|
Honda CBX550F
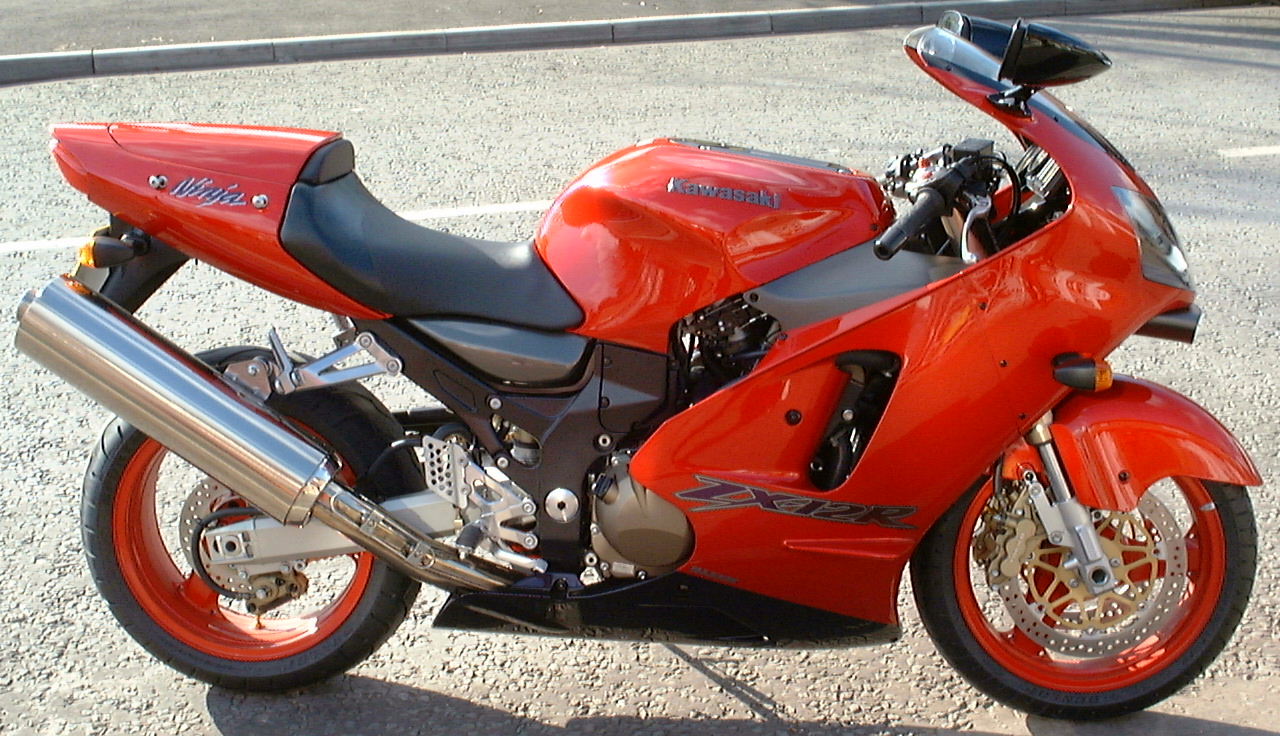
The Honda CBX550F is a four-stroke, in line four cylinder, sport tourer motorcycle produced from 1982 to 1986 by the Honda Motor Company. The CBX550F II is identical apart from the addition of a half-fairing. Although the model was designated ''550'', the actual capacity was . Honda developed a completely new, unusual design of engine to compete in the middleweight-sector with twin overhead camshafts acting on rockers, having screw-adjusters for clearance which actuated the sixteen valves ( four per cylinder). The engine featured a standard oil-cooler and a distinctive, unusual exhaust system, a first for Honda, with cross-over pipes directly in front of the engine linking cylinders one to four and a separate pair of pipes connecting cylinders two and three. The CV carburettors were of a new type using mixture-enriching internal fuel passages for cold-starts, with careful engineering of the inlet tracts to achieve smooth gasflow.''Motor Cycle News'' (UK weekly newspaper) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honda CBX (other)
{{disambiguation, geo, given name ...
The Honda CBX is a six-cylinder motorcycle made from 1978 to 1982. Honda CBX may also refer to Honda motorcycles whose model designations begin with the prefix CBX, including: * Honda CBX750 * Honda CBX400F * Honda CBX series - about Honda motorcycles prefixed "CBX" * Honda CBX550F The Honda CBX550F is a four-stroke, in line four cylinder, sport tourer motorcycle produced from 1982 to 1986 by the Honda Motor Company. The CBX550F II is identical apart from the addition of a half-fairing. Although the model was designat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honda CBX400F
The Honda CBX400F is a motorcycle manufactured by Honda between 1981 and 1984. z400FX After the ''Dream'' CB400 Four, Honda made the ''Hawk'' series for mid-sized sports models which were powered by obsolete SOHC straight-twin engines. Those models were not popular in the market. In comparison, Kawasaki's Z400FX, powered by high-class inline-four engines, became a hit as a sports model in 1979. XJ400 and GSX400F In 1980, Yamaha and Suzuki introduced the XJ400 and GSX400F respectively, also powered by in-line-four engines. In addition, Yamaha introduced the RZ 250, with a water-cooled two-stroke engine, which is as powerful as ''400cc'' class. CBX400F In order to break through the market and to address the demand to introduce an in-line-four engine model, Honda introduced the CBX400F in 1981. Features The CBX400F had; a compact body reminiscent of the CB400 Four, a meter panel resembling that of the CB750F, forged separated-handles, forged pedals, "x" shaped 4-1-2 exhaust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honda Motorcycles
is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles, and power equipment, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, reaching a production of 400 million by the end of 2019, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than 14 million internal combustion engines each year. Honda became the second-largest Japanese automobile manufacturer in 2001. In 2015, Honda was the eighth largest automobile manufacturer in the world. Honda was the first Japanese automobile manufacturer to release a dedicated luxury brand, Acura, in 1986. Aside from their core automobile and motorcycle businesses, Honda also manufactures garden equipment, marine engines, personal watercraft, power generators, and other products. Since 1986, Honda has been involved with artificial intelligence/robotics research and released their ASIMO robo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disc Brakes
A disc brake is a type of brake that uses the calipers to squeeze pairs of pads against a disc or a "rotor" to create friction. This action slows the rotation of a shaft, such as a vehicle axle, either to reduce its rotational speed or to hold it stationary. The energy of motion is converted into waste heat which must be dispersed. Hydraulically actuated disc brakes are the most commonly used form of brake for motor vehicles, but the principles of a disc brake are applicable to almost any rotating shaft. The components include the disc, master cylinder, and caliper (which contains a cylinder and two brake pads) on both sides of the disc. Design The development of disc-type brakes began in England in the 1890s. In 1902, the Lanchester Motor Company designed brakes that looked and operated in a similar way to a modern disc-brake system even though the disc was thin and a cable activated the brake pad. Other designs were not practical or widely available in cars for another 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Cycle News
''MCN'' or ''Motor Cycle News'' is a UK weekly Motorcycle, motorcycling newspaper published by Bauer Verlagsgruppe, Bauer Consumer Media, based in Peterborough, United Kingdom. It claims to be "the world’s biggest weekly motorcycle newspaper". The title was founded in late 1955 as ''Motorcycle News'' by Cyril Quantrill, a former employee of Motor Cycling (magazine), Motor Cycling, and was sold to EMAP in 1956. Bauer bought Emap's consumer media division in 2008. The brand has expanded to include the MCN website, MCN Mobile, iPhone app, the 'MCN Compare' Insurance Comparison service, MCN London and Scottish Motorcycle Show and the MCN Live! at Skegness party weekend. In 2009, average weekly circulation was 114,304 copies according to the Audit Bureau of Circulations (UK), Audit Bureau of Circulations, and 2010 it was 106,446 copies. The figure for 2018 was 56,839. Early years Cyril Quantrill was an employee of ''Motor Cycling'' under famous editor Graham Walker (motorcyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main metering circuit, however various other components are also used to provide extra fuel or air in specific circumstances. Since the 1990s, carburetors have been largely replaced by fuel injection for cars and trucks, however carburetors are still used by some small engines (e.g. lawnmowers, generators and concrete mixers) and motorcycles. Diesel engines have always used fuel injection instead of carburetors. Etymology The name "carburetor" is derived from the verb ''carburet'', which means "to combine with carbon," or in particular, "to enrich a gas by combining it with carbon or hydrocarbons." Thus a carburetor mixes intake air with hydrocarbon-based fuel, such as petrol or autogas (LPG). The name is spelled "carburetor" in American English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Cooling
Oil cooling is the use of engine oil as a coolant, typically to remove surplus heat from an internal combustion engine. The hot engine transfers heat to the oil which then usually passes through a heat-exchanger, typically a type of radiator known as an oil cooler. The cooled oil flows back into the hot object to cool it continuously. Usage Oil cooling is commonly used to cool high-performance motorcycle engines that are not liquid-cooled. Typically, the cylinder barrel remains air-cooled in the traditional motorcycle fashion, but the cylinder head benefits from additional cooling. As there is already an oil circulation system available for lubrication, this oil is also piped to the cylinder head and used as a liquid coolant. Compared to an oil system used solely for lubrication, oil cooling requires additional oil capacity, a greater flow rate through the oil pump, and an oil cooler (or a larger cooler than normal). If air-cooling proves sufficient for much of the running ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-valve
In automotive engineering a multi-valve or multivalve engine is one where each cylinder has more than two valves. A multi-valve engine has better breathing and may be able to operate at higher revolutions per minute (RPM) than a two-valve engine, delivering more power. Multi-valve rationale Multi-valve engine design A multi-valve engine design has three, four, or five valves per cylinder to achieve improved performance. Any four-stroke internal combustion engine needs at least two valves per cylinder: one for ''intake'' of air (and often fuel), and another for ''exhaust'' of combustion gases. Adding more valves increases valve area and improves the flow of intake and exhaust gases, thereby enhancing combustion, volumetric efficiency, and power output. Multi-valve geometry allows the spark plug to be ideally located within the combustion chamber for optimal flame propagation. Multi-valve engines tend to have smaller valves that have lower reciprocating mass, which can red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocker Arm
In the context of an internal combustion engine, a rocker arm is a valvetrain component that typically transfers the motion of a pushrod to the corresponding intake/exhaust valve. Rocker arms in automobiles are typically made from stamped steel, or aluminum in higher-revving applications. Some rocker arms (called ''roller rockers'') include a bearing at the contact point, to reduce wear and friction at the contact point. Overview In the typical use-case of an overhead valve (pushrod) engine, the camshaft at the bottom of the engine pushes the pushrod upwards. The top of the pushrod presses upwards on one side of the rocker arm (located at the top of the engine), which causes the rocker arm to rotate. This rotation causes the other end of the rocker arm to press downwards on the top of the valve, which opens the valve by moving it downwards. A ''roller rocker'' is a rocker arm that uses needle bearings (or a single bearing ball in older engines) at the contact point between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Camshaft
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine where the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion chamber in the engine block. ''Single overhead camshaft'' (SOHC) engines have one camshaft per bank of cylinders. ''Dual overhead camshaft'' (DOHC, also known as "twin-cam".) engines have two camshafts per bank. The first production car to use a DOHC engine was built in 1910. Use of DOHC engines slowly increased from the 1940s, leading to many automobiles by the early 2000s using DOHC engines. Design In an OHC engine, the camshaft is located at the top of the engine, above the combustion chamber. This contrasts the earlier overhead valve engine (OHV) and flathead engine configurations, where the camshaft is located down in the engine block. The valves in both OHC and OHV engines are located above the combustion chamber; however an OHV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorcycle Fairing
A motorcycle fairing is a shell placed over the frame of a motorcycle, especially racing motorcycles and sport bikes, to deflect wind and reduce air drag. The secondary functions are the protection of the rider from airborne hazards and wind-induced hypothermia and of the engine components in the case of an accident. A motorcycle windshield will usually be integrated into the design of the fairing.Tony Foale, ''Motorcycle Handling and Chassis Design'', , Chapter 5: "Aerodynamics" The major benefit of a fairing on sport touring and touring motorcycles is a reduction in aerodynamic drag, which allows for reduced fuel consumption and permits higher speeds at lower engine rpm, which in turn increases engine life. A motorcycle may have a front fairing, a rear fairing, a belly fairing, or any combination of these. Alternatively, a single fairing may partially or fully enclose the entire motorcycle, and may even enclose the rider. History The importance of streamlining was known ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-stroke Engine
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed: #Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve must be in the open position while the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing vacuum pressure into the cylinder through its downward motion. The piston is moving down as air is being sucked in by the downward motion against the piston. #Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)