|
Hrušica (plateau) , modern traffic including the railroad and the freeway bypass Hrušica. Hrušica was the location of an ancient Roman Fortress called Ad Pirum, which was part of the Hrušica (; German: ''Birnbaumer Wald'' iterally, 'pear tree forest' Italian: ''Selva di Piro'') is a plateau at the northern end of the Postojna Gate. The plateau can be viewed as the end or extension of the Trnovo Forest Plateau (), and to the west is Mount Nanos. The limestone plateau reaches an elevation of 1,080 m, while the road crosses it at 883 m. Because the Postojna Gate is crossed at a lower point of 606 m at nearby Postojna Postojna (; , ) is a town in the traditional region of Inner Carniola, from Trieste, in southwestern Slovenia. It is the seat of the Municipality of Postojna. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RK 0707 1702 Nanos Planote
RK may refer to: Science and technology * Radial keratotomy, a surgical procedure on the eye * Rhodopsin kinase, an enzyme * r/K selection theory, in biology, relating to the trade-off between quantity and quality of offspring * Runge–Kutta methods, in numerical analysis Airlines * Royal Khmer Airlines (former IATA code: RK), ceased operations 2007 * R Airlines (former IATA code: RK), ceased operations 2018 * Ryanair UK (IATA code: RK), UK based subsidiary airline of Ryanair Other uses * Raising Kaine, a defunct Virginia political blog * Reichskommissariat, a historical Nazi territorial division * Rangkasbitung railway station, station code RK * Ridwan Kamil, former governor of West Java province since 2018-2023 See also * RK (), Finnish assault rifles; for example RK 62 * Republic of Korea (ROK) * Republic of Kazakhstan Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postojna Gate
The Postojna Gate, less often the Postojna Gap (), named after the local town of Postojna, is a major mountain pass of the Dinaric Alps. It lies in southwestern Slovenia, between the Hrušica Plateau to the north and the Javornik Hills to the south, at an elevation of . It formed due to tectonic subsidence and fluvial erosion by the Pivka River, which in the Pliocene flew superficially in this section. The terrain is significantly karstified. This relatively wide pass enables for the easiest passage from northeastern Italy and northwestern Adriatic Sea to the Pannonian Plain, and had a very important strategic role in the past. Today, a rail line and the Slovenian A1 freeway traverse it. History The gate was used by a section of the Amber Road that connected the Baltic lands with the Adriatic. It has been proposed that the voyage of the Argonauts is based on the possibility to travel the Danube, the Sava, and the Ljubljanica rivers upstream, cross the Postojna Gate, and come to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trnovo Forest Plateau
The Trnovo Forest Plateau () is a karst plateau that constitutes the extreme northwest end of the Dinaric Alps.Perko, Drago, & Milan Orožen Adamič. 1998. ''Slovenija: pokrajine in ljudje''. Ljubljana: Mladinska knjiga, p. 324. The Trnovo Forest Plateau has a karst character, without surface watercourses and broken up by closed valleys, outcroppings, hills, caves, shafts, and smaller karst features: solution pans, rills, karrens, and other features. Significant karst features include ice caves. The vegetation inversion at Big Paradana Ice Cave () in the eastern part of the plateau, measuring by , is a ''locus classicus'' and in the past ice was harvested from it and exported via Gorizia and Trieste to Egypt. The Trnovo Forest Plateau has three nature reserves: * Big Paradana Ice Cave * Golak Peaks () and Spruce Valley (, a karst depression) * The Smrečje forest reserve The southern ridge of the Trnovo Forest Plateau is Čaven. Terrain The influence of tectonic activity is v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanos, Slovenia
Nanos (; ) is a karst limestone plateau at the eastern border of the Inner Carniola in southwestern Slovenia. Geography The plateau is about wide and long in the northern extension of the Dinaric Alps. The highest point of the plateau is Dry Peak (, ). The plateau is traversed by the Slovenian Mountain Hiking Trail, Slovene Mountain Trail, the oldest interconnecting trail in Slovenia. The most popular destination on Nanos and part of the trail is Pleša Peak () with the Vojko Lodge (, named for the Slovene Partisans, Slovene Partisan Janko Premrl, a.k.a. Vojko) below its summit. In 1987, the southern and western slopes of Nanos were declared a Nature reserve, regional park with an area of . History In Antiquity, Nanos was known as ''Ocra''. Strabo reckoned it the last peak of the Alps. In the 1st century, the pass at Nanos was an important route for civilian and military traffic from Trieste (Tergeste) to Ljubljana (Emona) and beyond to Carnuntum at the Danube. It lost its impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postojna
Postojna (; , ) is a town in the traditional region of Inner Carniola, from Trieste, in southwestern Slovenia. It is the seat of the Municipality of Postojna.Postojna municipal site It includes the hamlet of Ravbarkomanda (sometimes also spelled ''Ravberkomanda'', ) to the northeast. History The area is known to have been populated since the era due to the discovery of a cave settlement near the town of Postojna called Betal Rock Shelter (). The town lies on the Pivka River. Written sources ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad Pirum
''Ad Pirum'' was a Roman fortress active during the time of the late Roman Empire. It is located on the Hrušica Plateau in southwestern Slovenia, in the hamlet of Hrušica in Podkraj. It was built in the 320s. Structure and function Excavations reveal the fortress to have an oval shape, in length, in width, and with a wall at a height of 6–8 m and a thickness of about 2.7 m; the wall towers were 10 m high. This structure represented a major fort of the Claustra Alpium Iuliarum, a network of forts and walls to securing Roman Italy from eastern invasions, including the road between Roman Italy and Pannonia Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It .... It was typically manned by 500 soldiers. Further reading * References External links Ad Pirum (Hrušica) on DEDI.s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
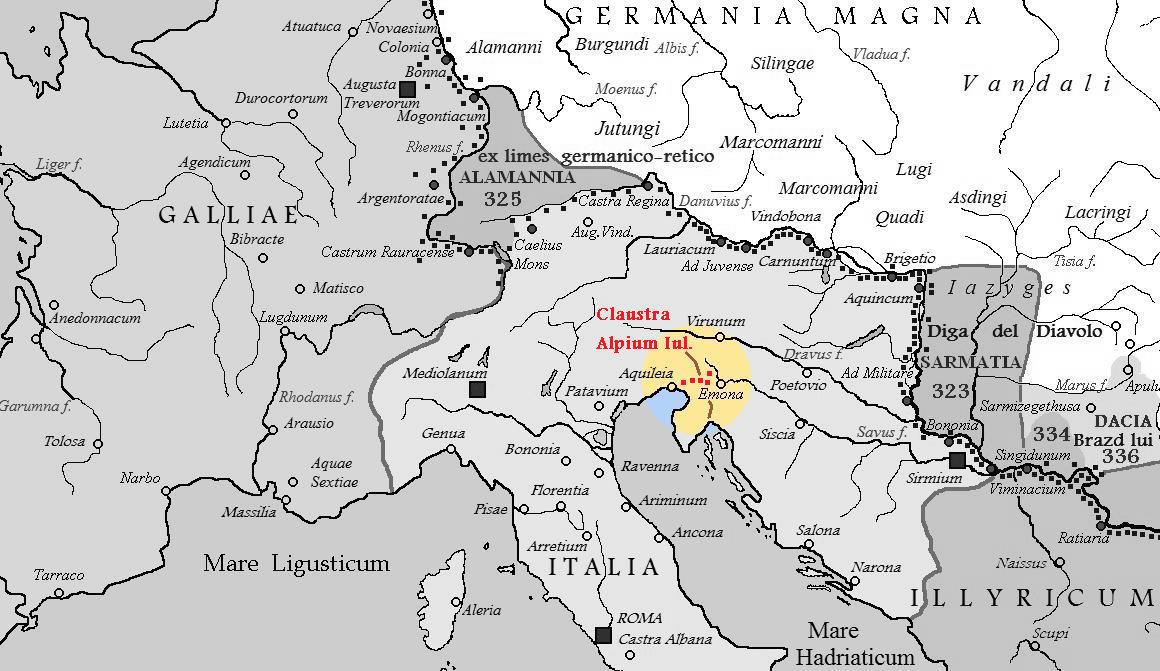
Claustra Alpium Iuliarum
(Latin for 'Barrier of the Julian Alps'; hereby, the term Julian Alps refers to the wider mountainous and hilly region from the Julian Alps to the Kvarner Gulf) was a defense system within the Roman Empire between Italia and Pannonia that protected Italy from possible invasions from the East. It secured the Postojna Gate, the land link between the eastern and western part of the empire, and thus the Claustra represented an inner border defense of the empire. Unlike a linear rampart, the Claustra consisted of a series of interconnected fortifications with its center at Castra ad Fluvium Frigidum (in the area of today's town of Ajdovščina, the Vipava Valley); other important fortresses were '' Ad Pirum'' on today's Hrušica Plateau and '' Tarsatica'', now a part of the city of Rijeka. They had been governed from the town of Aquileia. Development In the year 6 AD the Great Illyrian Revolt took place threatening the Roman heartland. Subsequently, in order to protect Italy, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |