|
Horn Island (Mississippi)
Horn Island is a long, thin barrier island off the Gulf Coast of Mississippi, south of Ocean Springs, Mississippi, Ocean Springs. It is one of the Mississippi–Alabama barrier islands and part of the Gulf Islands National Seashore. Horn Island is several miles long, but less than a mile wide at its widest point. It occupies about . Description The island, in part, shelters and bounds the Mississippi Sound to its north, and has a long beach on the Gulf of Mexico on its south side. The island is undeveloped, except for a small ranger station mid-island. Part of the Gulf Islands National Seashore, it is a favorite boating destination for those living on the Mississippi Gulf Coast. Horn Island has long stretches of sugar-white sand, dunes punctuated with sea oats, tall pines on small Grove (nature), groves, saw palmettos on small Grove (nature), groves, and a few inland lagoons. It is home to varied wildlife including alligators, ospreys, pelicans, anhingas, ibises, manatees, ducks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi–Alabama Barrier Islands
The Mississippi–Alabama barrier islands are a chain of barrier islands in the Gulf of Mexico along the coasts of Mississippi and Alabama enclosing the Mississippi Sound. The major islands are Cat Island, Ship Island, Horn Island, Petit Bois Island, and Dauphin Island; in the early 20th century the chain also included the Isle of Caprice, which has since been submerged. The islands are separated by wide inlets, several of which have been channelized to form the shipping channels for Gulf coast ports. The shapes and sizes of the islands have changed significantly since the 1800s, with the islands generally shrinking and shifting westward, especially after major tropical cyclones. Most of the islands are uninhabited. Much of the Mississippi portion of the chain is included in the Gulf Islands National Seashore. Geography The Mississippi–Alabama barrier island chain sits offshore from the Mississippi Gulf Coast and runs parallel to the coast for , roughly from the Bay of St. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Oat
''Uniola paniculata'', also known as sea oats, seaside oats, araña, and arroz de costa, is a tall subtropical grass that is an important component of coastal sand dune and beach plant communities in the southeastern United States, eastern Mexico and some Caribbean islands. Its large seed heads that turn golden brown in late summer give the plant its common name. Its tall leaves trap wind-blown sand and promote sand dune growth, while its deep roots and extensive rhizomes act to stabilize them, so the plant helps protect beaches and property from damage due to high winds, storm surges and tides. It also provides food and habitat for birds, small animals and insects. Description ''Uniola paniculata'' is a tall, erect perennial grass that can grow to in height. Its long, thin leaves reach lengths of and are about in width, tapering to a pointed apex. The plant produces inflorescences of flat spikelets, each of which contains 10 to 12 wind-pollinated florets. These rip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tern
Terns are seabirds in the family Laridae that have a worldwide distribution and are normally found near the sea, rivers, or wetlands. Terns are treated as a subgroup of the family Laridae which includes gulls and skimmers and consists of eleven genera. They are slender, lightly built birds with long, forked tails, narrow wings, long bills, and relatively short legs. Most species are pale grey above and white below, with a contrasting black cap to the head, but the marsh terns, the Inca tern, and some noddies have dark plumage for at least part of the year. The sexes are identical in appearance, but young birds are readily distinguishable from adults. Terns have a non-breeding plumage, which usually involves a white forehead and much-reduced black cap. Terns are long-lived birds and are relatively free from natural predators and parasites; most species are declining in numbers due directly or indirectly to human activities, including habitat loss, pollution, disturbance, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form taxon; they do not represent a monophyletic group (the group of all descendants of a single common ancestral species), since swans and geese are not considered ducks. Ducks are mostly aquatic birds, and may be found in both fresh water and sea water. Ducks are sometimes confused with several types of unrelated water birds with similar forms, such as loons or divers, grebes, gallinules and coots. Etymology The word ''duck'' comes from Old English 'diver', a derivative of the verb 'to duck, bend down low as if to get under something, or dive', because of the way many species in the dabbling duck group feed by upending; compare with Dutch and German 'to dive'. This word replaced Old English / 'duck', possibly to avoid confusion with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
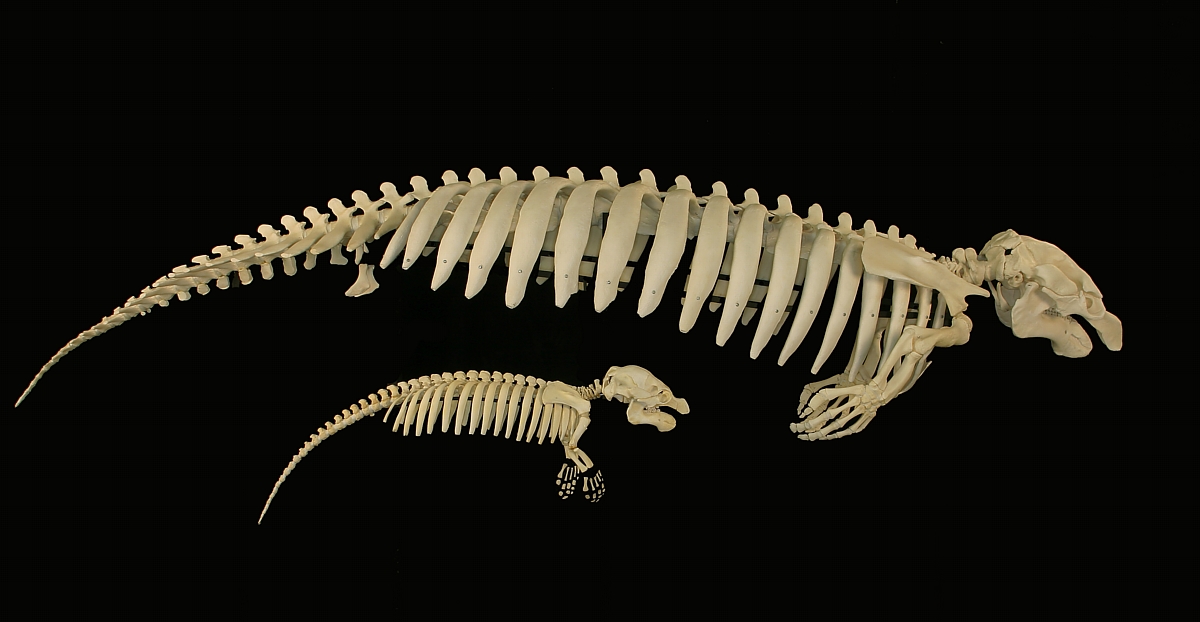
Manatee
Manatees (family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living species in the order Sirenia: the Amazonian manatee (''Trichechus inunguis''), the West Indian manatee (''Trichechus manatus''), and the West African manatee (''Trichechus senegalensis''). They measure up to long, weigh as much as , and have paddle-like tails. Manatees are herbivores and eat over 60 different freshwater and saltwater plants. Manatees inhabit the shallow, marshy coastal areas and rivers of the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, the Amazon basin, and West Africa. The main causes of death for manatees are human-related issues, such as habitat destruction and human objects. Their slow-moving, curious nature has led to violent collisions with propeller-driven boats and ships. Some manatees have been found with over 50 scars on them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
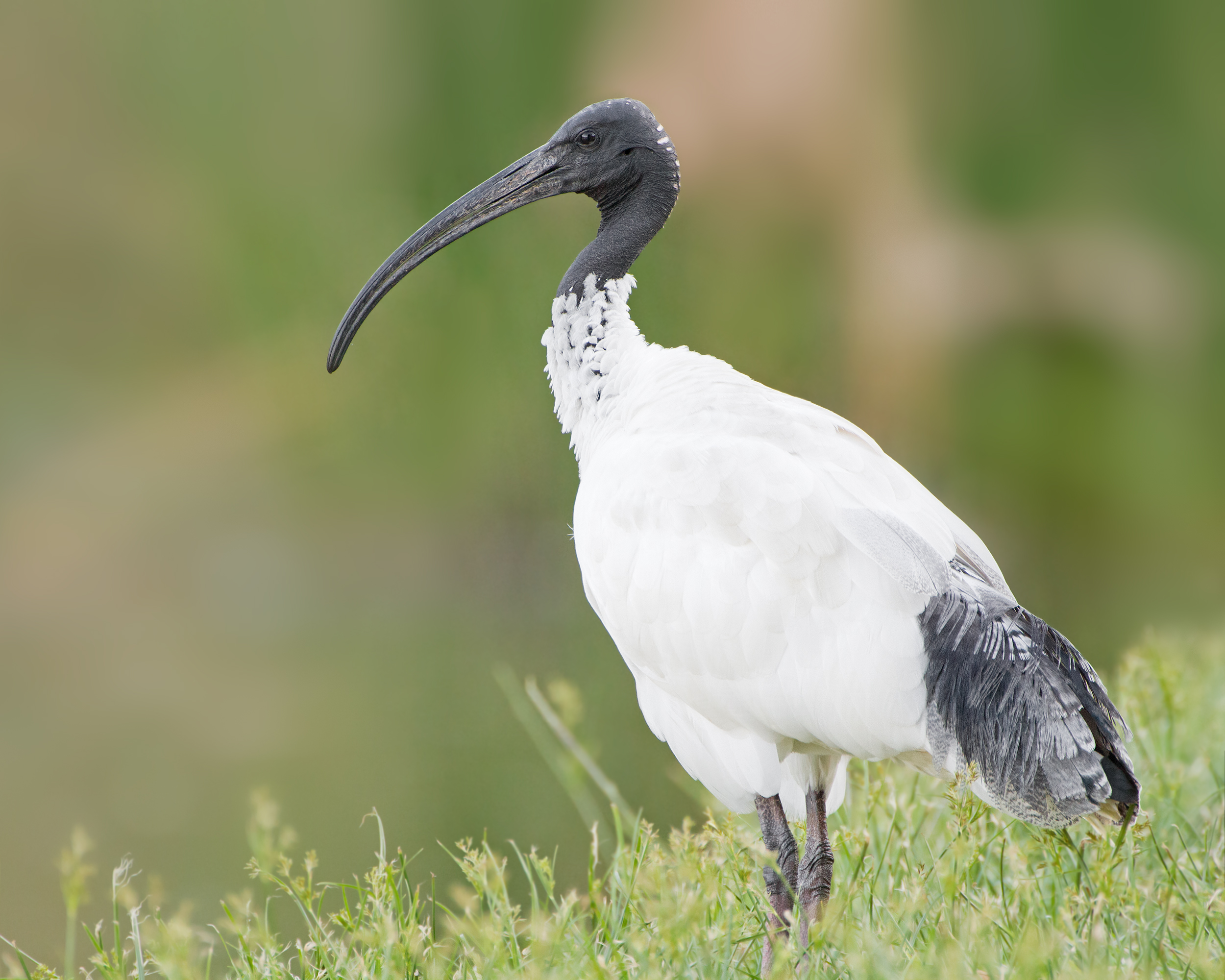
Ibis
The ibises () (collective plural ibis; classical plurals ibides and ibes) are a group of long-legged wading birds in the family Threskiornithidae, that inhabit wetlands, forests and plains. "Ibis" derives from the Latin and Ancient Greek word for this group of birds. It also occurs in the scientific name of the cattle egret (''Bubulcus ibis'') mistakenly identified in 1757 as being the sacred ibis. Description Ibises all have long, downcurved bills, and usually feed as a group, probing mud for food items, usually crustaceans. They are monogamous and highly territorial while nesting and feeding. Most nest in trees, often with spoonbills or herons. All extant species are capable of flight, but two extinct genera were flightless, namely the kiwi-like ''Apteribis'' in the Hawaiian Islands, and the peculiar '' Xenicibis'' in Jamaica. The word ''ibis'' comes from Latin ''ibis'' from Greek ἶβις ''ibis'' from Egyptian ''hb'', ''hīb''. Beekes, R. S. P. (2009) ''Etymological Dicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhinga
The anhinga (; ''Anhinga anhinga''), sometimes called snakebird, darter, American darter, or water turkey, is a water bird of the warmer parts of the Americas. The word ''anhinga'' comes from ''a'ñinga'' in the Brazilian Tupi language and means "devil bird" or "snake bird". The origin of the name is apparent when swimming: only the neck appears above water so the bird looks like a snake ready to strike. They do not have external nares (nostrils) and breathe solely through their epiglottis. The anhinga is placed in the darter family, Anhingidae, and is closely related to Indian (''Anhinga melanogaster''), African (''Anhinga rufa''), and Australian (''Anhinga novaehollandiae'') darters. Like other darters, the anhinga hunts by spearing fish and other small prey using its sharp, slender beak. Distribution and migration ''Anhinga'' species are found all over the world in warm shallow waters. The American anhinga has been subdivided into two subspecies, ''A. a. anhinga'' and ''A. a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelican
Pelicans (genus ''Pelecanus'') are a genus of large water birds that make up the family Pelecanidae. They are characterized by a long beak and a large throat pouch used for catching prey and draining water from the scooped-up contents before swallowing. They have predominantly pale plumage, except for the brown and Peruvian pelicans. The bills, pouches, and bare facial skin of all pelicans become brightly coloured before the breeding season. The eight living pelican species have a patchy global distribution, ranging latitudinally from the tropics to the temperate zone, though they are absent from interior South America and from polar regions and the open ocean. Long thought to be related to frigatebirds, cormorants, tropicbirds, and gannets and boobies, pelicans instead are now known to be most closely related to the shoebill and hamerkop, and are placed in the order Pelecaniformes. Ibises, spoonbills, herons, and bitterns have been classified in the same order. Fossil ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osprey
The osprey (''Pandion haliaetus''), , also called sea hawk, river hawk, and fish hawk, is a diurnal, fish-eating bird of prey with a cosmopolitan range. It is a large raptor reaching more than in length and across the wings. It is brown on the upperparts and predominantly greyish on the head and underparts. The osprey tolerates a wide variety of habitats, nesting in any location near a body of water providing an adequate food supply. It is found on all continents except Antarctica, although in South America it occurs only as a non-breeding migrant. As its other common names suggest, the osprey's diet consists almost exclusively of fish. It possesses specialised physical characteristics and exhibits unique behaviour to assist in hunting and catching prey. As a result of these unique characteristics, it has been given its own taxonomic genus, ''Pandion'', and family, Pandionidae. Taxonomy The osprey was described by Carl Linnaeus under the name ''Falco haliaeetus'' in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alligator
An alligator is a large reptile in the Crocodilia order in the genus ''Alligator'' of the family Alligatoridae. The two extant species are the American alligator (''A. mississippiensis'') and the Chinese alligator (''A. sinensis''). Additionally, several extinct species of alligator are known from fossil remains. Alligators first appeared during the Oligocene epoch about 37 million years ago. The name "alligator" is probably an anglicized form of ', the Spanish term for "the lizard", which early Spanish explorers and settlers in Florida called the alligator. Later English spellings of the name included ''allagarta'' and ''alagarto''. Evolution Alligators and caimans split in North America during the early Tertiary or late Cretaceous (about 53 million to about 65 million years ago). The Chinese alligator split from the American alligator about 33 million years ago and probably descended from a lineage that crossed the Bering land bridge during the Neogene. The modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildlife
Wildlife refers to domestication, undomesticated animal species (biology), species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wilderness, wild in an area without being species, introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game (hunting), game: those birds and mammals that were trophy hunting, hunted for sport. Wildlife can be found in all ecosystems. Deserts, plains, grasslands, woodlands, forests, and other areas, including the most developed urban areas, all have distinct forms of wildlife. While the term in popular culture usually refers to animals that are untouched by human factors, most scientists agree that much wildlife is human impact on the environment, affected by human behavior, human activities. Some wildlife threaten human safety, health, property, and quality of life. However, many wild animals, even the dangerous ones, have value to human beings. This value might be economic, educational, or emotional in nature. Humans have historically t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') and ''atoll lagoons''. They have also been identified as occurring on mixed-sand and gravel coastlines. There is an overlap between bodies of water classified as coastal lagoons and bodies of water classified as estuaries. Lagoons are common coastal features around many parts of the world. Definition and terminology Lagoons are shallow, often elongated bodies of water separated from a larger body of water by a shallow or exposed shoal, coral reef, or similar feature. Some authorities include fresh water bodies in the definition of "lagoon", while others explicitly restrict "lagoon" to bodies of water with some degree of salinity. The distinction between "lagoon" and "estuary" also varies between authorities. Richard A. Davis Jr. restrict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_in_Florida.jpg)






.jpg)
