|
Honda RS125R
The Honda RS125R was a 125 cc two-stroke Grand Prix racing motorcycle manufactured by Honda Racing Corporation for racing purposes only. It debuted in 1980, racing in the All Japan Road Race Championship. In 1987 a redesigned version was entered in the World Championship ridden by Ezio Gianola; since 1988 the new bikes were manufactured also for customer teams. The Honda RS125R has won nine World Championship titles for riders, with Loris Capirossi, Dirk Raudies, Haruchika Aoki, Emilio Alzamora, Dani Pedrosa, Andrea Dovizioso and Thomas Lüthi Thomas Lüthi (born 6 September 1986) is a Swiss sporting director at Prüstel GP, and former Grand Prix motorcycle racer. He spent 19 years in Grand Prix world championships, becoming one of only six riders to reach 300 race starts, spending m ..., while Honda was crowned Constructors' World Champion eleven times. 1995 Honda RS125R specifications References RS125R Grand Prix motorcycles Motorcycles introduced in 1987 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honda Racing Corporation
Honda Racing Corporation (HRC) is a division of the Honda Motor Company formed in 1982. The company combines participation in motorcycle races throughout the world with the development of racing machines. Its racing activities are an important source for the creation of technologies used in the development of Honda motorcycles. HRC activities include sales of production racing motorcycles, support for satellite teams, and rider education programs. History Initially, Honda's racing efforts were run from within the company. In the early 1970s, the Racing Service Center (RSC) was created as a separate company to oversee racing. On September 1, 1982, RSC became HRC, and ran Honda's road racing, endurance, trials and motocross racing programs. Research and development User support HRC has HRC Service Shops at 23 locations in Japan and seven sites overseas. Ownership HRC is a wholly owned subsidiary of Honda is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haruchika Aoki
is a former Grand Prix motorcycle road racer. He was a two-time F.I.M. 125cc world champion. He is the youngest of three Aoki brothers who have competed in motorcycle Grand Prix races. Aoki began his Grand Prix career in 1993 with Honda. He won two consecutive 125cc world championships in 1995 and 1996 with Honda before moving up to the 250cc class in 1997. After two years in the 250cc class, Aoki made the move to the 500cc class in 1999. In , he competed in the Superbike World Championship on a Ducati before returning to Grand Prix racing in 2001. Racing a V-twin, two-stroke Honda NSR500V, he finished the season as the top privateer. He almost pulled off an upset that year when he "won" the second half of the restarted Italian Grand Prix in torrential rain, but the race was decided on aggregate times from the first and second parts, meaning he was classified only fifth. Aoki retired after the 2002 season. Afterwards, he participated in the Japanese Auto Race Auto racing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are the mechanical horsepower (or imperial horsepower), which is about 745.7 watts, and the metric horsepower, which is approximately 735.5 watts. The term was adopted in the late 18th century by Scottish engineer James Watt to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses. It was later expanded to include the output power of other types of piston engines, as well as turbines, electric motors and other machinery. The definition of the unit varied among geographical regions. Most countries now use the SI unit watt for measurement of power. With the implementation of the EU Directive 80/181/EEC on 1 January 2010, the use of horsepower in the EU is permitted only as a supplementary unit. History The development of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke (engine)
In the context of an internal combustion engine, the term stroke has the following related meanings: * A phase of the engine's cycle (e.g. compression stroke, exhaust stroke), during which the piston travels from top to bottom or vice versa. * The type of power cycle used by a piston engine (e.g. two-stroke engine, four-stroke engine). * "Stroke length", the distance travelled by the piston during each cycle. The stroke length––along with bore diameter––determines the engine's displacement. Phases in the power cycle Commonly used engine phases or strokes (i.e. those used in a four-stroke engine) are described below. Other types of engines can have very different phases. Induction-intake stroke The induction stroke is the first phase in a four-stroke (e.g. Otto cycle or Diesel cycle) engine. It involves the downward movement of the piston, creating a partial vacuum that draws a air-fuel mixture (or air alone, in the case of a direct injection engine) into the combus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bore (engine)
In a piston engine, the bore (or cylinder bore) is the diameter of each cylinder. Engine displacement is calculated based on bore, stroke length and the number of cylinders: displacement = The stroke ratio, determined by dividing the bore by the stroke, traditionally indicated whether an engine was designed for power at high engine speeds ( rpm) or torque at lower engine speeds. The term "bore" can also be applied to the bore of a locomotive cylinder or steam engine pistons. Steam locomotive The term bore also applies to the cylinder of a steam locomotive or steam engine. See also * Bore pitch * Compression ratio * Engine displacement Engine displacement is the measure of the cylinder volume swept by all of the pistons of a piston engine, excluding the combustion chambers. It is commonly used as an expression of an engine's size, and by extension as a loose indicator of t ... References {{Steam engine configurations Engine technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Displacement
Engine displacement is the measure of the cylinder volume swept by all of the pistons of a piston engine, excluding the combustion chambers. It is commonly used as an expression of an engine's size, and by extension as a loose indicator of the power an engine might be capable of producing and the amount of fuel it should be expected to consume. For this reason displacement is one of the measures often used in advertising, as well as regulating, motor vehicles. It is usually expressed using the metric units of cubic centimetres (cc or cm3, equivalent to millilitres) or litres (l or L), orparticularly in the United States cubic inches (CID, cu in, or in3). Definition The overall displacement for a typical reciprocating piston engine is calculated by multiplying together three values; the distance travelled by the piston (the stroke length), the circular area of the cylinder, and the number of cylinders in the whole engine. The formula is: : \text = \text \times \frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-stroke Cycle
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle during two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust (or scavenging) functions occurring at the same time. Two-stroke engines often have a high power-to-weight ratio, power being available in a narrow range of rotational speeds called the power band. Two-stroke engines have fewer moving parts than four-stroke engines. History The first commercial two-stroke engine involving cylinder compression is attributed to Scottish engineer Dugald Clerk, who patented his design in 1881. However, unlike most later two- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Cooling
Cooling tower and water discharge of a nuclear power plant Water cooling is a method of heat removal from components and industrial equipment. Evaporative cooling using water is often more efficient than air cooling. Water is inexpensive and non-toxic; however, it can contain impurities and cause corrosion. Water cooling is commonly used for cooling automobile internal combustion engines and power stations. Water coolers utilising convective heat transfer are used inside high-end personal computers to lower the temperature of CPUs. Other uses include the cooling of lubricant oil in pumps; for cooling purposes in heat exchangers; for cooling buildings in HVAC and in chillers. Mechanism Advantages Water is inexpensive, non-toxic, and available over most of the earth's surface. Liquid cooling offers higher thermal conductivity than air cooling. Water has unusually high specific heat capacity among commonly available liquids at room temperature and atmospheric pressure allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caster Angle
250px, θ is the caster angle, the red line is the pivot line, and the grey area is the tire. 250px, Front suspension of a race car, the caster angle is formed by the line between upper and lower ball joint. The caster angle or castor angle is the angular displacement of the steering axis from the vertical axis of a steered wheel in a car, motorcycle, bicycle, other vehicle or a vessel, as seen from the side of the vehicle. The steering axis in a car with dual ball joint suspension is an imaginary line that runs through the center of the upper ball joint to the center of the lower ball joint, or through the center of the kingpin for vehicles having a kingpin. Caster causes a wheel to align with the direction of travel, and can be accomplished either by caster displacement or caster angle. Caster displacement moves the steering axis ahead of the axis of wheel rotation, as with the front wheels of a shopping cart. Caster angle moves the steering axis from vertical. In automo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ride Height
Ride height or ground clearance is the amount of space between the base of an automobile tire and the lowest point of the automobile (typically the axle); or, more properly, to the shortest distance between a flat, level surface, and the lowest part of a vehicle other than those parts designed to contact the ground (such as tires, tracks, skis, etc.). Ground clearance is measured with standard vehicle equipment, and for cars, is usually given with no cargo or passengers. Function Ground clearance is a critical factor in several important characteristics of a vehicle. For all vehicles, especially cars, variations in clearance represent a trade-off between handling, ride quality, and practicality. A higher ride height and ground clearance means that the wheels have more vertical room to travel and absorb road shocks. Also, the car is more capable of being driven on roads that are not level, without the scraping against surface obstacles and possibly damaging the chassis and unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
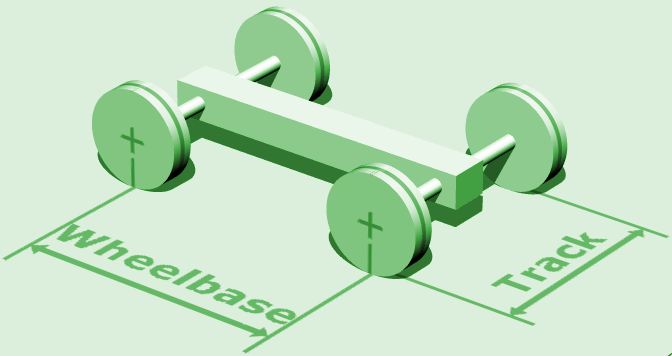
Wheelbase
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front) axle and the centerpoint of the driving axle group. In the case of a tri-axle truck, the wheelbase would be the distance between the steering axle and a point midway between the two rear axles. Vehicles The wheelbase of a vehicle equals the distance between its front and rear wheels. At equilibrium, the total torque of the forces acting on a vehicle is zero. Therefore, the wheelbase is related to the force on each pair of tires by the following formula: :F_f = mg :F_r = mg where F_f is the force on the front tires, F_r is the force on the rear tires, L is the wheelbase, d_r is the distance from the center of mass (CM) to the rear wheels, d_f is the distance from the center of mass to the front wheels (d_f + d_r = L), m is the mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Lüthi
Thomas Lüthi (born 6 September 1986) is a Swiss sporting director at Prüstel GP, and former Grand Prix motorcycle racer. He spent 19 years in Grand Prix world championships, becoming one of only six riders to reach 300 race starts, spending much of his career with the Interwetten Paddock team, with who he became the 2005 season's 125cc world champion. Career Early career Lüthi was born in Oberdiessbach, Kanton Bern, Switzerland, but grew up in Emmental. Lüthi started racing pocket bikes at the age of nine. He won pocket bike championships in 1999 and 2000. In 2002, he finished second overall in the European 125cc Championship, and third in the German 125cc series. 125cc World Championship Lüthi made his first 125cc World Championship appearance at the 2002 German Grand Prix, which he finished in 26th place. In the 2003 Grand Prix motorcycle racing season, Lüthi was invited by Daniel Epp to ride for his team, known as the "Elit Grand Prix Team"; Epp became his manager. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)