|
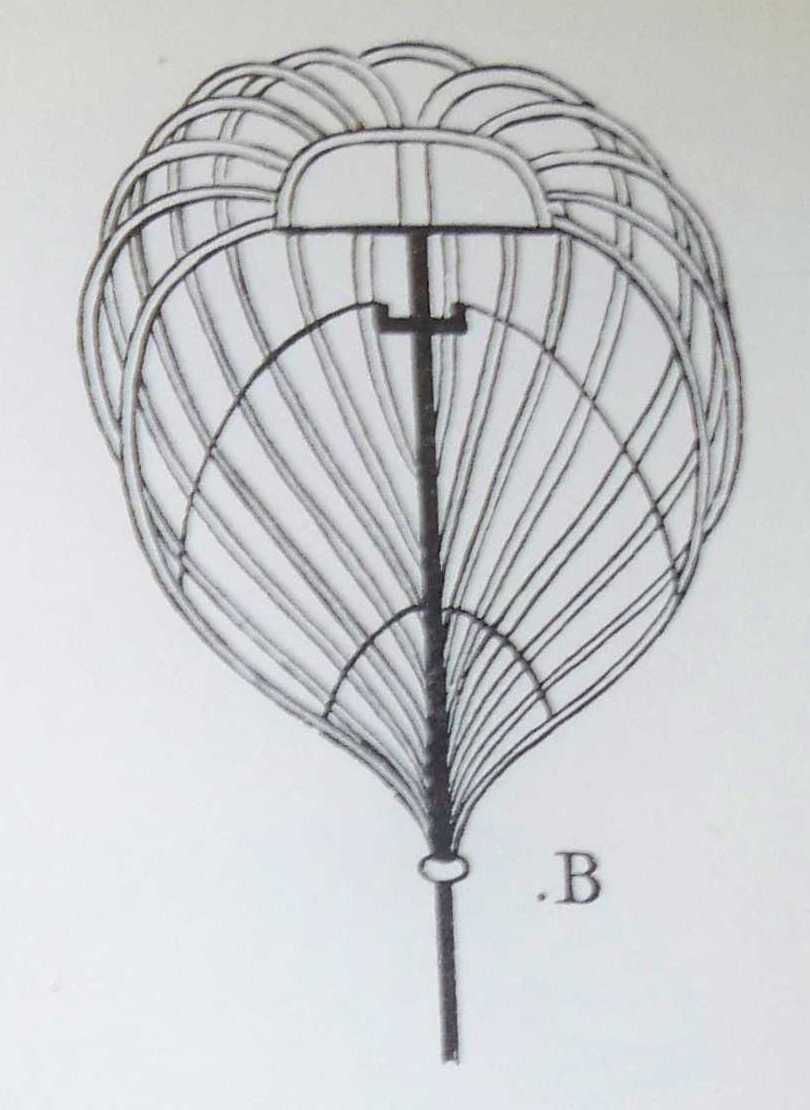
Horo (cloak)
A was a type of cloak or garment attached to the back of the armour worn by samurai on the battlefields of feudal Japan. Description A ''horo'' was around 1.8 m (6 ft) long and made from several strips of cloth sewn together with a fringe on the top and bottom edges. The cloth strips were sewn together and formed into a sort of bag which would fill with air like a balloon when the wearer was riding a horse. A light framework of wicker, bamboo or whale bone known as an ''oikago'', similar to a crinoline, which is said to have been invented by Hatakeyama Masanaga during the ŇĆnin War (1467‚Äď1477), was sometimes used to keep the ''horo'' expanded. Attaching the ''horo'' generally involved a combination of fastening cords and possibly a staff. The top cords were attached to either the helmet or cuirass of the wearer while the bottom cords were attached to the waist. The family emblem ( ''mon'') of the wearer was marked on the ''horo''. Use ''Horo'' were used as far back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Japanese Words And Phrases
{{Commons Words and phrases by language Words Words A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consen ... Words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mon (emblem)
, also , , and , are Japanese emblems used to decorate and identify an individual, a family, or (more recently) an institution or business entity. While is an encompassing term that may refer to any such device, and refer specifically to emblems used to identify a family. An authoritative reference compiles Japan's 241 general categories of based on structural resemblance (a single may belong to multiple categories), with 5,116 distinct individual . However, it is well-acknowledged that there exist a number of lost or obscure . The devices are similar to the badges and coats of arms in European heraldic tradition, which likewise are used to identify individuals and families. are often referred to as crests in Western literature, the crest being a European heraldic device similar to the in function. History may have originated as fabric patterns to be used on clothes in order to distinguish individuals or signify membership of a specific clan or organization. By the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samurai Weapons And Equipment
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of medieval and early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retainers of the ''daimyo'' (the great feudal landholders). They had high prestige and special privileges such as wearing two swords and ''Kiri-sute gomen'' (right to kill anyone of a lower class in certain situations). They cultivated the ''bushido'' codes of martial virtues, indifference to pain, and unflinching loyalty, engaging in many local battles. Though they had predecessors in earlier military and administrative officers, the samurai truly emerged during the Kamakura shogunate, ruling from 1185 to 1333. They became the ruling political class, with significant power but also significant responsibility. During the 13th century, the samurai proved themselves as adept warriors against the invading Mongols. During the peaceful Edo period (1603 to 1868), they became the stewards and chamberlains of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Heraldry
, also , , and , are Japanese emblems used to decorate and identify an individual, a family, or (more recently) an institution or business entity. While is an encompassing term that may refer to any such device, and refer specifically to emblems used to identify a family. An authoritative reference compiles Japan's 241 general categories of based on structural resemblance (a single may belong to multiple categories), with 5,116 distinct individual . However, it is well-acknowledged that there exist a number of lost or obscure . The devices are similar to the badges and coats of arms in European heraldic tradition, which likewise are used to identify individuals and families. are often referred to as crests in Western literature, the crest being a European heraldic device similar to the in function. History may have originated as fabric patterns to be used on clothes in order to distinguish individuals or signify membership of a specific clan or organization. By the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Communication In Feudal Japan
A variety of procedures were used to communicate across the battlefield in feudal Japan, much like in any other culture. These methods included visual signals like flags and banners and audible signals using drums and horns. Messengers on horseback used ciphers and other methods to prevent their messages from falling into the wrong hands. By the beginning of the Sengoku Period, battlefield communications had become fairly complicated affairs, with larger armies than ever before, and a multitude of flags and banners covered in a myriad of colors and designs. Flags and banners Since the beginnings of what we would today recognize as Japanese culture, and probably earlier, various symbols, crests, banners, or markings on armor were used to help identify and distinguish warriors on the battlefield. The '' mon'', or symbol, of a clan or a ''daimyŇć'' was particularly common, identifying which side a warrior fought on; some samurai used their own names or ''mon'' rather than that of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sashimono
''Sashimono'' (śĆáÁČ©, Ś∑ģÁČ©, śĆŅÁČ©) were small banners historically worn by soldiers in feudal Japan, for identification during battles. Description Sashimono poles were attached to the backs of the chest armor (''dŇć'') by special fittings. Sashimono were worn both by foot soldiers - including common soldiers, known as ''ashigaru'', as well as the elite samurai and members of the shogunate - and in special holders on the horses of some cavalry soldiers. The banners, resembling small flags and bearing clan symbols, were most prominent during the ''Sengoku period''—a long period of civil war in Japan from the middle 15th to early 17th century. Variety Given the great variety in Japanese armour, sashimono were used to provide a sense of ‚Äúuniform‚ÄĚ to the armies. The sashimono were typically black and white and came in either square or short rectangular forms, although many variations existed. A variation that is often bigger and coloured is the ''uma-jirushi'', which w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Discoveries
''Ancient Discoveries'' is a television series that premiered on December 21, 2003, on The History Channel. The program focused on ancient technologies. The show's theme was that many inventions which are thought to be modern have ancient roots or in some cases may have been lost and then reinvented. The program was a follow-up to a special originally broadcast in 2005 which focused on technologies from the Ancient Roman era such as the Antikythera mechanism and inventors such as Heron of Alexandria. Episodes of the regular series expanded to cover other areas such as Egypt, China and East Asia, and the Islamic world. ''Ancient Discoveries'' was made for The History Channel by Wild Dream Films based in Cardiff in the UK. Much of the filming was on location across the world. The series used contributions from archaeologists and other experts, footage of historical sites and artifacts, computer generated reconstructions, and dramatized reconstructions along with experiments an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamakura Period
The is a period of Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura by the first ''shŇćgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the Genpei War, which saw the struggle between the Taira and Minamoto clans. The period is known for the emergence of the samurai, the warrior caste, and for the establishment of feudalism in Japan. During the early Kamakura period, the shogunate continued warfare against the Northern Fujiwara which was only defeated in 1189. Then, the authority to the Kamakura rulers waned in the 1190s and power was transferred to the powerful HŇćjŇć clan in the early 13th century with the head of the clan as regent (Shikken) under the shogun which became a powerless figurehead. The later Kamakura period saw the invasions of the Mongols in 1274 and again in 1281. To reduce the amount of chaos, the HŇćjŇć rulers decided to decentralize power by allowing two imperial lines ‚Äď Northern and Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DŇć (armour)
is one of the major components of Japanese armour worn by the samurai and ashigaru or foot soldiers of feudal Japan. History The predecessor of the dŇć was manufactured in Japan as early as the fourth century. ''TankŇć'', worn by foot soldiers, and ''keikŇć'', worn by horsemen, were both pre-samurai types of early Japanese ''cuirass'' constructed from iron plates connected by leather thongs. During the Heian period (794 to 1185), the cuirass evolved into the more familiar style of armour worn by the samurai known as the ''dŇć''. Japanese armourers started to use hardened leather along with iron in their construction methods, and lacquer was used to weather-proof the parts. By the end of the Heian period the Japanese cuirass had arrived at the shape recognized as being distinctly samurai. Leather and or iron scales were used to construct samurai armours, with leather and eventually silk lace used to connect the individual scales (''kozane'') which these cuirasses were now bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabuto
' (ŚÖú, ŚÜĎ) is a type of helmet first used by ancient Japanese warriors which, in later periods, became an important part of the traditional Japanese armour worn by the samurai class and their retainers in feudal Japan. Note that in the Japanese language, the word is an appellative, not a type description, and can refer to any combat helmet. History Japanese helmets dating from the fifth century have been found in excavated tombs. Called (visor-attached helmet), the style of these kabuto came from China and Korea and they had a pronounced central ridge. , which is now known as a samurai helmet, first appeared in the 10th century Heian period with the appearance of ''Ňć-yoroi''. Until the early Muromachi period, were made by combining dozens of thin iron plates. Generally, only daimyo and samurai at the rank of commander wore ornaments called , which were shaped like a pair of hoes. In the middle of the Muromachi period, as the number of large-scale group battles increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ŇĆnin War
The , also known as the Upheaval of ŇĆnin and ŇĆnin-Bunmei war, was a civil war that lasted from 1467 to 1477, during the Muromachi period in Japan. ''ŇĆnin'' refers to the Japanese era during which the war started; the war ended during the Bunmei era. A dispute between a high official, Hosokawa Katsumoto, and a regional lord, Yamana SŇćzen, escalated into a nationwide civil war involving the Ashikaga shogunate and a number of ''daimyŇć'' in many regions of Japan. The war initiated the Sengoku period, "the Warring States period". This period was a long, drawn-out struggle for domination by individual ''daimyŇć'', resulting in a mass power-struggle between the various houses to dominate the whole of Japan. Origin The ''ŇĆnin'' conflict began as a controversy over who would succeed ''shŇćgun'' Ashikaga Yoshimasa. In 1464, Yoshimasa had no heir. He persuaded his younger brother, Ashikaga Yoshimi, to abandon the life of a monk, and named him heir. In 1465, the unanticipated birth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_A_back_view_of_Onikojima_Yatar√ī_Kazutada_in_armor_holding_a_spear_and_a_severed_head.jpg)

.png)

