|
Horbruch
Horbruch is an ''Ortsgemeinde'' – a Municipalities of Germany, municipality belonging to a ''Verbandsgemeinde'', a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld (district), Birkenfeld Districts of Germany, district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' Herrstein-Rhaunen, whose seat is in Herrstein. Geography Location The municipality lies in the Hunsrück northwest of the 746 m-high Idarkopf. The municipal area is 44.3% wooded, and its elevation is 460 m above sea level. Neighbouring municipalities Horbruch borders in the north on the municipality of Hirschfeld, Rhineland-Palatinate, Hirschfeld (Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis), in the east on the municipality of Krummenau and in the west on the municipality of Hochscheid (Bernkastel-Wittlich district). Constituent communities Also belonging to Horbruch are the outlying homesteads of Bergmühle, Emmerichsmühle, Forsthaus Horbruch, Hockenmühle and Neumühle. History Archaeology, Arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krummenau
Krummenau is an '' Ortsgemeinde'' – a municipality belonging to a ''Verbandsgemeinde'', a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' Herrstein-Rhaunen, whose seat is in Herrstein. Geography Location The municipality lies in the Hunsrück north of the 746 m-high Idarkopf in the Idar Forest. The municipal area is 61.6% wooded. The Idarbach flows through the village. Neighbouring municipalities Krummenau borders in the north on the municipality of Niederweiler, in the east on the municipality of Laufersweiler and in the west on the municipality of Horbruch. Constituent communities Also belonging to Krummenau is the outlying homestead of Weylandsmühle. History First documentary mention On 20 November 1086, Krummenau had its first documentary mention in a donation document From Archbishop Wezilo. A manuscript from the late 18th century – kept at the archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birkenfeld (district)
Birkenfeld () is a district (''Landkreis'') in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Its seat is the town of Birkenfeld. It is bounded by (from the south and clockwise) the districts of Sankt Wendel (Saarland), Trier-Saarburg, Bernkastel-Wittlich, Rhein-Hunsrück, Bad Kreuznach and Kusel. History In the early nineteenth century, the Nahe River was the boundary between two tiny principalities: Birkenfeld, west of the Nahe; and Lichtenberg, east of it. The principality of Birkenfeld was annexed by Oldenburg in 1817; Lichtenberg became an exclave of the Duchy Saxe-Coburg (Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld until 1826, Saxe-Coburg and Gotha thereafter). Prussia bought Lichtenberg in 1834 and made it the District of Sankt Wendel. After World War I, the southern half of Sankt Wendel had to be ceded to the newly created Saar Territory, and the small part remaining in Prussia was then officially called the ''Restkreis Sankt Wendel'' ("remaining district of Sankt Wendel"). In 1937 the Oldenburgian Dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hochscheid
Hochscheid is an ''Ortsgemeinde'' – a municipality belonging to a ''Verbandsgemeinde'', a kind of collective municipality – in the Bernkastel-Wittlich district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Geography Location This rural municipality lies in the middle of low-mountain country in the Hunsrück, at the foot of the Idarkopf. Hochscheid belongs to the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Bernkastel-Kues, whose seat is in the like-named town. Neighbouring municipalities Neighbouring municipalities within a five-kilometre radius are Horbruch (1.19 km away as the crow flies), Wahlenau (3.02 km), Hirschfeld (3.02 km), Kleinich (3.03 km) and Krummenau (3.58 km). The nearest middle centre is Bernkastel-Kues. History Antiquity The most important sanctuary to the Gallic divinity Sirona stands in Hochscheid, where a Latin inscription “DEO APOLLINI ET SANCTE SIRONE” (Eng. "To the god Apollo and holy Sirona") can also be found, in which the Roman Apollo like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herrstein-Rhaunen
Herrstein-Rhaunen is a ''Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") in the district of Birkenfeld, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The seat of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' is in Herrstein. It was formed on 1 January 2020 by the merger of the former ''Verbandsgemeinden'' Herrstein and Rhaunen. The ''Verbandsgemeinde'' Herrstein-Rhaunen consists of the following ''Ortsgemeinden'' ("local municipalities"): # Allenbach # Asbach # Bergen # Berschweiler bei Kirn # Bollenbach # Breitenthal # Bruchweiler # Bundenbach # Dickesbach # Fischbach # Gerach # Gösenroth # Griebelschied # Hausen # Hellertshausen # Herborn # Herrstein # Hettenrodt # Hintertiefenbach # Horbruch # Hottenbach # Kempfeld # Kirschweiler # Krummenau # Langweiler # Mackenrodt # Mittelreidenbach # Mörschied # Niederhosenbach # Niederwörresbach # Oberhosenbach # Oberkirn # Oberreidenbach # Oberwörresbach # Rhaunen # Schauren # Schmidthachenbach # Schwerbach # Sensweiler # Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ortsgemeinde
A Verbandsgemeinde (; plural Verbandsgemeinden) is a low-level administrative division, administrative unit in the Germany, German States of Germany, federal states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Saxony-Anhalt. A Verbandsgemeinde is typically composed of a small group of villages or towns. Rhineland-Palatinate The state of Rhineland-Palatinate is divided into 163 Verbandsgemeinden, which are municipal associations grouped within the 24 Districts of Germany, districts of the state and subdivided into 2,257 Ortsgemeinden (singular Ortsgemeinde) which comprise single settlements. Most of the Verbandsgemeinden were established in 1969. Formerly the name for an administrative unit was ''Amt (political division), Amt''. Most of the functions of municipal government for several municipalities are consolidated and administered centrally from a larger or more central town or municipality among the group, while the individual municipalities (Ortsgemeinden) still maintain a limited degree of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idar Forest
The Idar Forest (German: ''Idarwald'', Celtic: ''"id ar"'' - hill forest above the land) is part of the Hunsrück low mountain range in the German federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Geography The Idar Forest lies in the districts of Bernkastel-Wittlich and Birkenfeld in the northeast of the Saar-Hunsrück Nature Park. It lies more or less in the triangle formed by the villages of Morbach (in the northwest), Rhaunen (northeast) and Idar-Oberstein (southeast), but apart from Morbach – does not extend as far as these places. The underlying rocks are primarily made up of Lower Devonian quartzites. Mountains Amongst the highest mountains in the Idar Forest are: * An den zwei Steinen (766 m) * Kahlheid (766 m) * Steingerüttelkopf (757 m) * Ruppelstein (755 m) * Idarkopf (746 m) - crowned by the Idarkopf Tower * Usarkopf (724 m) Bodies of water Streams The following streams rise in, or on the edge of, the Idar Forest: * Dhron * Idarbach (Nahe) - rises ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir), Buddhism, Sikhism (whose temples are called gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Islam (whose temples are called mosques), Judaism (whose temples are called synagogues), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baha'i Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baha'i House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are sometimes called Jinja), Confucianism (which are sometimes called the Temple of Confucius), and ancient religions such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. The form and function of temples are thus very variable, though they are often considered by believers to be, in some sense, the "house" of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirona
In Celtic polytheism, Sirona was a goddess worshipped predominantly in East Central Gaul and along the Danubian limes. A healing deity, she was associated with healing springs; her attributes were snakes and eggs. She was sometimes depicted with Apollo Grannus or Apollo Borvo. She was particularly worshipped by the Treveri in the Moselle Valley. Sirona's name The name of the goddess was written in various ways: ''Sirona'', ''Đirona'', ''Thirona'', indicating some difficulty in capturing the initial sound in the Latin alphabet. The symbol Đ is used here to represent the ''tau gallicum'', an additional letter used in Gaulish representing the cluster ''ts'' which was interchangeable with ''st''- in word-initial position and it is not a form of the letter "D". The root is a long vowel Gaulish variant of proto-Celtic ''*ster-'' (''*h2ster'') meaning ‘star’. The same root is found in Old Irish as ''ser'', Welsh ''seren'', Middle Cornish ''sterenn'' and Breton ''steren(n)''. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
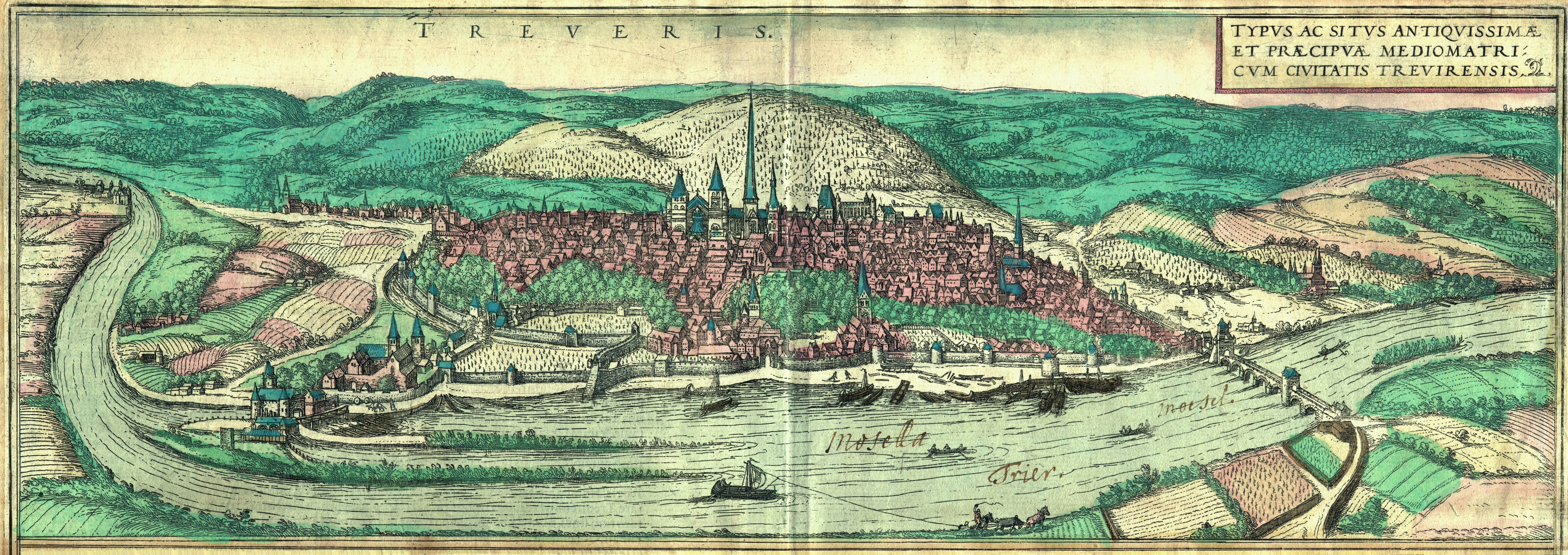
History Of Trier
Trier in Rhineland-Palatinate, whose history dates to the Roman Empire, is often claimed to be the oldest city in Germany. Traditionally it was known in English by its French name of Treves. Prehistory The first traces of human settlement in the area of the city show evidence of linear pottery settlements dating from the early Neolithic period. Since the last pre-Christian centuries, members of the Celtic tribe of the Treveri settled in the area of today's Trier. Roman Empire The Romans under Julius Caesar first subdued the Treveri in 58 to 50 BC. No later than 16 BC, at the foot of the hill later christened the Petrisberg, upon which a military camp had been set up in 30 BC and abandoned again a few months later, the Romans founded the city of ("City of Augustus in the land of the Treveri"), which has a claim to being the oldest city in Germany. The honour of being named after the Emperor was only locally shared by Augsburg and Augst in northern Switzerland. Followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grannus
Grannus (also ''Granus'', ''Mogounus,'' and ''Amarcolitanus'') was a Celtic deity of classical antiquity. He was regularly identified with Apollo as Apollo Grannus and frequently worshipped in conjunction with Sirona, and sometimes with Mars and other deities. Name Etymology The theonym ''Grannus'' is a latinized form of Gaulish ''Grannos''. The same stem appears in the personal names ''Grania'', ''Grannia'', ''Grannicus'', and ''Grannica'', as well as in the place names ''Grignols'' (from an earlier *''Granno-ialon'' 'Grannus' clearing'), ''Aquae Granni'' (> '' Aachen''), and ''Granéjouls''. Its etymology remains debated. The name could be connected to Proto-Celtic *''grand''-''/grend-'', meaning 'beard' (cf. Middle Irish ''grend'', Middle Welsh ''grann'' 'chin, beard, cheek', Middle Breton ''grann'' 'eyebrow'), although some scholars have pointed that the god is never actually portrayed with a beard. Old French ''grenon'' ('small beard'), Old Spanish ''greñon'' ('beard') and Oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grave Goods
Grave goods, in archaeology and anthropology, are the items buried along with the body. They are usually personal possessions, supplies to smooth the deceased's journey into the afterlife or offerings to the gods. Grave goods may be classed as a type of votive deposit. Most grave goods recovered by archaeologists consist of inorganic objects such as pottery and stone and metal tools but organic objects that have since decayed were also placed in ancient tombs. The grave goods were to be useful to the deceased in the afterlife; therefore their favorite foods or everyday objects were left with them. Often times social status played a role in what was left and how often it was left. Funerary art is a broad term but generally means artworks made specifically to decorate a burial place, such as miniature models of possessions including slaves or servants for "use" in the afterlife. Although, in ancient Egypt they would sometimes bury the real servants with the deceased. Where grave go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |