|
Hot Dark Matter
Hot dark matter (HDM) is a theoretical form of dark matter which consists of particles that travel with ultrarelativistic velocities. Dark matter is a form of matter that neither emits nor absorbs light. Within physics, this behavior is characterized by dark matter not interacting with electromagnetic radiation, hence making it ''dark'' and rendering it undetectable via conventional instruments in physics. Data from galaxy rotation curves indicate that approximately 80% of the mass of a galaxy cannot be seen, forcing researchers to innovate ways that ''indirectly'' detect it through dark matter's effects on gravitational fluctuations. As we shall see below, it is useful to differentiate dark matter into "hot" (HDM) and "cold" (CDM) types–some even suggesting a middle-ground of "warm" dark matter (WDM). The terminology refers to the mass of the dark matter particles (which dictates the speed at which they travel): HDM travels faster than CDM because the HDM particles are theoriz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
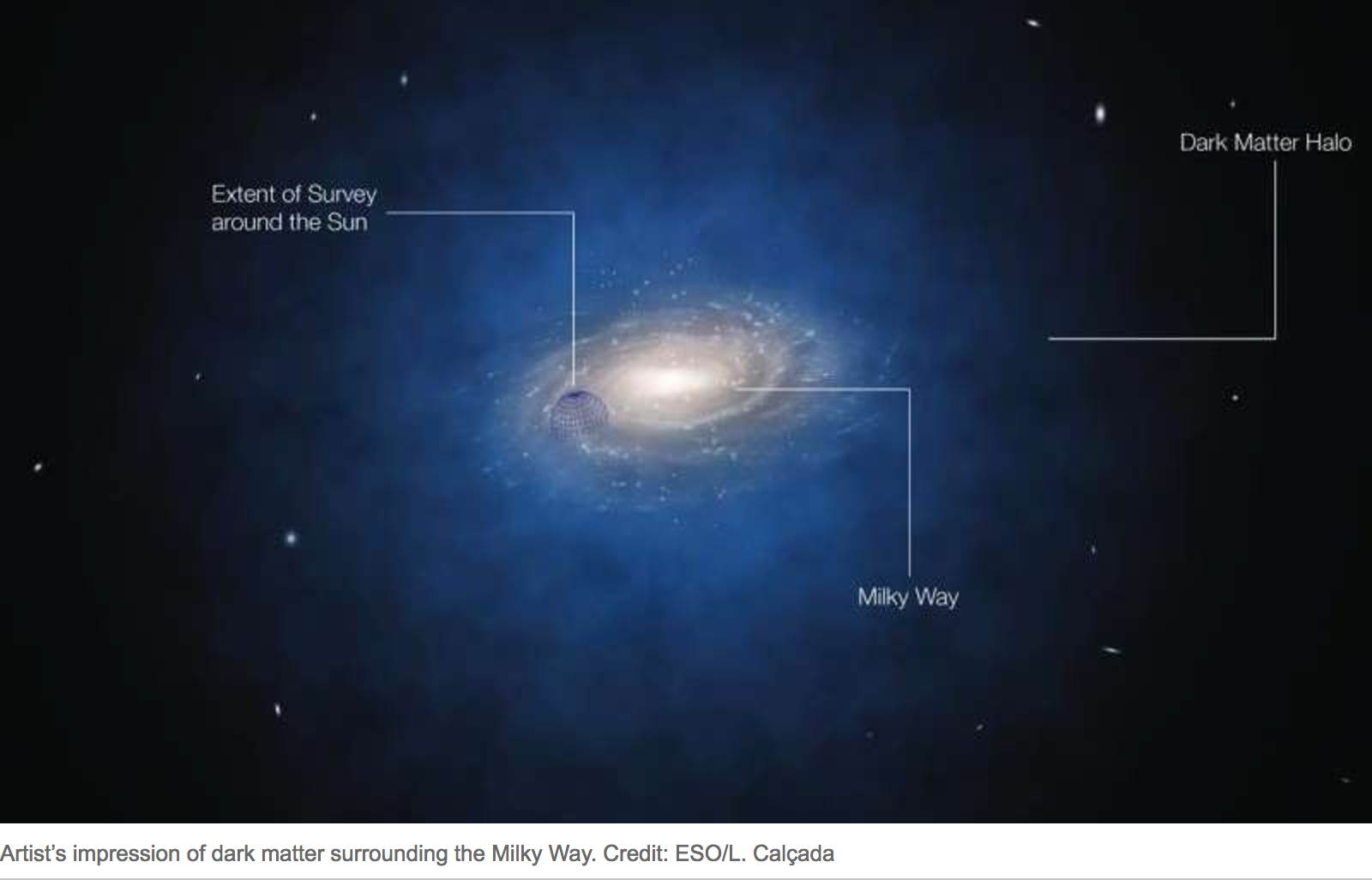
Dark Matter
Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter thought to account for approximately 85% of the matter in the universe. Dark matter is called "dark" because it does not appear to interact with the electromagnetic field, which means it does not absorb, reflect, or emit electromagnetic radiation and is, therefore, difficult to detect. Various astrophysical observationsincluding gravitational effects which cannot be explained by currently accepted theories of gravity unless more matter is present than can be seenimply dark matter's presence. For this reason, most experts think that dark matter is abundant in the universe and has had a strong influence on its structure and evolution. The primary evidence for dark matter comes from calculations showing that many galaxies would behave quite differently if they did not contain a large amount of unseen matter. Some galaxies would not have formed at all and others would not move as they currently do. Other lines of evidence include obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. According to this theory, space and time emerged together ago, and the universe has been expanding ever since the Big Bang. While the spatial size of the entire universe is unknown, it is possible to measure the size of the observable universe, which is approximately 93 billion light-years in diameter at the present day. Some of the earliest cosmological models of the universe were developed by ancient Greek and Indian philosophers and were geocentric, placing Earth at the center. Over the centuries, more precise astronomical observations led Nicolaus Copernicus to develop the heliocentric model with the Sun at the center of the Solar System. In developing the law of universal gravitation, Isaac Newton built upon Copernicus's wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WISP (particle Physics)
In particle physics, the acronym WISP refers to a largely hypothetical weakly interacting sub-eV particle, or ''weakly interacting ''slender'' particle'', or ''weakly interacting ''slim'' particle'' – low-mass particles which rarely interact with conventional particles. The term is used to generally categorize a type of dark matter candidate, and is essentially synonymous with '' axion-like particle'' (ALP). With the exception of “active” neutrinos, all WISPs are hypothetical particles. WISPs are the low-mass counterpart of weakly interacting massive particles (WIMPs). Discussion Except for conventional, active neutrinos, all WISPs are candidate dark matter constituents, and many proposed experiments to detect WISPs might possibly be able to detect several different kinds. “WISP” is most often used to refer to a low-mass hypothetical particles which are viable dark matter candidates. Examples include: * Axion – long standing hypothetical strong force related light pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gifu, Gifu
is a city located in the south-central portion of Gifu Prefecture, Japan, and serves as the prefectural capital. The city has played an important role in Japan's history because of its location in the middle of the country. During the Sengoku period, various warlords, including Oda Nobunaga, used the area as a base in an attempt to unify and control Japan. Gifu continued to flourish even after Japan's unification as both an important ''shukuba'' along the Edo period NakasendōNakasendo to Shukuba-machi Gifu City Hall. Accessed September 9, 2007. and, later, as one of Japan's fashion centers. It has been designated a by the national government. Overview L ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
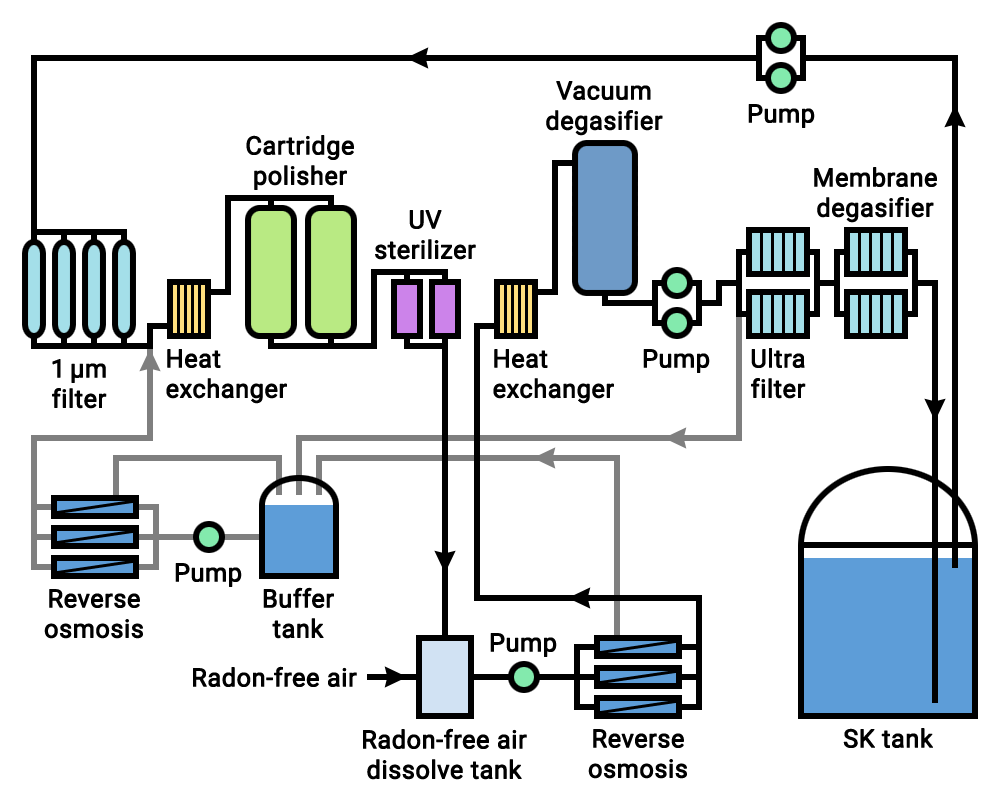
Super-Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ja, スーパーカミオカンデ) is a Neutrino detector, neutrino observatory located Kamioka Observatory, under Mount Ikeno near the city of Hida, Gifu, Hida, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. It is located underground in the Mozumi Mining, Mine in Hida's Kamioka area. The observatory was designed to detect high-energy neutrinos, to search for proton decay, study solar neutrino, solar and Neutrino#Atmospheric neutrinos, atmospheric neutrinos, and keep watch for supernovae in the Milky Way Galaxy. It consists of a cylindrical stainless steel tank about in height and diameter holding 50,000 metric tons (55,000 US tons) of ultrapure water. Mounted on an inside superstructure are about 13,000 photomultiplier tubes that detect light from Cherenkov radiation. A neutrino interaction with the electrons or nuclei of water can produce an electron or positron that moves faster t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction. As a result, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. However, gravity is the most significant interaction between objects at the macroscopic scale, and it determines the motion of planets, stars, galaxies, and even light. On Earth, gravity gives weight to physical objects, and the Moon's gravity is responsible for sublunar tides in the oceans (the corresponding antipodal tide is caused by the inertia of the Earth and Moon orbiting one another). Gravity also has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of plants through the process of gravitropism and influencing the circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weak Interaction
In nuclear physics and particle physics, the weak interaction, which is also often called the weak force or weak nuclear force, is one of the four known fundamental interactions, with the others being electromagnetism, the strong interaction, and gravitation. It is the mechanism of interaction between subatomic particles that is responsible for the radioactive decay of atoms: The weak interaction participates in nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. The theory describing its behaviour and effects is sometimes called quantum flavourdynamics (QFD); however, the term QFD is rarely used, because the weak force is better understood by electroweak theory (EWT). The effective range of the weak force is limited to subatomic distances and is less than the diameter of a proton. Background The Standard Model of particle physics provides a uniform framework for understanding electromagnetic, weak, and strong interactions. An interaction occurs when two particles (typically, but not nec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strong Interaction
The strong interaction or strong force is a fundamental interaction that confines quarks into proton, neutron, and other hadron particles. The strong interaction also binds neutrons and protons to create atomic nuclei, where it is called the nuclear force. Most of the mass of a common proton or neutron is the result of the strong interaction energy; the individual quarks provide only about 1% of the mass of a proton. At the range of 10−15 m (slightly more than the radius of a nucleon), the strong force is approximately 100 times as strong as electromagnetism, 106 times as strong as the weak interaction, and 1038 times as strong as gravitation. The strong interaction is observable at two ranges and mediated by two force carriers. On a larger scale (of about 1 to 3 fm), it is the force (carried by mesons) that binds protons and neutrons (nucleons) together to form the nucleus of an atom. On the smaller scale (less than about 0.8 fm, the radius of a nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Interaction
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions of atoms and molecules. Electromagnetism can be thought of as a combination of electricity and magnetism, two distinct but closely intertwined phenomena. In essence, electric forces occur between any two charged particles, causing an attraction between particles with opposite charges and repulsion between particles with the same charge, while magnetism is an interaction that occurs exclusively between ''moving'' charged particles. These two effects combine to create electromagnetic fields in the vicinity of charge particles, which can exert influence on other particles via the Lorentz force. At high energy, the weak force and electromagnetic force are unified as a single electroweak force. The electromagnetic force is responsible for many o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles excluding massless particles. The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the strong interaction. Thus, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and undetected. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three Lepton, leptonic Flavor (particle physics), flavors: electron neutrinos muon neutrinos (), or tau neutrinos (), in association with the corresponding charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be massless, it is now kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Dark Matter
Mixed dark matter (MDM) is a dark matter (DM) model proposed during the late 1990s. Mixed dark matter is also called hot + cold dark matter. The most abundant form of dark matter is cold dark matter, almost one fourth of the energy contents of the Universe. Neutrinos are the only known particles whose Big-Bang thermal relic should compose at least a fraction of Hot dark matter (HDM), albeit other candidates are speculated to exist.Bogdan A. Dobrescu and Don LincolnA Hidden World of Complex Dark Matter Could Be Uncovered Scientific American. Volume 313, Issue 1. pp. 20-27. In the early 1990s, the power spectrum of fluctuations in the galaxy clustering did not agree entirely with the predictions for a standard cosmology built around pure cold DM. Mixed dark matter with a composition of about 80% cold and 20% hot (neutrinos) was investigated and found to agree better with observations. This large amount of HDM was made obsolete by the discovery in 1998 of the acceleration of universal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |