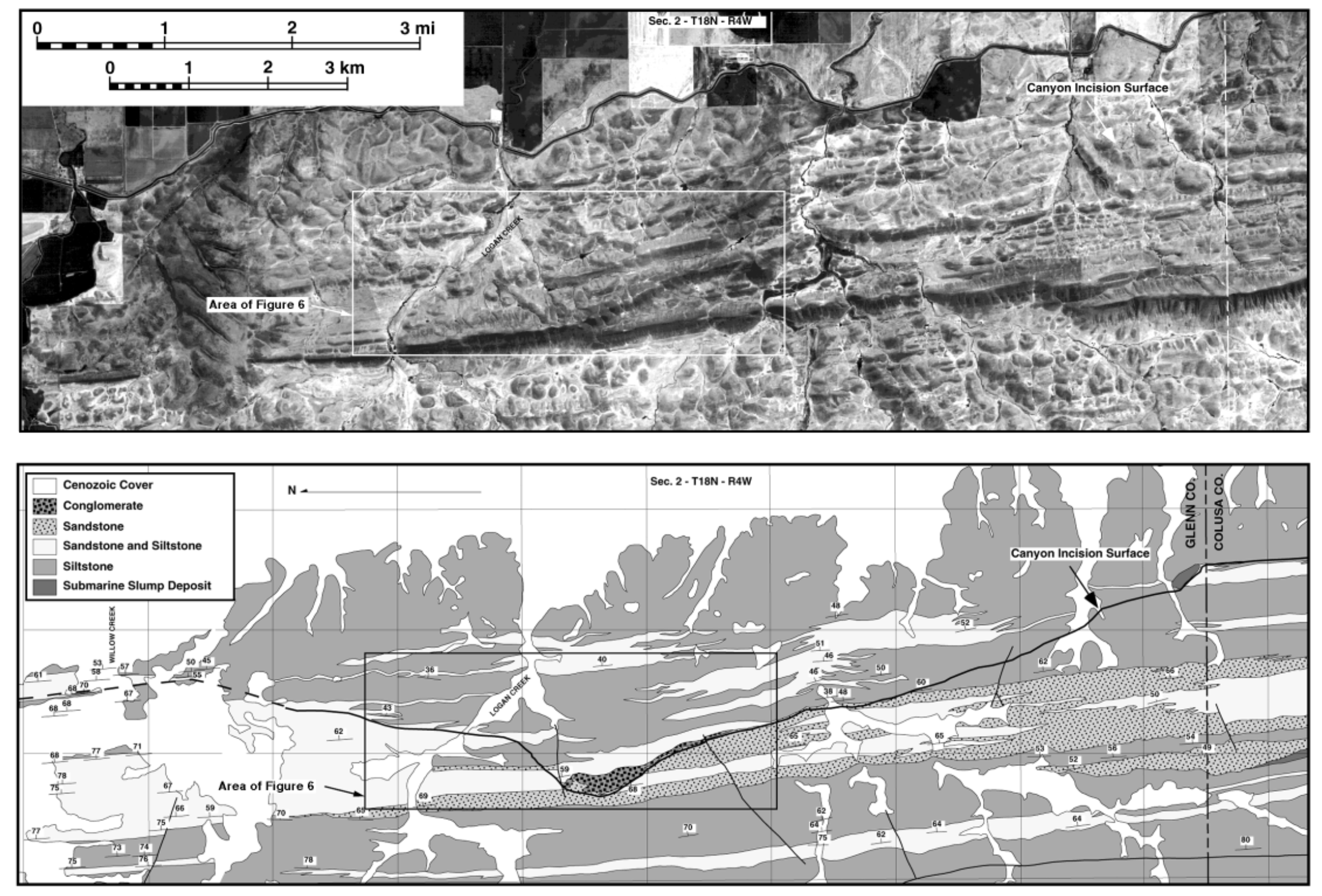
|
Howell Mountains
The Howell Mountains, which are also known as the Mt. George Range, are one of the California Coast Ranges. They divide the Suisun Valley on the east side, from Napa Valley on the west. Historically the southern part of the range has been referred to as both the Sierra de Suscol (Suscol Hills) and as the Sierra de Napa (Napa Hills). Geography The Howell Mountains begin at Sulphur Springs Mountain, near the towns of Vallejo and Benicia, and just north of the estuary where the Sacramento River flows into San Francisco Bay. The range then trends to the north and northwest for about to Howell Mountain, just northeast of St. Helena, California, where it merges with the Mayacamas Mountains. The Vaca Mountains, which are separated from the Howell Mountains by Suisun Valley on the east side, merge with the latter range northeast of St. Helena also. The crest of the range, which culminates at feet in the twin summit of Twin Sisters, represents the divide between the drainage of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin Sisters (California)
thumbnail, 275px, Twin Sisters seen from the top of Mount Vaca. Twin Sisters are the twin summits of the highest peak in the Howell Mountains of Solano and Napa Counties, California. Description The peak straddles a ridge separating the Suisun Valley wine region in Solano County on the east side from the Napa Valley wine region on the west side, and is a prominent landmark visible from most points in Suisun Valley. The north summit at an elevation of is the tallest of the two, and the lower south summit rises to an elevation of . It is the second highest peak in Solano County, Mount Vaca being the highest. Origin of name The origin of the name Twin sisters is unknown. However, the name was evidently well established when Munro-Fraser (1879) wrote his ''History of Solano County''. B18A bomber crash site The lower (south) summit of Twin Sisters is the site of a pre World War II crash on 24 October 1941 of an Army Air Corps B-18A Bolo bomber that killed all five crew memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napa River
The Napa River is a river approximately long in the U.S. state of California. It drains a famous wine-growing region called the Napa Valley, in the mountains north of the San Francisco Bay. Milliken Creek and Mt. Veeder watersheds are a few of its many tributaries. The river mouth is at Vallejo, where the intertidal zone of fresh and salt waters flow into the Carquinez Strait and the San Pablo Bay. Course The Napa River rises in northwestern Napa County just south of the summit of Mt. St. Helena in the Mayacamas Mountains of the California Coast Ranges. The source begins as seasonal Kimball Canyon Creek in Robert Louis Stevenson State Park at an elevation of which descends the southern slope of Mt. St. Helena to Kimball Canyon Dam. It flows south for 4 miles (6 km), entering the head of the slender Napa Valley north of Calistoga. In the valley, it flows southeast past Calistoga, St Helena, Rutherford, Oakville and through Napa, its head of navigation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and most abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Notable examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, silica gel, opal and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics (as an electrical insulator), and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Structure In the majority of silicates, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a linear molecule. The starkly different structures of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Hennessey
Lake Hennessey is a reservoir in the Vaca Mountains, east of St. Helena and the Napa Valley, within Napa County, California. The reservoir is formed by Conn Creek Dam, built in across Conn Creek. Construction of the earthen dam was authorized by the United States Congress when it passed the Flood Control Act of 1944 in order to mitigate flooding downstream in Napa, California. Funding for the dam was never appropriated by Congress, so in 1946 the City of Napa took on the project and built it at a cost of $550,000 dollars plus $250,000 for the land. The cost of laying the diameter pipeline from the dam to the city of Napa was $1.7 million. The 30 miles of pipe for the project was manufactured at the Basalt Rock Company plant located south of Napa. The design of the dam did not include a way to drain water from the reservoir when it comes close to full capacity. Once the lake is full, water drains from a spillway causing potential flooding dangers downstream. The reservoir and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Valley Sequence
The Great Valley Sequence of California is a -thick group of related geologic formations that are Late Jurassic through Cretaceous in age (150–65 Ma) on the geologic time scale. These sedimentary rocks were deposited during the late Mesozoic Era in an ancient seaway that corresponds roughly to the outline of the modern Great Valley (Central Valley) of California. Description Image:Franciscan subduction model.gif, Diagram showing depositional setting of the Great Valley Sequence and coeval Franciscan Assemblage Although the total thickness of the Great Valley Sequence in places is upwards of , most of these rocks today are buried beneath the thick Cenozoic sedimentary fill of the Great Valley of California. A number of gas and oil wells do penetrate these rocks in the subsurface of the valley, and these same rocks also crop out extensively along the west margin of the valley and to a lesser extent along the northern and eastern margins. The sequence overlies the Franciscan As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', " chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonoma Volcanics
The Sonoma Volcanics are a geologic formation of volcanic origin that is widespread in Napa and Sonoma counties, California. Most of the formation is Pliocene in age and includes obsidian, perlitic glass, diatomaceous mud, pyroclastic tuff, pumice, rhyolite tuffs, andesite breccias and interbedded volcanic (basalt) lava flows. The formation serves as the parent material for many of the soils in the Napa and Sonoma wine regions. "The Sonoma volcanics underlie and form most of the mountain areas bordering the Napa and Sonoma Valleys except for small areas underlain by the older sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. A thick extensive body of tuffs and flows forms the Howell Mountains east of Napa and extends from Jamison Canyon northward into the area north of Mount St. Helena. The volcanic rocks crop out in a narrow, discontinuous strip along the west side of the alluvial plain of Napa Valley, and on that side also they extend northward to Mount St. Helena. They compose most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
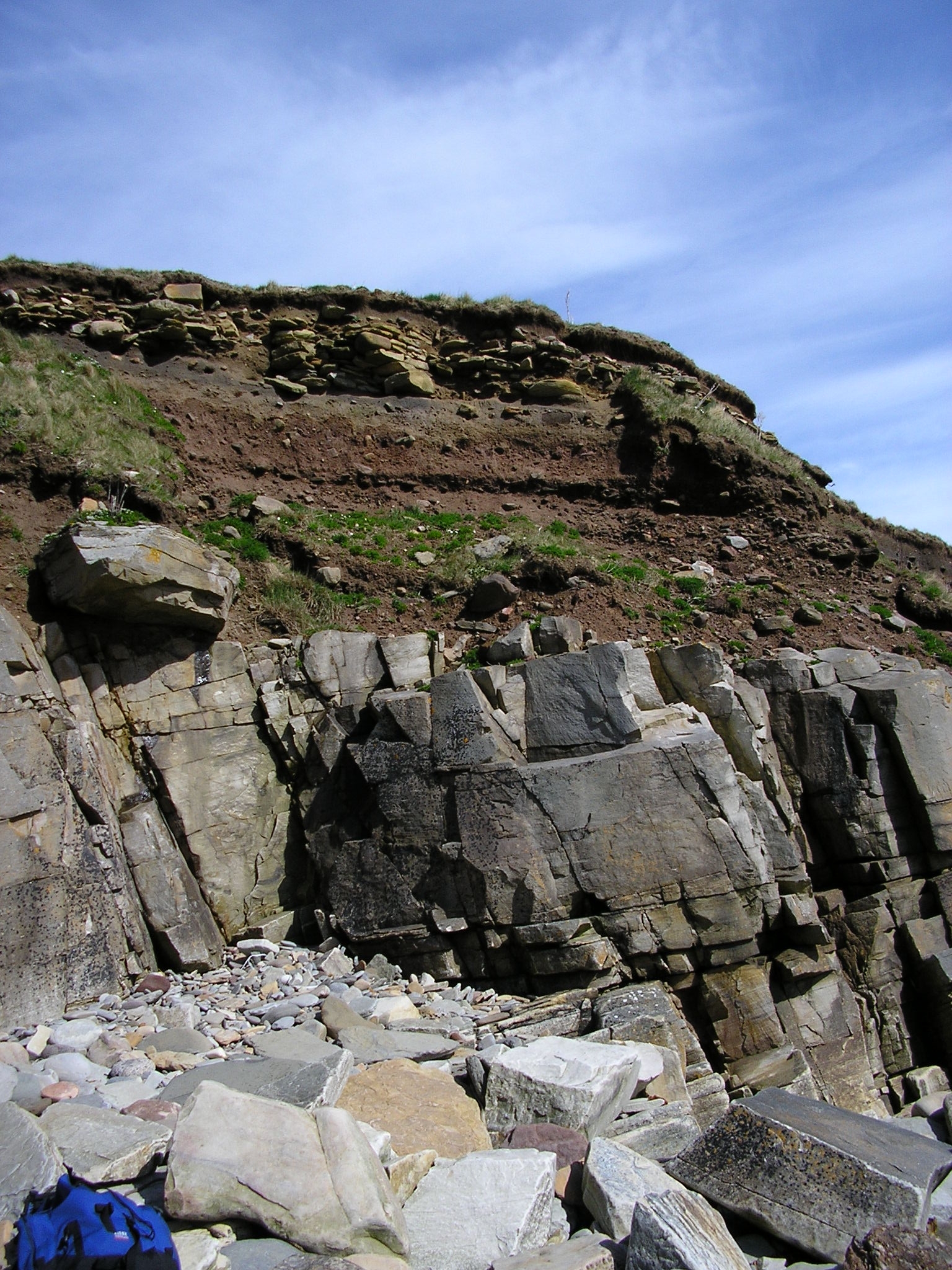
Bedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid rock that lies under loose material ( regolith) within the crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet. Definition Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface material. An exposed portion of bedrock is often called an outcrop. The various kinds of broken and weathered rock material, such as soil and subsoil, that may overlie the bedrock are known as regolith. Engineering geology The surface of the bedrock beneath the soil cover (regolith) is also known as ''rockhead'' in engineering geology, and its identification by digging, drilling or geophysical methods is an important task in most civil engineering projects. Superficial deposits can be very thick, such that the bedrock lies hundreds of meters below the surface. Weathering of bedrock Exposed bedrock experiences weathering, which may be physical or chemical, and which alters the structure of the rock to leave it susceptible to erosion. Bedrock may also experience ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |