|
Host–pathogen Interaction
The host–pathogen interaction is defined as how microbes or viruses sustain themselves within host organisms on a molecular, cellular, organismal or population level. This term is most commonly used to refer to disease-causing microorganisms although they may not cause illness in all hosts. Because of this, the definition has been expanded to how known pathogens survive within their host, whether they cause disease or not. On the molecular and cellular level, microbes can infect the host and divide rapidly, causing disease by being there and causing a homeostatic imbalance in the body, or by secreting toxins which cause symptoms to appear. Viruses can also infect the host with virulent DNA, which can affect normal cell processes ( transcription, translation, etc.), protein folding, or evading the immune response. Pathogenicity Pathogen history One of the first pathogens observed by scientists was ''Vibrio cholerae'', described in detail by Filippo Pacini in 1854. His initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, dysfunction, distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injuries, disabilities, disorders, syndromes, infections, isolated symptoms, deviant behaviors, and atypical variations of stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helminths
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in their mammalian hosts for many years due to their ability to manipulate the host's immune response by secreting immunomod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
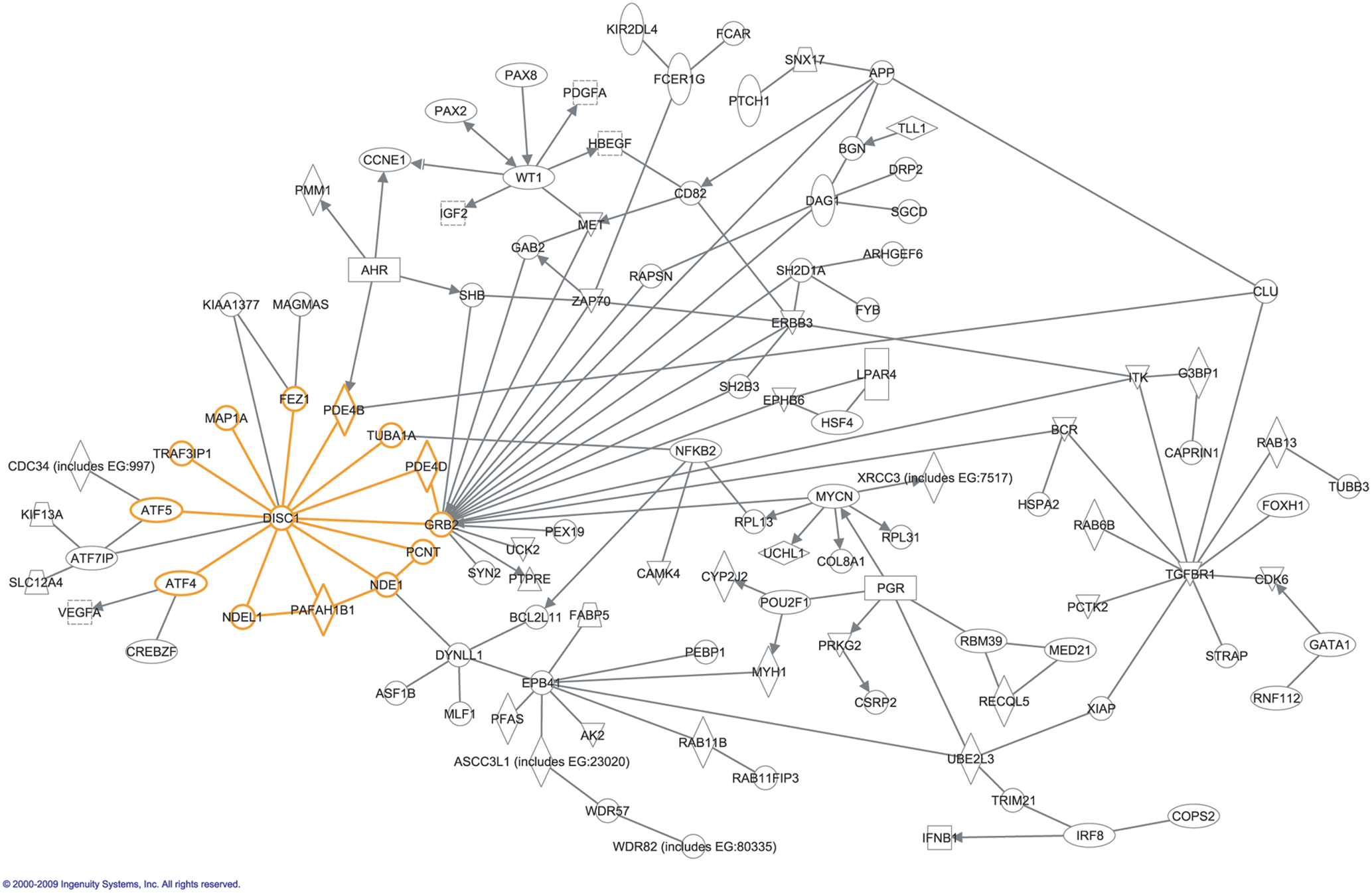
Interactome
In molecular biology, an interactome is the whole set of molecular interactions in a particular cell. The term specifically refers to physical interactions among molecules (such as those among proteins, also known as protein–protein interactions, PPIs; or between small molecules and proteins) but can also describe sets of indirect interactions among genes ( genetic interactions). The word "interactome" was originally coined in 1999 by a group of French scientists headed by Bernard Jacq. Mathematically, interactomes are generally displayed as graphs. Though interactomes may be described as biological networks, they should not be confused with other networks such as neural networks or food webs. Molecular interaction networks Molecular interactions can occur between molecules belonging to different biochemical families (proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, etc.) and also within a given family. Whenever such molecules are connected by physical interactions, they form mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It caused more than 100,000 deaths attributable to antimicrobial resistance in 2019. MRSA is any strain of ''S. aureus'' that has developed (through natural selection) or acquired (through horizontal gene transfer) a multiple drug resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics are a broad-spectrum group that include some penams (penicillin derivatives such as methicillin and oxacillin) and cephems such as the cephalosporins. Strains unable to resist these antibiotics are classified as methicillin-susceptible ''S. aureus'', or MSSA. MRSA is common in hospitals, prisons, and nursing homes, where people with open wounds, invasive devices such as catheters, and weakened immune systems are at greater risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise from both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious. Carcinogens, as mentioned, are agents in the environment capable of contributing to cancer growth. Carcinogens can be categorized into two different types: activation-dependent and activation-independent, and each nature impacts their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are various poisonous carcinogens and mutagens that are produced by certain molds, particularly '' Aspergillus'' species. The fungi grow in soil, decaying vegetation and various staple foodstuffs and commodities such as hay, sweetcorn, wheat, millet, sorghum, cassava, rice, chili peppers, cottonseed, peanuts, tree nuts, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, and various spices. In short, the relevant fungi grow on almost any crop or food. When such contaminated food is processed or consumed, the aflatoxins enter the general food supply. They have been found in both pet and human foods, as well as in feedstocks for agricultural animals. Animals fed contaminated food can pass aflatoxin transformation products into eggs, milk products, and meat. For example, contaminated poultry feed is the suspected source of aflatoxin-contaminated chicken meat and eggs in Pakistan. Children are particularly affected by aflatoxin exposure, which is associated with stunted growth, delaye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus
'''' () is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. ''Aspergillus'' was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli. Viewing the fungi under a microscope, Micheli was reminded of the shape of an '' aspergillum'' (holy water sprinkler), from Latin ''spargere'' (to sprinkle), and named the genus accordingly. Aspergillum is an asexual spore-forming structure common to all ''Aspergillus'' species; around one-third of species are also known to have a sexual stage. While some species of ''Aspergillus'' are known to cause fungal infections, others are of commercial importance. Taxonomy Species ''Aspergillus'' consists of 837 species of fungi. Growth and distribution ''Aspergillus'' is defined as a group of conidial fungi—that is, fungi in an asexual state. Some of them, however, are known to have a teleomorph (sexual state) in the Ascomycota. With DNA evidence, all members of the genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection. Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. For others, symptoms may appear 30 to 180 days after becoming infected and can include a rapid onset of sickness with nausea, vomiting, yellowish skin, fatigue, dark urine, and abdominal pain. Symptoms during acute infection typically last for a few weeks, though some people may feel sick for up to six months. Deaths resulting from acute stage HBV infections are rare. An HBV infection lasting longer than six months is usually considered chronic. The likelihood of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for those who are infected with HBV at a younger age. About 90% of those infected during or shortly after birth develop chronic hepatitis B, while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five develop chronic cases. Most of those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clostridium Botulinum
''Clostridium botulinum'' is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, anaerobic, spore-forming, motile bacterium with the ability to produce the neurotoxin botulinum. The botulinum toxin can cause botulism, a severe flaccid paralytic disease in humans and other animals, and is the most potent toxin known to mankind, natural or synthetic, with a lethal dose of 1.3–2.1 ng/kg in humans.(2010). Chapter 19. ''Clostridium'', ''Peptostreptococcus'', ''Bacteroides'', and Other Anaerobes. In Ryan K.J., Ray C (Eds), ''Sherris Medical Microbiology'', 5th ed. ''C. botulinum'' is a diverse group of pathogenic bacteria initially grouped together by their ability to produce botulinum toxin and now known as four distinct groups, ''C. botulinum'' groups I–IV, as well as some strains of ''Clostridium butyricum'' and ''Clostridium baratii'', are the bacteria responsible for producing botulinum toxin. ''C. botulinum'' is responsible for foodborne botulism (ingestion of preformed toxin), infant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life Cell may also refer to: Locations * Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ... of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae. When first introduced by Georg Goldfuss (originally spelled Goldfuß) in 1818, the taxon Protozoa was erected as a class within the Animalia, with the word 'protozoa' meaning "first animals". In later classification schemes it was elevated to a variety of higher ranks, including phylum, subkingdom and kingdom, and sometimes included within Protoctista or Protista. The approach of classifying Protozoa within the context of Animalia was widespread in the 19th and early 20th century, but not universal. By the 1970s, it became usual to require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |