|
Hua Phan Tang Ha Tang Hok
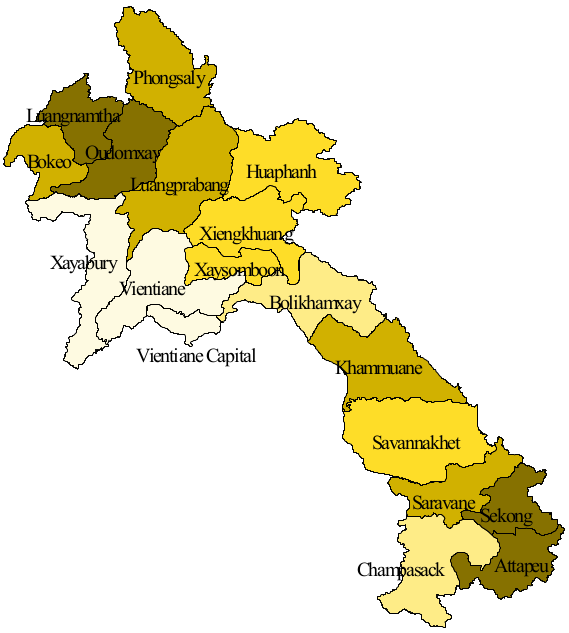
Houaphanh province ( Laotian: ຫົວພັນ ; Romanization of Lao: ''Houaphan'') is a province in eastern Laos. Its capital is Xam Neua. Houaphanh province covers an area of . The province is bordered by Vietnam to the north, east, and southeast, Xiangkhouang province to the south and southwest, and Luang Prabang province to the west. The terrain is rugged, with dense, forested mountains forming much of the province, particularly on the western side. The main road running through the province is Route 6. The principal rivers are the Nam Ma, which flows from and into Vietnam, passing the village of Ban Muang-Et, and the Nam Sam, on which the towns of Sam Neua and Sam Tai lie. The province is the home to the Viengxay caves, an extensive network of caves used by the Pathet Lao, and the Hintang Archaeological Park, one of the most important pre-historic sites in northern Laos, dotted with standing megaliths. Houaphanh is one of the poorest areas of Laos, but has dramatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Laos
Laos, officially the ''Lao People's Democratic Republic'', is divided into 17 provinces ( Lao ແຂວງ, , , or ) and one prefecture, the Vientiane capital city municipality (ນະຄອນຫຼວງ, nakhon louang, or ''Na Kone Luang Vientiane''). The special administrative zone (ເຂດພິເສດ, ''khet phiset''), Xaisomboun, created in 1994, was dissolved on 13 January 2006. In 2013, parts of the former special administrative zone was reestablished as Xaisomboun province. Provinces and prefectures of Laos Population The population of each province in 2015 is given in the census data. History In 1989 Vientiane prefecture was split from Vientiane province and the capital of Vientiane province moved from Vientiane to Muang Phôn-Hông. In 1994 Xaisômboun khetphiset (special region) was formed from parts of the Bolikhamxai, Vientiane, and Xiangkhoang provinces. In 2006 Xaisomboun special region was dissolved and the Longsan, Xaysomboun, Phun, and Hom dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-historic
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nôy
Chao N√¥y (also spelled Noy or Noi, lo, ‡ªÄ‡∫à‡∫ª‡ªâ‡∫≤‡∫ô‡ªâ‡∫≠‡∫ç, th, ‡πć∏à‡πâ‡∏≤‡∏ô‡πâ‡∏≠‡∏¢, ?–1829), also known as Chao Southaka Souvanna Koumar ( th, ‡πć∏à‡πâ‡∏≤‡∏™‡∏∏‡∏ó‡∏ò‡∏Ň∏∞‡∏™‡∏∏‡∏߇∏£‡∏£‡∏ô‡∏∞‡∏Ň∏∏‡∏°‡∏≤‡∏£), was the prince ruler of Muang Phuan from 1803 to 1831. In Vietnamese record, he was called ''Chi√™u N·ªôi'' (Êò≠ÂÖß). N√¥y was a nephew of Chao Somphou. A power struggle happened after the death of Chao Somphou in 1803, N√¥y fled to Tr√† L√¢n (Ëå∂ÈÑ∞, present-day T∆∞∆°ng D∆∞∆°ng, Vietnam). At Vientiane's request, he was sent back to Muang Phuan to succeed the throne.'' Qu·ªëc Tri·ªÅu ch√≠nh bi√™n to√°t y·∫øu'', vol. 2 It proved that N√¥y was an authoritarian ruler. During his reign, he increased taxes in order to spend more on his court and palace. In 1814, he brutely put down a Khmu revolt. In 1823, Noy was accused of by a half-brother of seeking independence. He was summoned to Vientiane to account for his oppressive actions during 1814, and put ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lao Rebellion (1826–1828)
The Lao Rebellion of 1826–1828 (also known as Anouvong's Rebellion or the Vientiane-Siam War) was an attempt by King Anouvong (Xaiya Sethathirath V) of the Kingdom of Vientiane to end the suzerainty of Siam and recreate the former kingdom of Lan Xang. In January 1827 the Lao armies of the kingdoms of Vientiane and Champasak moved south and west across the Khorat Plateau, advancing as far as Saraburi, just three days march from the Siamese capitol of Bangkok. The Siamese mounted a counterattack to the north and east, forcing the Lao forces to retreat and ultimately taking the capital of Vientiane. Anouvong failed in both his attempt to resist Siamese encroachment, and to check the further political fragmentation among the Lao. The kingdom of Vientiane was abolished, its population was forcibly moved to Siam, and its former territories fell under the direct control of Siamese provincial administration. The kingdoms of Champasak and Lan Na were drawn more closely into the Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Vientiane
Kingdom of Vientiane was formed in 1707 as a result of the split of the Kingdom of Lan Xang. The kingdom was a Burmese vassal from 1765 to 1824. It then became a Siamese vassal until 1828 when it was annexed by Siam. History In 1779, under the reign of King Setthathirath II of Lan Xang, Kitsarat, an heir of Sourigna Vongsa, declared separation of Luang Prabang. He marched on Vientiane to attack Setthathirath. King Setthathirath II turned to Ayutthaya for help. The Siamese army helped defend Vientiane but cannot stop Kitsarat to form his own kingdom. Kitsarat crowned the king in 1707, creating the Kingdom of Luang Phrabang,converting Lan Xang into the Kingdom of Vientiane. The kingdoms of Champasak and Muang Phuan also seceded during the following years. In 1773, Vientiane was attacked by Luang Prabang forces. King Ong Bun contacted the Konbaung dynasty for help, turning Vientiane into a Burmese vassal. This angered the Thonburi court. After the Burmese-Siamese War of 1775 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguy·ªÖn Dynasty
The Nguyễn dynasty (chữ Nôm: 茹阮, vi, Nhà Nguyễn; chữ Hán: 阮朝, vi, Nguyễn triều) was the last Vietnamese dynasty, which ruled the unified Vietnamese state largely independently from 1802 to 1883. During its existence, the empire expanded into modern-day southern Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos through a continuation of the centuries-long Nam tiến and Siamese–Vietnamese wars. After 1883, the Nguyễn emperors ruled nominally as heads of state of the French protectorates of Annam and Tonkin until the final months of WWII; they later nominally ruled over the Empire of Vietnam until the August Revolution. The House of Nguyễn Phúc, Nguyễn Phúc family established feudal rule over large amounts of territory as the Nguyễn lords by the 16th century before defeating the Tây Sơn dynasty and establishing their own imperial rule in the 19th century. The dynastic rule began with Gia Long ascending the throne in 1802, after ending the previous Tây Sơn d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
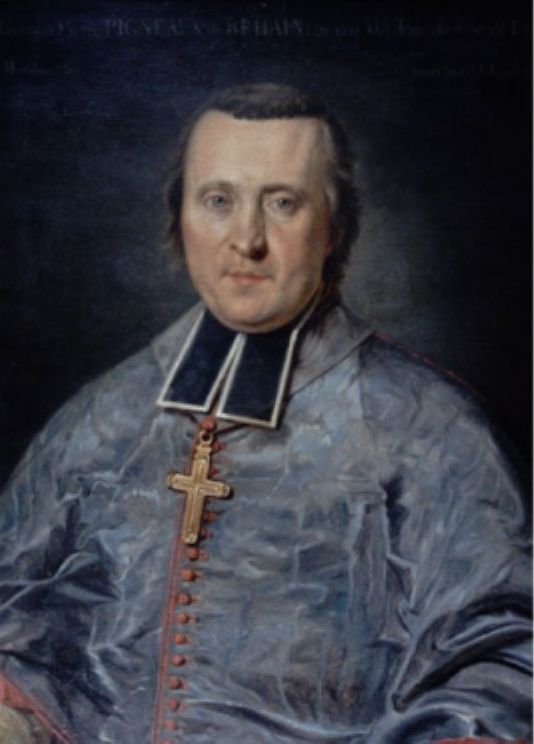
Gia Long
Gia Long ( (''North''), ('' South''); 8 February 1762 – 3 February 1820), born Nguyễn Phúc Ánh (阮福暎) or Nguyễn Ánh, was the founding emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty, the last dynasty of Vietnam. His dynasty would rule the unified territories that constitute modern-day Vietnam until 1945. A nephew of the last Nguyễn lord who ruled over south Vietnam, Nguyễn Ánh was forced into hiding in 1777 as a fifteen-year-old when his family was slain in the Tây Sơn revolt. After several changes of fortune in which his loyalists regained and again lost Saigon, he befriended the French Catholic Bishop Pierre Pigneau de Behaine. Pigneau championed his cause to the French government and managed to recruit volunteers when that fell through to help Nguyễn Ánh regain the throne. From 1789, Nguyễn Ánh was once again in the ascendancy and began his northward march to defeat the Tây Sơn, reaching the border with China by 1802, which had previously been under the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lê Duy Mật
L√™ Duy M·∫≠t ( vi-hantu, ȪéÁ∂≠, 1738–1767) was a Vietnamese rebel leader who was active in the 18th century. M·∫≠t was a son of Emperor L√™ D·ª• T√¥ng. In 1738, he planned a plot against the Tr·ªãnh lord together with two princes, his brother L√™ Duy Qu√Ω and L√™ Duy Ch√∫c (son of L√™ Hy T√¥ng), but failed. They had to flee, and hid somewhere in Thanh H√≥a.''Vi·ªát Nam s·ª≠ l∆∞·ª£c'', Quy·ªÉn 2, Ch∆∞∆°ng 5 In 1740, M·∫≠t launched a rebellion against the Tr·ªãnh lords in Thanh H√≥a. He attacked H∆∞ng H√≥a and S∆°n T√¢y. He was defeated by the Tr·ªãnh army, retreated to Ngh·ªá An, then to Muang Phuan, and occupied Tr√¨nh Quang Mountain as his base area. In 1764, he sought aid from Nguy·ªÖn Ph√∫c Kho√°t, but was refused because the Nguy·ªÖn lords did not want to engage in conflict with the Tr·ªãnh lords. In 1767, Tr·ªãnh Doanh died, and his son Tr·ªãnh S√¢m succeeded him as the head of the Trinh lords. Hearing the news, M·∫≠t attacked Thanh Ch∆∞∆°ng and H∆∞∆°ng S∆°n, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hua Phan Tang Ha Tang Hok
Houaphanh province ( Laotian: ຫົວພັນ ; Romanization of Lao: ''Houaphan'') is a province in eastern Laos. Its capital is Xam Neua. Houaphanh province covers an area of . The province is bordered by Vietnam to the north, east, and southeast, Xiangkhouang province to the south and southwest, and Luang Prabang province to the west. The terrain is rugged, with dense, forested mountains forming much of the province, particularly on the western side. The main road running through the province is Route 6. The principal rivers are the Nam Ma, which flows from and into Vietnam, passing the village of Ban Muang-Et, and the Nam Sam, on which the towns of Sam Neua and Sam Tai lie. The province is the home to the Viengxay caves, an extensive network of caves used by the Pathet Lao, and the Hintang Archaeological Park, one of the most important pre-historic sites in northern Laos, dotted with standing megaliths. Houaphanh is one of the poorest areas of Laos, but has dramatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Đại Việt
Đại Việt (, ; literally Great Việt), often known as Annam ( vi, An Nam, Chữ Hán: 安南), was a monarchy in eastern Mainland Southeast Asia from the 10th century AD to the early 19th century, centered around the region of present-day Hanoi, Northern Vietnam. Its early name, Đại Cồ Việt,( Hán tự: 大瞿越) was established in 968 by Vietnamese ruler Đinh Bộ Lĩnh after he ended the Anarchy of the 12 Warlords, until the beginning of the reign of Lý Thánh Tông (r. 1054–1072), the third emperor of the Lý dynasty. Đại Việt lasted until the reign of Gia Long (r. 1802–1820), the first emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty, when the name was changed to Việt Nam. Đại Việt's history is divided into the rule of eight dynasties: Đinh (968–980), Early Lê (980–1009), Lý (1009–1226), Trần (1226–1400), Hồ (1400–1407), and Later Lê (1428–1789); the Mạc dynasty (1527–1677); and the brief Tây Sơn dynasty (1778–1802). It was bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)



