|
Horae Canonicae
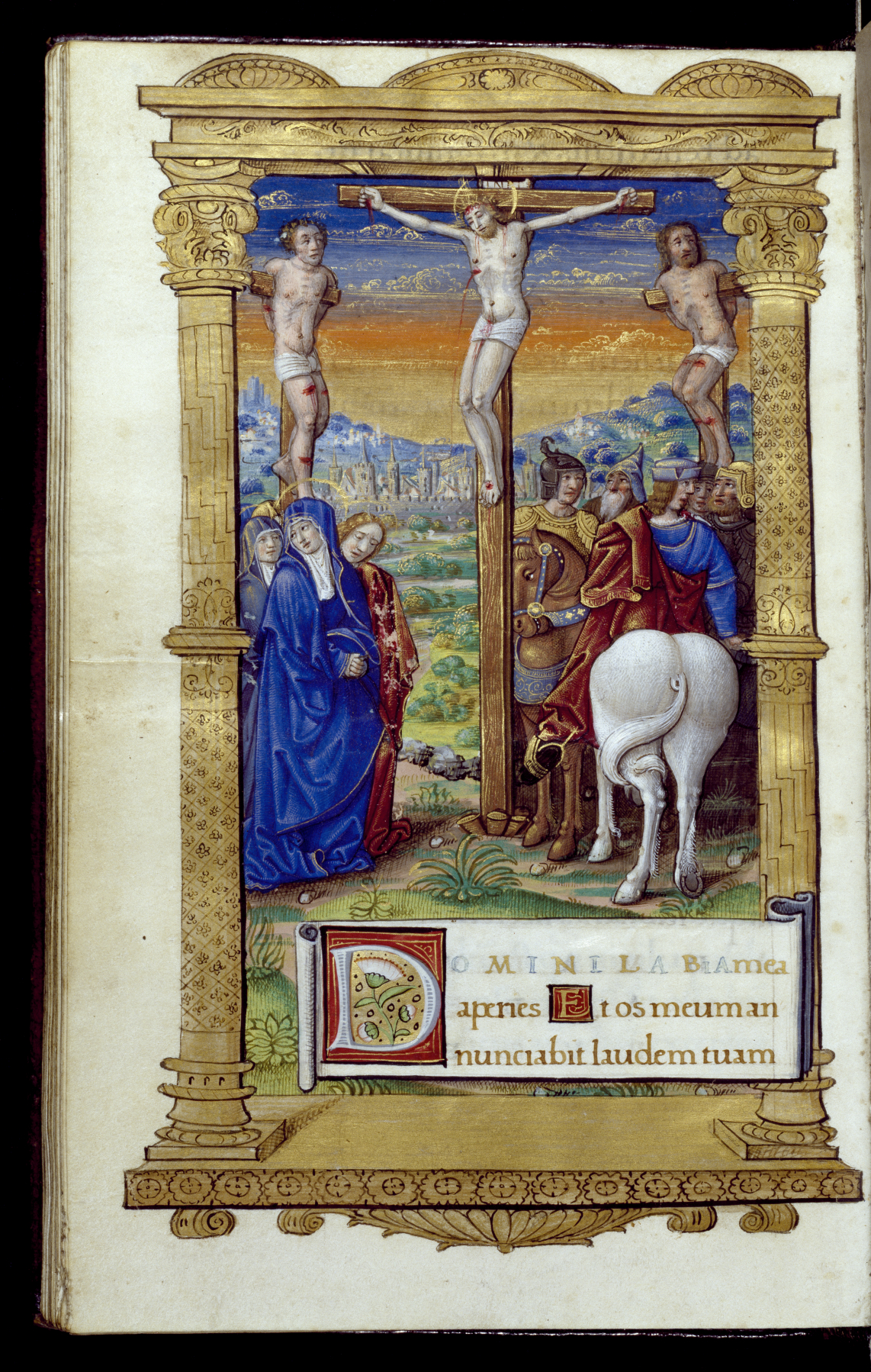
''Horae Canonicae'' is a series of poems by W. H. Auden written between 1949 and 1955. The title is a reference to the canonical hours of the Christian Church, as are the titles of the seven poems constituting the series: "Prime", "Terce", "Sext", "Nones", "Vespers", "Compline", and "Lauds". Each refers to a fixed time of the day for prayer. The canonical hours create a framework for the dramatization of Auden's religious position, which he described in a letter as "very much the same as Reinhold eibuhrs, i.e. Augustinian, not Thomist (I would allow a little more place, perhaps, for the '' Via Negativa''.) Liturgically, I am Anglo-Catholic...". "Prime" and "Nones" were first published in Auden's collection ''Nones'' (1951). ''Horae Canonicae'' was published as a unity in Auden's ''The Shield of Achilles'' (1955). See also *Diurnal offices In the practice of Christianity, canonical hours mark the divisions of the day in terms of fixed times of prayer at regular interv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canonical Hours
In the practice of Christianity, canonical hours mark the divisions of the day in terms of fixed times of prayer at regular intervals. A book of hours, chiefly a breviary, normally contains a version of, or selection from, such prayers. In the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church, canonical hours are also called ''offices'', since they refer to the official set of prayers of the Church, which is known variously as the ("divine service" or "divine duty"), and the ("work of God"). The current official version of the hours in the Roman Rite is called the Liturgy of the Hours ( la, liturgia horarum) in North America or divine office in Ireland and Britain. In Lutheranism and Anglicanism, they are often known as the daily office or divine office, to distinguish them from the other "offices" of the Church (e.g. the administration of the sacraments). In the Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Catholic Churches, the canonical hours may be referred to as the divine services, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustinianism
Augustinianism is the philosophical and theological system of Augustine of Hippo and its subsequent development by other thinkers, notably Boethius, Anselm of Canterbury and Bonaventure. Among Augustine's most important works are ''The City of God'', '' De doctrina Christiana'', and '' Confessions''. Originally, Augustinianism developed in opposition to Pelagianism; it was widespread in medieval western philosophy until the arrival of Thomism and Aristotelianism. Plato and Plotinus influenced Augustine in many ways, and he is considered a Neoplatonic philosopher. The Augustinian theodicy and other Augustinian doctrines such as the divine illumination and the invisible church show a strong Platonic influence. Pope Benedict XVI cautioned that all of the Western Church teaching leads to him: View of humanity "Augustine considered the human race as a compact mass, a collective body, responsible in its unity and solidarity. Carrying out his system in all its logical consequences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diurnal Offices
In the practice of Christianity, canonical hours mark the divisions of the day in terms of Fixed prayer times#Christianity, fixed times of prayer at regular intervals. A book of hours, chiefly a breviary, normally contains a version of, or selection from, such prayers. In the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church, canonical hours are also called ''offices'', since they refer to the official set of prayers of the Church, which is known variously as the ("divine service" or "divine duty"), and the ("work of God"). The current official version of the hours in the Roman Rite is called the Liturgy of the Hours ( la, liturgia horarum) in North America or divine office in Ireland and Britain. In Lutheranism and Anglicanism, they are often known as the daily office or divine office, to distinguish them from the other "offices" of the Church (e.g. the administration of the sacraments). In the Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Rite, Byzantine Catholic Churches, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Shield Of Achilles
''The Shield of Achilles'' is a poem by W. H. Auden first published in 1952, and the title work of a collection of poems by Auden, published in 1955. It is Auden's response to the detailed description, or ''ekphrasis'', of the Shield of Achilles, shield borne by the hero Achilles in Homer's epic poem the ''Iliad''. Description Auden's poem is written in two different stanza forms, one form with shorter lines, the other with longer lines. The stanzas with shorter lines describe the making of the shield by the god Hephaestus, and report the scenes that Achilles' mother, the Nereid Thetis, expects to find on the shield and which Hephaestus, in Auden's version, does not make. Thetis expects to find scenes of happiness and peace like those described by Homer. The stanzas with longer lines describe the scenes of a barren and impersonal modern world that Hephaestus creates in Auden's version. In the first scene described by these stanzas, an anonymous, dispassionate army listens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1951 In Poetry
Nationality words link to articles with information on the nation's poetry or literature (for instance, Irish or France). Events * Poet Cid Corman begins ''Origin'' magazine in response to the failure of a magazine that Robert Creeley had planned. The magazine typically features one writer per issue and runs, with breaks, until the mid-1980s. Poets featured include Robert Creeley, Robert Duncan, Larry Eigner, Denise Levertov, William Bronk, Theodore Enslin, Charles Olson, Louis Zukofsky, Gary Snyder, Lorine Niedecker, Wallace Stevens, William Carlos Williams and Paul Blackburn. The magazine also leads to the establishment of Origin Press, which publishes books by a similar range of poets. * ''Bad Lord Byron'', a film directed by David MacDonald about the Romantic poet.Web page title"A Time-Line of Poetry in English"at the Representative Poetry Online website of the University of Toronto, retrieved December 20, 2008 * Czesław Miłosz, Polish poet, translator, literary critic, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nones (Auden)
''Nones'' is a book of poems by W. H. Auden published in 1951 by Faber & Faber. The book contains Auden's shorter poems written between 1946 and 1950, including " In Praise of Limestone", "Prime", "Nones," "Memorial for the City", "Precious Five", and "A Walk After Dark". "Nones" is a contemporary setting of the Good Friday Passion. The book includes "Barcarolle" (barcarolle), a poem from Auden's libretto for Igor Stravinsky's ''The Rake's Progress'', the only poem in the book that did not appear in Auden's later collections. The book is dedicated to Protestant theologian Reinhold Niebuhr and his wife Ursula. Composer Luciano Berio named his orchestral piece ''Nones'', originally planned as an oratorio, after Auden's poem. References * John Fuller, ''W. H. Auden: A Commentary'' (1999) *Edward Mendelson __NOTOC__ Edward Mendelson (born March 15, 1946) is a professor of English and Comparative Literature and the Lionel Trilling Professor in the Humanities at Columbia Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Catholic
Anglo-Catholicism comprises beliefs and practices that emphasise the Catholic heritage and identity of the various Anglican churches. The term was coined in the early 19th century, although movements emphasising the Catholic nature of Anglicanism already existed. Particularly influential in the history of Anglo-Catholicism were the Caroline Divines of the 17th century, the Jacobite Nonjuring schism of the 17th and 18th centuries, and the Oxford Movement, which began at the University of Oxford in 1833 and ushered in a period of Anglican history known as the "Catholic Revival". A minority of Anglo-Catholics, sometimes called Anglican Papalists, consider themselves under papal supremacy even though they are not in communion with the Roman Catholic Church. Such Anglo-Catholics, especially in England, often celebrate Mass according to the Mass of Paul VI and are concerned with seeking reunion with the Roman Catholic Church. Members of the Roman Catholic Church's personal ordinar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Negativa
Apophatic theology, also known as negative theology, is a form of theological thinking and religious practice which attempts to approach God, the Divine, by negation, to speak only in terms of what may not be said about the perfect goodness that is God. It forms a pair together with cataphatic theology, which approaches God or the Divine by affirmations or positive statements about what God ''is''. The apophatic tradition is often, though not always, allied with the approach of mysticism, which aims at the vision of God, the perception of the divine reality beyond the realm of ordinary perception. Etymology and definition "Apophatic", grc, ἀπόφασις (noun); from ἀπόφημι ''apophēmi'', meaning 'to deny'. From '' Online Etymology Dictionary'': ''Via negativa'' or ''via negationis'' (Latin), 'negative way' or 'by way of denial'. The negative way forms a pair together with the '' kataphatic'' or positive way. According to Deirdre Carabine, Origins and dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomist
Thomism is the philosophical and theological school that arose as a legacy of the work and thought of Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274), the Dominican philosopher, theologian, and Doctor of the Church. In philosophy, Aquinas' disputed questions and commentaries on Aristotle are perhaps his best-known works. In theology, his ''Summa Theologica'' is amongst the most influential documents in medieval theology and continues to be the central point of reference for the philosophy and theology of the Catholic Church. In the 1914 motu proprio ''Doctoris Angelici'', Pope Pius X cautioned that the teachings of the Church cannot be understood without the basic philosophical underpinnings of Aquinas' major theses: Overview Thomas Aquinas held and practiced the principle that truth is to be accepted no matter where it is found. His doctrines drew from Greek, Roman, Islamic and Jewish philosophers. Specifically, he was a realist (i.e. unlike skeptics, he believed that the world can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinhold Neibuhr
Karl Paul Reinhold Niebuhr (June 21, 1892 – June 1, 1971) was an American Reformed theologian, ethicist, commentator on politics and public affairs, and professor at Union Theological Seminary for more than 30 years. Niebuhr was one of America's leading public intellectuals for several decades of the 20th century and received the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1964. A public theologian, he wrote and spoke frequently about the intersection of religion, politics, and public policy, with his most influential books including ''Moral Man and Immoral Society'' and ''The Nature and Destiny of Man''. The latter is ranked number 18 of the top 100 non-fiction books of the twentieth century by Modern Library. Andrew Bacevich labelled Niebuhr's book ''The Irony of American History'' "the most important book ever written on U.S. foreign policy." The historian Arthur Schlesinger Jr. described Niebuhr as "the most influential American theologian of the 20th century" and ''Time'' posthumousl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym for Christianity, despite the fact that it is composed of multiple churches or denominations, many of which hold a doctrinal claim of being the "one true church", to the exclusion of the others. For many Protestant Christians, the Christian Church has two components: the church visible, institutions in which "the Word of God purely preached and listened to, and the sacraments administered according to Christ's institution", as well as the church invisible—all "who are truly saved" (with these beings members of the visible church). In this understanding of the invisible church, "Christian Church" (or catholic Church) does not refer to a particular Christian denomination, but includes all individuals who have been saved. The branch theory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lauds
Lauds is a canonical hour of the Divine office. In the Roman Rite Liturgy of the Hours it is one of the major hours, usually held after Matins, in the early morning hours. Name The name is derived from the three last psalms of the psalter (148, 149, 150), the Laudate psalms, which in former versions of the Lauds of the Roman Rite occurred every day, and in all of which the word ''laudate'' is repeated frequently. At first, the word ''Lauds'' designated only the end, that is to say, these three psalms. Little by little the ''Lauds'' was applied to the whole office. History Lauds, or the Morning Office or Office of Aurora, is one of the most ancient Offices and can be traced back to Apostolic times. The earliest evidence of Lauds appears in the second and third centuries in the Canons of Hippolytus and in writings by St. Cyprian, and the Apostolic Fathers. Descriptions during the fourth and fifth centuries appear in writings by John Cassian, St. Melania the Younger, St. Hilary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)