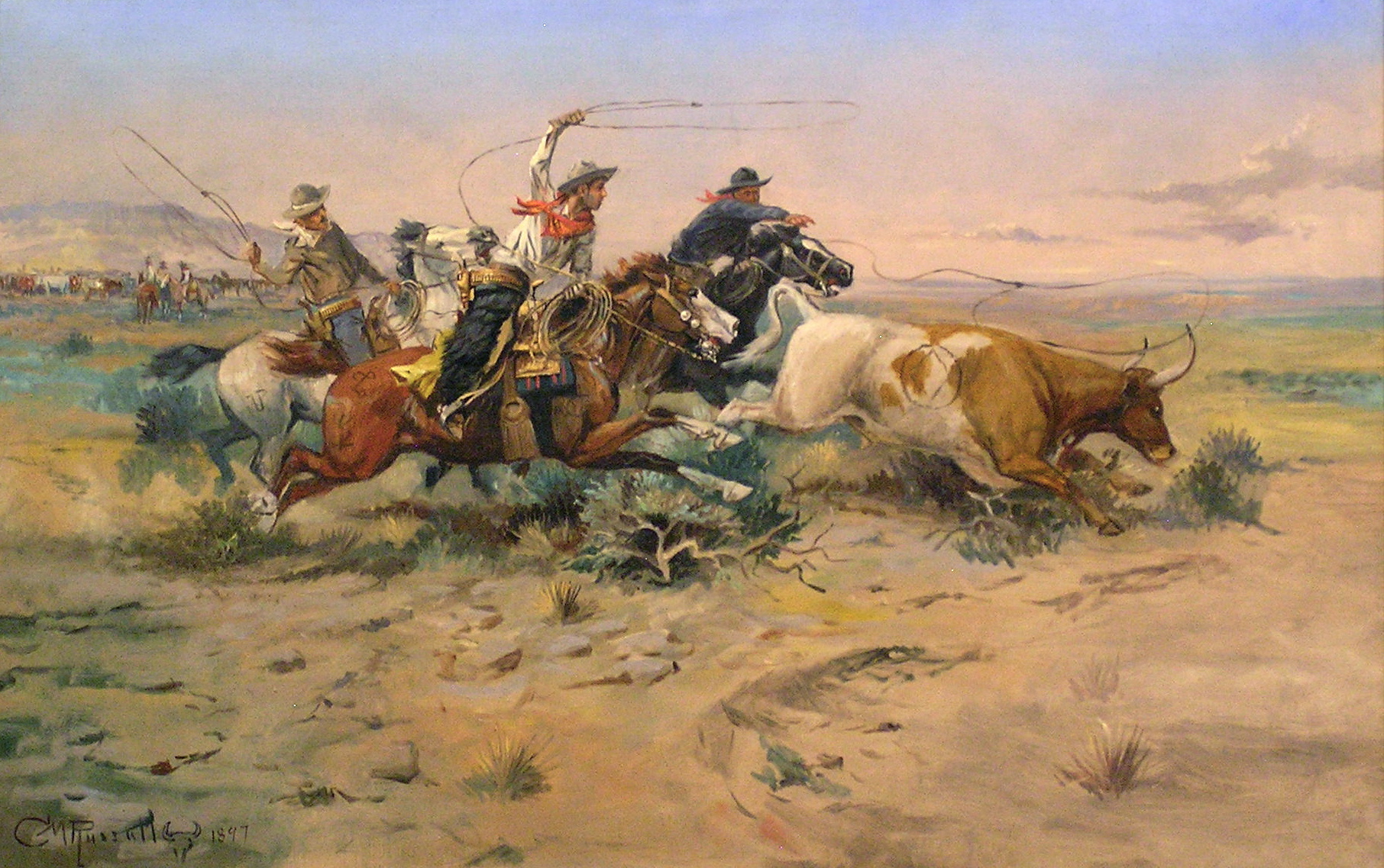
A huaso () is a Chilean countryman and skilled horseman, similar to the American cowboy, the Mexican charro (and its northern equivalent, the vaquero), the gaucho of Argentina, Uruguay and Rio Grande Do Sul, and the Australian stockman. A female ''huaso'' is called a huasa, although the term china is far more commonly used for his wife or sweetheart, whose dress can be seen in cueca dancing. Huasos are found all over Central and Southern Chile while the Aysén and Magallanes Region sheep raisers are gauchos. The major difference between the huaso and the gaucho is that huasos are involved in farming as well as cattle herding. Huasos are generally found in Chile's central valley. They ride horses and typically wear a straw hat called a '' chupalla''. They also wear a poncho—called a ''manta'' or a '' chamanto'' (although this was originally reserved to land owners, as it is much more expensive)—over a short Andalusian waist jacket, as well as tooled leather legging o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Chile
The culture of Chile reflects the population and the geographic isolation of the country in relation to the rest of South America. Since colonial times, the Chilean culture has been a mix of Spanish colonial elements with elements of indigenous (mostly Mapuche) culture, as well as that of other immigrant cultures. The Huasos of Central Chile and their native or folk music and dance are central to Chilean folk culture. Even though the folk traditions of Central Chile are central to Chilean cultural and national identity, Chile is both geographically and culturally diverse with both the North and the South having their own folk music and dance due to different indigenous peoples and different immigrant groups settling there. Additionally, while some regions of Chile have very strong indigenous heritage, such as Araucanía Region, Easter Island, and Arica y Parinacota Region, some regions lack considerable indigenous communities and a few other regions have noteworthy non-Spanish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaucho
A gaucho () or gaúcho () is a skilled horseman, reputed to be brave and unruly. The figure of the gaucho is a folk symbol of Argentina, Uruguay, Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil, and the south of Chilean Patagonia. Gauchos became greatly admired and renowned in legend, folklore, and literature and became an important part of their regional cultural tradition. Beginning late in the 19th century, after the heyday of the gauchos, they were celebrated by South American writers. The gaucho in some respects resembled members of other nineteenth century rural, horse-based cultures such as the North American cowboy ( in Spanish), of Central Chile, the Peruvian or , the Venezuelan and Colombian , the Ecuadorian , the Hawaiian , the Mexican , and the Portuguese . According to the , in its historical sense a gaucho was a "mestizo who, in the 18th and 19th centuries, inhabited Argentina, Uruguay, and Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil, and was a migratory horseman, and adept in cattle work". In Arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cueca
Cueca () is a family of musical styles and associated dances from Chile, Argentina, and Bolivia. In Chile, the cueca holds the status of national dance, where it was officially declared as such by the Pinochet dictatorship on September 18, 1979. Origins While cueca's origins are not clearly defined, it is considered to have mostly European Spanish and arguably indigenous influences. The most widespread version of its origins relates it with the zamacueca which arose in Peru as a variation of Spanish Fandango dancing with '' criollo''. The dance is then thought to have passed to Chile and Bolivia, where its name was shortened and where it continued to evolve. Due to the dance's popularity in the region, the Peruvian evolution of the zamacueca was nicknamed "la chilena", "the Chilean", due to similarities between the dances. Later, after the Pacific War, the term marinera, in honor of Peru's naval combatants and because of hostile attitude towards Chile, was used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowboy
A cowboy is an animal herder who tends cattle on ranches in North America, traditionally on horseback, and often performs a multitude of other ranch-related tasks. The historic American cowboy of the late 19th century arose from the ''vaquero'' traditions of northern Mexico and became a figure of special significance and legend.Malone, J., p. 1. A subtype, called a wrangler, specifically tends the horses used to work cattle. In addition to ranch work, some cowboys work for or participate in rodeos. Cowgirls, first defined as such in the late 19th century, had a less-well documented historical role, but in the modern world work at identical tasks and have obtained considerable respect for their achievements. Cattle handlers in many other parts of the world, particularly South America and Australia, perform work similar to the cowboy. The cowboy has deep historic roots tracing back to Spain and the earliest European settlers of the Americas. Over the centuries, difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palena Province
Palena Province ( es, Provincia de Palena) is the southernmost administrative area in Chile's Los Lagos Region Los Lagos Region, Los Lagos (X). The area is also called Continental Chiloe or Northern Patagonia, as geographers consider the Palena Province to be the starting point of Chilean Patagonia which extends south from Palena all the way to Tierra del Fuego. Palena Province is remote, beautiful, and difficult to access. In fact, Palena is one of the most sparsely populated provinces in the country and features a stunning geography characterized by steep fjords, wild rivers, hot springs, and numerous snow-capped volcanos. Chile's Austral Highway (Carretera Austral) is not continuous through the jagged geography of Palena Province. Motorists accessing the area by car are required to take two ferries across fjords to cross the province. Historically, Chaiten was the provincial capital. Due to the eruption of Chaitén Volcano and the subsequent destruction of that town, Futaleufú ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chupalla
The chupalla () is a traditional Chilean horseman's hat made of straw. Many people in rural areas of Central Chile use it as well. In addition, it is often used when dancing the cueca (a Chilean folk dance) and during Chilean rodeos. The name chupalla comes from ''achupalla'', a local name given to a bromelia plant that was used to make these hats. Today, chupallas are made of various types of straw, including rice and wheat. The phrase ''"por la chupalla"'' may be heard frequently in Chile. It is an interjection An interjection is a word or expression that occurs as an utterance on its own and expresses a spontaneous feeling or reaction. It is a diverse category, encompassing many different parts of speech, such as exclamations ''(ouch!'', ''wow!''), curse ... which, loosely translated, means "what the heck!". The chupalla has a flat top and a perfectly circular rim. References Hats Rider apparel Chilean culture Chilean clothing Rodeo in Chile {{Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poncho
A poncho (; qu, punchu; arn, pontro; "blanket", "woolen fabric") is an outer garment designed to keep the body warm. A rain poncho is made from a watertight material designed to keep the body dry from the rain. Ponchos have been used by the Native American peoples of the Andes, Valley of Mexico and Patagonia since pre-Hispanic times, from places now under the territory of Mexico, Ecuador, Colombia, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, and Argentina and are now considered typical American garments. Types In its simplest form, the poncho is essentially a single large sheet of fabric with an opening in the center for the head. It often has an extra piece of fabric serving as a hood. Rainproof ponchos are normally fitted with fasteners to close the sides once the poncho is draped over the body, with openings provided for the arms. Many ponchos have hoods attached to ward off wind and rain. Alternative ponchos are now designed as fashion items. They are the same shape but of different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamanto
A ''chamanto'' (Mapudungun ''chamall'', woolen fabric) is a traditional decorative garment from central Chile, similar to a poncho and woven in silk thread and wool. Its entire contour is finished with ribbon edging. Traditionally, Chilean festive ponchos incorporate colors such as grey, brown, red, black, and white. The difference between a ''chamanto'' and other ponchos is their reversibility, as both sides — one light, one dark — are fully finished. Traditionally, the dark side of the poncho is used during the day, while its light side is mostly worn at night. The ''chamantos'' gained world attention when they were worn by the 21 leaders of the Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation during the 2004 summit's official photo. The making of a ''chamanto'' demands great diligence, because of the exquisiteness involved in the weaving of the silk and wool, plus the intricacy of the design sketched by crossing the threads. The figures embellishing the ''chamantos'' include '' copihues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aysén Region
The Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region ( es, Región de Aysén, , '), often shortened to Aysén Region or Aisén,Examples of name usage1, official regional government site refers to the region as "Región de Aysén"., Chile's official meteorological agency refers to the region as "Región de Aisén".3 Chilean government official website refers of Pilar Cuevas Mardones as intendant of "Región de Aysén" .4 Chile's Ministry of Public Works calls the region "Región de Aysén" in the title of their 2011 report on that region.5, Corporación Nacional Forestal, a government agency refers to the region as "Región de Aysén" in their homepage. Here is some evidence of the short name use in English:I ''The Guardian'' reports on the 2012 Aysén protest.II ''Santiago Times'', a local English language newspaper use "Aysén Region" in a note referring to the same protest.III''Santiago Times'' again. *Vscientific paper in '' Journal of Hospital Infection'' referring to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
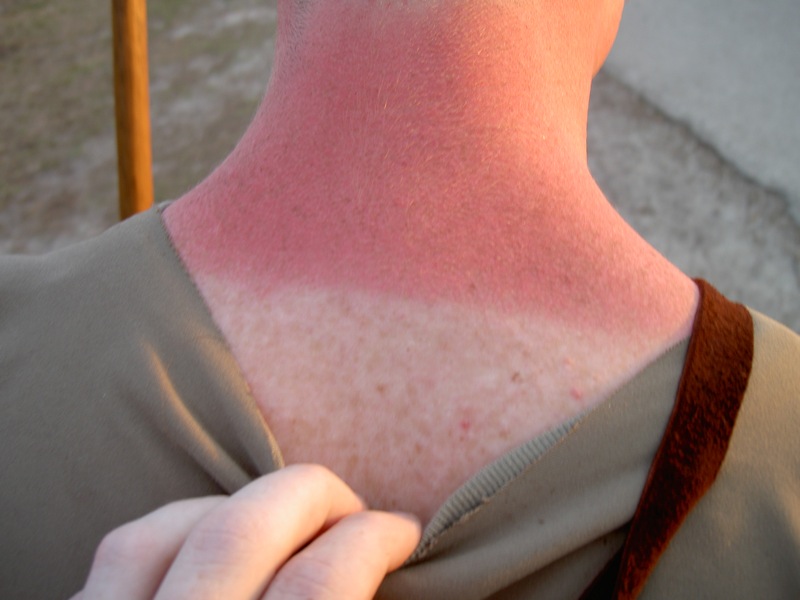
Redneck
''Redneck'' is a derogatory term chiefly, but not exclusively, applied to white Americans perceived to be crass and unsophisticated, closely associated with rural whites of the Southern United States.Harold Wentworth, and Stuart Berg Flexner, ''Dictionary of American Slang'' (1975) p. 424. Its meaning possibly stems from the sunburn found on farmers' necks dating back to the late 19th century. Its modern usage is similar in meaning to ''cracker'' (especially regarding Texas, Georgia, and Florida), '' hillbilly'' (especially regarding Appalachia and the Ozarks), and '' white trash'' (but without the last term's suggestions of immorality). In Britain, the ''Cambridge Dictionary'' definition states: "A poor, white person without education, esp. one living in the countryside in the southern US, who is believed to have prejudiced ideas and beliefs. This word is usually considered offensive." People from the white South sometimes jocularly call themselves "rednecks" as insider humor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |