|
Hot Plate Test
The hot plate test is a test of the pain response in animals, similar to the tail flick test. Both hot plate and tail-flick methods are used generally for centrally acting analgesic, while peripherally acting drugs are ineffective in these tests but sensitive to acetic acid-induced writhing test. The hot plate test is used in basic pain research and in testing the effectiveness of analgesics by observing the reaction to pain caused by heat. It was proposed by Eddy and Leimbach in 1953. They used a behavioral model of nociception where behaviors such as jumping and hind paw-licking are elicited following a noxious thermal stimulus. Licking is a rapid response to painful thermal stimuli that is a direct indicator of nociceptive threshold. Jumping represents a more elaborated response, with a latency, and encompasses an emotional component of escaping. Procedure * A transparent glass cylinder is used to keep the animal on the heated surface of the plate. * The temperature of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
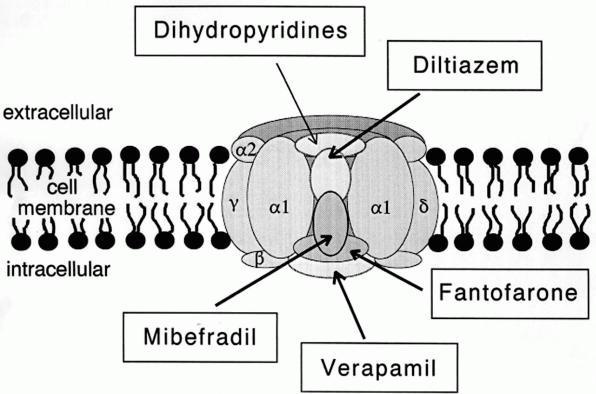
Calcium Channel
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels. Comparison tables The following tables explain gating, gene, location and function of different types of calcium channels, both voltage and ligand-gated. Voltage-gated Ligand-gated *the ''receptor-operated calcium channels'' (in vasoconstriction) ** P2X receptors Page 479 Pharmacology L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body, depolarization is mediated by sodium influx into a cell; changing the calcium permeability has little effect on action potentials. However, in many smooth muscle tissues, depolarization is mediated primarily by calcium influx into the cell. L-type calcium channel blockers selectively inhibit these action potentials in smooth muscle which leads to dilation of blood vessels; this in turn corrects hype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pain Scales
A pain scale measures a patient's pain intensity or other features. Pain scales are a common communication tool in medical contexts, and are used in a variety of medical settings. Pain scales are a necessity to assist with better assessment of pain and patient screening. Pain measurements help determine the severity, type, and duration of the pain, and are used to make an accurate diagnosis, determine a treatment plan, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. Accurately measuring pain is a necessity in medical settings, especially if the pain measurement is going to be used as a screening tool, either for potential diseases or medical problems, or as a type of triage to determine urgency of one patient over another. Pain scales are based on trust, cartoons (behavioral), or imaginary data, and are available for neonates, infants, children, adolescents, adults, seniors, and persons whose communication is impaired. Pain assessments are often regarded as "the 5th Vital Sign". It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institutional Animal Care And Use Committee
Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUCs) are centrally important in applying laws about animal research in the United States. Similar systems operate in other countries, but generally under different titles; for example, in Canada a typical title would be the University Animal Care Committee (UACC), while in the United Kingdom it would be the Animal Welfare and Ethical Review Body (AWERB). Most research involving laboratory animals in the United States is funded by the United States National Institutes of Health or, to lesser extents, other federal agencies. The NIH Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare (OLAW) has been directed by law to develop policies that describe the role of Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees. Every institution that uses certain animals for federally funded laboratory research must have an Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). Each local IACUC reviews research protocols and conducts evaluations of the institution's animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiolytic
An anxiolytic (; also antipanic or antianxiety agent) is a medication or other intervention that reduces anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiogenic agents which increase anxiety. Anxiolytic medications are used for the treatment of anxiety disorders and their related psychological and physical symptoms. Nature of anxiety Anxiety is a naturally-occurring emotion and an innate response of the body to the environmental stimuli. Mild to moderate anxiety would increase level of performance. However, when anxiety levels exceed the tolerability of a person, anxiety disorders may occur. People with anxiety disorders can exhibit fear responses such as defensive behaviors, high levels of alertness and negative emotions, without external stimuli which induce anxiety within an individual. Those with anxiety disorders are also often found to have concurrent psychological disorders, most commonly depression. Anxiety disorders are divided into 6 types in clinical recognition. They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955 and was made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, who soon followed with diazepam (Valium) in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide. Benzodiazepines are depressants that enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABAA receptor, resulting in sedative, hypnotic ( sleep-inducing), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABAA Receptor
The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to chloride ions (Cl−) and, to a lesser extent, bicarbonate ions (HCO3−). Depending on the membrane potential and the ionic concentration difference, this can result in ionic fluxes across the pore. If the membrane potential is higher than the equilibrium potential (also known as the reversal potential) for chloride ions, when the receptor is activated Cl− will flow into the cell. This causes an inhibitory effect on neurotransmission by diminishing the chance of a successful action potential occurring at the postsynaptic cell. The reversal potential of the GABAA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) in normal solution is −70 mV, contrasting the GABAB IPSP (-100 mV). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazepam
Diazepam, first marketed as Valium, is a medicine of the benzodiazepine family that acts as an anxiolytic. It is commonly used to treat a range of conditions, including anxiety, seizures, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, muscle spasms, insomnia, and restless legs syndrome. It may also be used to cause memory loss during certain medical procedures. It can be taken by mouth, inserted into the rectum, injected into muscle, injected into a vein or used as a nasal spray. When given into a vein, effects begin in one to five minutes and last up to an hour. By mouth, effects begin after 15 to 60 minutes. Common side-effects include sleepiness and trouble with coordination. Serious side effects are rare. They include increased risk of suicide, decreased breathing, and an increased risk of seizures if used too frequently in those with epilepsy. Occasionally, excitement or agitation may occur. Long-term use can result in tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms on dose reduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. There are numerous methods used to administer morphine: oral; sublingual; via inhalation; injection into a muscle; by injection under the skin; intravenously; injection into the space around the spinal cord; transdermal; or via rectal suppository. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during labor. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administered intravenously and 60 minutes when administered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapentadol
Tapentadol, brand names Nucynta among others, is a centrally acting opioid analgesic of the benzenoid class with a dual mode of action as an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor and as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI). Analgesia occurs within 32 minutes of oral administration, and lasts for 4–6 hours. It is similar to tramadol in its dual mechanism of action; namely, its ability to activate the mu opioid receptor and inhibit the reuptake of norepinephrine. Unlike tramadol, it has only weak effects on the reuptake of serotonin and is a significantly more potent opioid with no known active metabolites. Tapentadol is not a pro-drug and therefore does not rely on metabolism to produce its therapeutic effects; this makes it a useful moderate-potency analgesic option for patients who do not respond adequately to more commonly used opioids due to genetic disposition (poor metabolizers of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6), as well as providing a more consistent dosage-response range among t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor
A norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI, NERI) or noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor or adrenergic reuptake inhibitor (ARI), is a type of drug that acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the neurotransmitters norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) by blocking the action of the norepinephrine transporter (NET). This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of norepinephrine and epinephrine and therefore can increase adrenergic neurotransmission. Medical use NRIs are commonly used in the treatment of conditions like ADHD and narcolepsy due to their psychostimulant effects and in obesity due to their appetite suppressant effects. They are also frequently used as antidepressants for the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety and panic disorder. Additionally, many addictive substances such as cocaine and methylphenidate possess NRI activity, though NRIs without combined dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) properties are not significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

4-3D-balls.png)

_DOJ.jpg)