|
Hovgaard Island
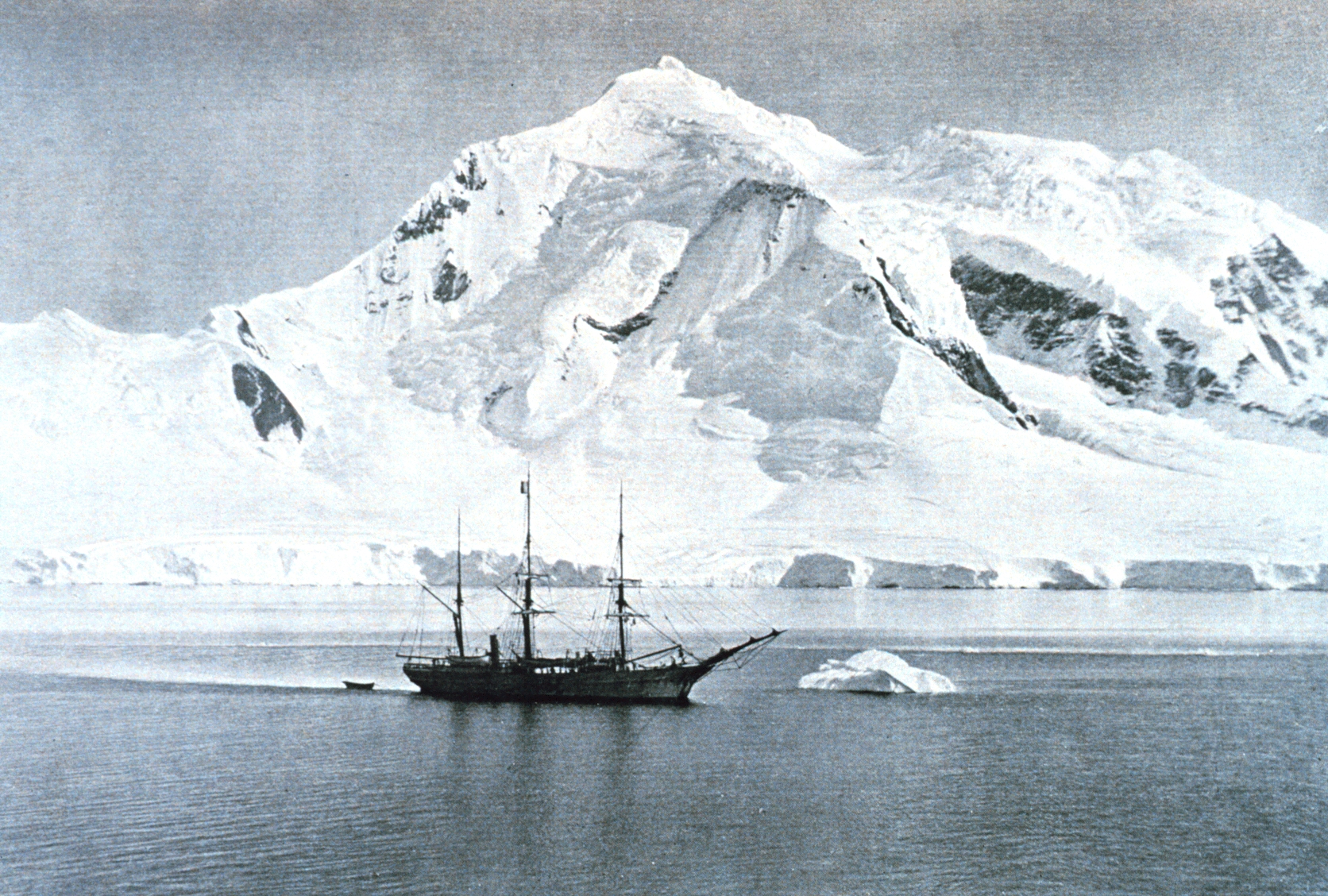
Hovgaard Island is an island long, lying off the northwest coast of Kyiv Peninsula, southwest of Booth Island in the Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica. It was discovered and named "Krogmann-Insel" (Krogmann Island) by the German 1873–74 expedition under Eduard Dallmann, but the name Hovgaard, after Polar explorer and officer of the Danish Navy Andreas Hovgaard,Hovgaard Ø. In: Anthony K. Higgins: ''Exploration history and place names of northern East Greenland.'' Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland Bulletin Bd. 21, 2010. Copenhagen 2010, applied by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1897–99, under Gerlache, has overtaken the original name in usage. The name Krogmann Point has been given to the western extremity of Hovgaard Island. Hovgaard Island is a popular location for camping in Antarctica among expedition groups due to the presence of a relatively flat campsite along Penola Strait. Campers dig "snow graves" to sleep in. The holes offer protection from the wind. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Archipelago
The Wilhelm Archipelago is an island archipelago off the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula in Antarctica. Wilhelm Archipelago consists of numerous islands, the largest of which are Booth Island and Hovgaard Island. The archipelago extends from Bismarck Strait southwest to Lumus Rock, off the west coast of Graham Land. It was discovered by a German expedition under Eduard Dallmann, 1873–74. He named them for Wilhelm I, then German Emperor and King of Prussia. Island groups * Anagram Islands * Argentine Islands * Betbeder Islands * Cruls Islands * Dannebrog Islands * Myriad Islands * Roca Islands * Vedel Islands * Wauwermans Islands * Yalour Islands See also * Ambrose Rocks * Bradley Rock * Guéguen Point * Petermann Island * Southwind Passage Southwind Passage () is a navigable passage between Betbeder Islands and Dickens Rocks, located at the north extremity of the Biscoe Islands Biscoe Islands is a series of islands, of which the principal ones are Renaud, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
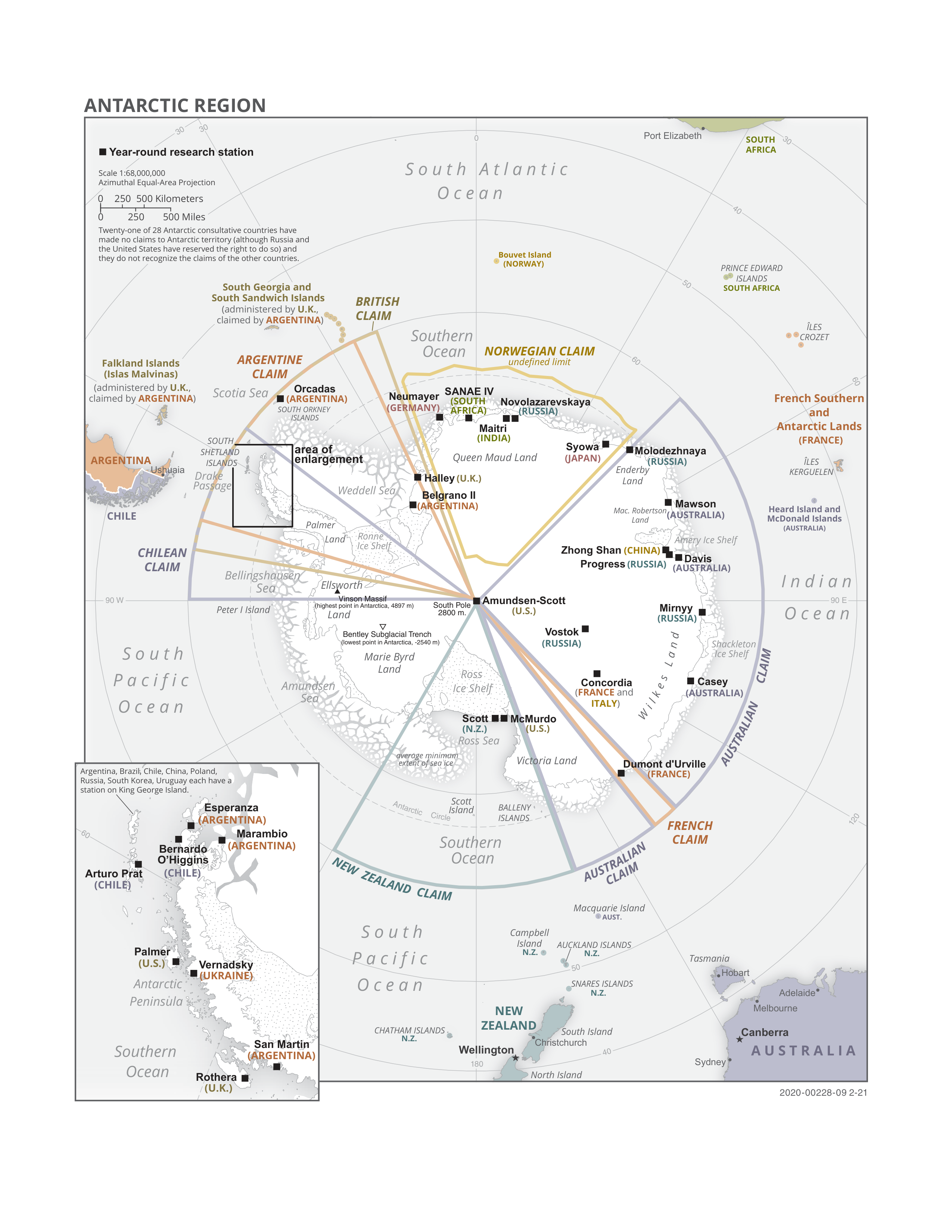
Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyiv Peninsula
Kyiv Peninsula (, ) is the predominantly ice-covered, oval shaped peninsula projecting 35 km in northwest direction from the west side of Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula. It is bounded by Flandres Bay to the northeast and Beascochea Bay to the southwest, and separated from Wilhelm Archipelago to the northwest by Lemaire Channel and Penola Strait. The peninsula's north extremity Cape Renard divides Graham Coast to the southwest from Danco Coast to the northeast. Mount Demaria is found on the west coast of the peninsula. Etymology The feature was first described and named in 2010 by the Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria after the capital city of Ukraine, in connection with the Ukrainian Antarctic base Vernadsky situated on nearby Galindez Island. The original naming was done in Bulgarian ( bg, полуостров Киев, poluostrov Kiev, ). Later, the name was adopted also by Ukraine in 2020 and translated ''Kyiv Peninsula''. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Booth Island
Booth Island (or Wandel Island) is a rugged, Y-shaped island, long and rising to off the northwest coast of Kyiv Peninsula in Graham Land, Antarctica in the northeastern part of the Wilhelm Archipelago. The narrow passage between the island and the mainland is the Lemaire Channel. History The island was discovered and named by a German expedition under Eduard Dallmann 1873–74, probably for Oskar Booth or Stanley Booth, or both, members of the Hamburg Geographical Society at that time. The Belgian Antarctic Expedition of 1897–1899 applied the name "Wandel Island", for Danish polar explorer and hydrographer Carl Frederick Wandel, but the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names rejected the name in favor of the earlier Booth Island. The name Wandel was retained for the island's highest point. Although many of the island's features were probably first seen by Dallmann's expedition, the island was not charted in detail until the Third French Antarctic Expedition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Dallmann
Eduard Dallmann (11 March 1830 – 23 December 1896) was a German whaler, trader, and Polar explorer. Dallmann was born in Blumenthal, at-the-time a village just to the north of Bremen. He began his adventures as a young sailor at the age of 15. In 1866, he became captain of the Hawaii-registered ship ''W.C. Talbot'' and undertook trading trips through the Bering and Chukchi Seas to locations in Alaska and Chukotka. He was the first European to set foot on Wrangel Island. From 1867 to 1870, he commanded the ''Count Bismarck'' on a whaling cruise to the Pacific tropics and the Bering and Chukchi seas.''Friend'', of Honolulu, December 1, 1869, Vol. 19, No. 12, p. 104. From 1872 to 1874, when whales became more of a rarity in Arctic waters, Dallmann was commissioned to explore the Antarctic seas on the sailing-steamer ''Grönland''. The operation was moderately successful from a whaling point-of-view, but more importantly, Dallmann made many discoveries around Antarctica� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Navy
The Royal Danish Navy ( da, Søværnet) is the sea-based branch of the Danish Defence force. The RDN is mainly responsible for maritime defence and maintaining the sovereignty of Danish territorial waters (incl. Faroe Islands and Greenland). Other tasks include surveillance, search and rescue, icebreaking, oil spill recovery and prevention as well as contributions to international tasks and forces. During the period 1509–1814, when Denmark was in a union with Norway, the Danish Navy was part of the Dano-Norwegian Navy. Until the copenhagenization of the navy in 1801, and again in 1807, the navy was a major strategic influence in the European geographical area, but since then its size and influence has drastically declined with a change in government policy. Despite this, the navy is now equipped with a number of large state-of-the-art vessels commissioned since the end of the Cold War. This can be explained by its strategic location as the NATO member controlling access t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andreas Peter Hovgaard
Andreas Peter Hovgaard (1 November 1853 – 15 March 1910) was a Danish naval officer and Arctic explorer. Hovgaard became a sub-lieutenant of the Danish Navy in 1874, rising to the rank of Lieutenant (navy), lieutenant in 1876, Captain (naval), captain in 1888 and Commander in 1901. He retired from active service in 1909. Career Andreas Hovgaard was the son of Ole Anton Hovgaard (1821–1891) and Louise Charlotte Munch (1823–1872). Little is known about his early life, except that he joined the Danish Navy and quickly rose in the ranks. In 1878 Hovgaard, as a young lieutenant, became a member of Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld's Vega Expedition in which he was in charge of making meteorological as well as geomagnetic observations. Shortly after returning to Denmark he married Sophie Christiane Nielsen (1856–1934) and published his report ''Nordenskiölds rejse omkring Asien og Europa'' about the first Arctic expedition that navigated successfully through the Northeast Passage. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgian Antarctic Expedition
The Belgian Antarctic Expedition of 1897–1899 was the first expedition to winter in the Antarctic region. Led by Adrien de Gerlache de Gomery aboard the RV ''Belgica'', it was the first Belgian Antarctic expedition and is considered the first expedition of the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration. Among its members were Frederick Cook and Roald Amundsen, explorers who would later attempt the respective conquests of the North and South Poles. Preparation and surveying In 1896, after a period of intensive lobbying, Adrien Victor Joseph de Gerlache de Gomery purchased the Norwegian-built whaling ship ''Patria'', which, following an extensive refit, he renamed . Gerlache had worked together with the Geographical Society of Brussels to organize a national subscription, but was able to outfit his expedition only after the Belgian government voted in favor of two large subsidies, making it a state-supported undertaking. With a multinational crew that included Roald Amundsen from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerlache
Baron Adrien Victor Joseph de Gerlache de Gomery (; 2 August 1866 – 4 December 1934) was a Belgian officer in the Belgian Royal Navy who led the Belgian Antarctic Expedition of 1897–99. Early years Born in Hasselt in eastern Belgium as the son of an army officer, de Gerlache was educated in Brussels. From a young age he was deeply attracted by the sea, and made three voyages in 1883 and 1884 to the United States as a cabin boy on an ocean liner. He studied Engineering at the Free University of Brussels. After finishing his third year in 1885, he quit the university and joined the Belgian Navy on 19 January 1886. After graduating from the nautical college of Ostend he worked on fishery protection vessels as second and third lieutenant. In October 1887 he signed on as seaman on the ''Craigie Burn'', an English ship, for a voyage to San Francisco, but the ship failed to round Cape Horn and was sold for scrap in Montevideo. He returned to Europe after spending time in Urug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krogmann Point
Krogmann Point () is the point forming the western extremity of Hovgaard Island, in the Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica. Hovgaard Island was first seen by a German expedition under Eduard Dallmann in January 1874 and named "Krogmann Insel". However, the name Hovgaard, applied by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Gerlache Baron Adrien Victor Joseph de Gerlache de Gomery (; 2 August 1866 – 4 December 1934) was a Belgian officer in the Belgian Royal Navy who led the Belgian Antarctic Expedition of 1897–99. Early years Born in Hasselt in eastern Belgium as ... in February 1898, has overtaken the original in usage. In order to preserve Dallmann's earlier name in this vicinity, the name Krogmann has been applied to the point. References Headlands of the Wilhelm Archipelago {{WilhelmArchipelago-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Antarctic Gazetteer
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - , G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |