|
Homostiidae
Homostiidae is a family of flattened arthrodire placoderms from the Early to Middle Devonian. Fossils appear in various strata in Europe, Russia, Morocco, Australia, Canada and Greenland. Many homostiids have " toothless" jaws, and large sizes. suggesting that many homostiids were probably filter feeders, like the also noticeably flattened Rhincodon typus. All homostiids have flattened and elongated skulls. According to Denison 1978, primitive homostiids have moderately long median dorsal plates, whereas in "advanced" homostiids, the median dorsal tends to be short and broad. Obruchev (1964) placed the following primitive genera ''Euleptaspis'', ''Lophostracon'' and ''Luetkeichthys'' in a separate family, "Euleptaspididae," and Ørvig (1969), claimed that the Euleptaspidids were totally unrelated to Homostiidae proper (i.e., being neither related to, nor ancestral), but, according to Denison, did not clearly explain his reasons why this was so. Genera ''Angarichthys'' A compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antineosteus
''Antineosteus'' is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Emsian, Early Devonian Kess-Kess Mounds, in the eastern Anti-Atlas Mountains, Morocco, and the Barrandian area of the Czech Republic. Description ''Antineosteus lehmani'' is rather fragmentary, known from a left anterior dorsolateral plate, a left paranuchal plate, and an inferognathal. ''A. rufus'' is known from a nearly-complete right head shield plate, and a right anterior dorsolateral plate. ''A. rufus'' is estimated to exceed , from measuring the plates with the ones from better-preserved, related taxa. Diet ''Antineosteus'', like many other members of Homostiidae, lacked bladed dentition on their jaws, and was large in size. These traits all in one animal support a planktivorous lifestyle, like baleen whales, or the whale shark, as supported by Denison, 1978, suggesting similar lifestyles for arthrodires like ''Homostius'', making it reasonable for many homostiids to be suspension-feeders like t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tityosteus
''Tityosteus'' is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Early Emsian of the Early Devonian, with fossils known from Germany, the Ibero-Armorican Trough, and southern Siberia. Description ''Tityosteus'' has only an 11 cm right marginal plate known, and margin ends and parts, in addition to the central plate overlap area being broken. According to "Tityosteus, A MARINE FISH (ARTHRODIRA, HOMOSTIIDAE) FROM THE EMSIAN OF ARAGÓN, SPAIN, AND ITS DISTRIBUTION", given Tityosteus's distribution, and Carolowilhelma (a pelagic arthrodire), being from similar facies as Tityosteus (Eifelian of Aragón, Spain), it may have been pelagic, and able to cross open waters. Diet While the inferognathals of ''Tityosteus'' have not been found, they could be either "toothless", like ''Homosteus'', which has been suggested to be planktivorous, or possessing fine denticles, like ''Antineosteus''. It has been suggested that ''Tityosteus'' probably was similar to the whale shark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homosteus
''Homosteus'' is a genus of flattened arthrodire placoderm from the Middle Devonian. Fossils are found primarily in Eifelian-epoch aged strata of Europe, Canada, Greenland, and Estonia. All of the species had comparatively large, flattened heads with, as suggested by the upward opening orbits, upward-pointing eyes. These adaptations suggest that the various species were benthic predators. A study on ''Titanichthys'', in contrast, suggests that species of ''Homosteus'' may have been filter-feeders instead. ''Homosteus'' specimens from the Old Red Sandstone of Scotland are known to be significantly radioactive, on the order of 1.2 * 104 gamma/min/g ic Notably, ''Homosteus'' specimens are the only fish fossils from the Old Red Sandstone to show significant radioactivity. This suggests that these specimens became radioactive from the animals ingesting radioactive isotopes in life (e.g., through ingesting radioactive sediment), rather than radioactive isotopes being absorbed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhanguura
''Dhanguura'' is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Early Devonian of Wee Jasper, NSW. It contains the single species ''D. johnstoni''. Etymology ''Dhanguura'' comes from the Aboriginal word "dhanguurr", meaning "fish", in the Wiradjuri tribe's language, because they inhabited the area, west of Wee Jasper. The species name, "johnstoni" is in honor of the discoverer of the genus, Dr. Paul Johnston, who found ''Dhanguura'' in 1993. Description ''Dhanguura'' is known from fossilized remains of an incomplete skull, the preserved portion around 29 cm in length. According to the paper cited, ''Dhanguura'' probably exceeded the contemporary ''Taemasosteus ''Taemasosteus'' is an extinct genus of arthrodire placoderm. Its fossils have been found in Emsian-Epoch (geology), aged marine strata in New South Wales, Australia. It contains two species, ''T. novaustrocambricus'', and ''T. maclartiensis''. ...'' in size. References Homostiidae Arthrodire gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathlesichthys
''Cathlesichthys'' is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from Wee Jasper, during the Early Devonian. Etymology The generic epithet honors Ian and Helen Cathles, being a compound of their surname combined with the Greek word for fish ιχθύς (ichthýs). The specific epithet refers to the location of where it was found (Wee Jasper Wee Jasper is a hamlet in the Goodradigbee River, Goodradigbee valley at the western foot of the Brindabella Ranges, near Burrinjuck Dam in New South Wales, Australia in Yass Valley Council, Yass Valley Shire. It is located about 90 km nort ...). Description ''Cathlesichthys'' is known from an incomplete paranuchal, and nuchal plates, attaining a skull length of around 20 cm. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q116235708 Homostiidae Arthrodire genera Placoderms of Australia Fossil taxa described in 2004 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavanosteus
''Cavanosteus'' is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Emsian of Victoria, and New South Wales, Australia. Description ''Cavanosteus'' is known from central plates of the skull, infragnathals with little or no dentition, similar in form to ''Homosteus ''Homosteus'' is a genus of flattened arthrodire placoderm from the Middle Devonian. Fossils are found primarily in Eifelian-epoch aged strata of Europe, Canada, Greenland, and Estonia. All of the species had comparatively large, flattened he ...'', and a bone from the dermal trunk shield. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q116198257 Homostiidae Arthrodire genera Fossil taxa described in 1876 Taxa named by Frederick McCoy Placoderms of Australia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccosteina
Coccosteina is an extinct infraorder of placoderms, armored fish most diverse during the Devonian.Heintz., Anatol, 1932, The structure of ''Dinichthys'', a contribution to your knowledge of the Arthrodira: In: The Bashford Dean Memorial Volume Archaic Fishes'', edited by Gudger, E. W., article IV, The American Museum of Natural History, 224pp. However, the term is no longer in use, as modern cladistical methods have produced alternative phylogenetic trees of Brachythoraci with new subdivisions. Systematics * Basal genus '' Maideria'' * Basal genus ''Xiangshuiosteus'' * Superfamily Buchanosteoidea ** Family Buchanosteidae * Superfamily Gemuendenaspoidea ** Family Gemuendenaspidae * Superfamily Homosteoidea ** Family Homostiidae * Superfamily Brachydeiroidea ** Family Brachydeiridae ** Family Leptosteidae * Superfamily Coccosteoidea ** Family Pholidosteidae ** Family Coccosteidae ** Family Plourdosteidae ** Family Torosteidae ** Family Incisoscutidae ** Family Camuropisc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantidosteus
''Atlantidosteus'' is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Early to Middle Devonian of Morocco and Queensland. It contains two known species, ''A. hollardi'' and ''A. pacifica''. Description ''Atlantidosteus pacifica'' is known from a right suborbital plate, found in the Broken River Group of Queensland, Australia. Phylogeny ''Atlantidosteus'' is part of the clade Migmatocephala, closer related to Homostius, than Antineosteus. {{Clade, style={{Clade , 1=''Tityosteus'' , 0=''Taemasosteus'', 4={{Clade , 1=''Antineosteus ''Antineosteus'' is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Emsian, Early Devonian Kess-Kess Mounds, in the eastern Anti-Atlas Mountains, Morocco, and the Barrandian area of the Czech Republic. Description ''Antineosteus lehmani'' i ...'' , 2={{Clade , 1=''Atlantidosteus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angarichthys
''Angarichthys hyperboreus'' is an extinct homostiid arthrodire placoderm from the Middle Devonian (either upper Eifelian or lower Givetian) of Siberia. It is known from an infragnathal plate, an intero-lateral plate, and a marginal plate found from the Middle Devonian strata of the Tynep Series formation, in the Bakhta River basin, Tunguska Plateau The Tunguska Plateau ( rus, Тунгусское плато) is a mountain plateau in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Siberia, Russia. It is a part of the Central Siberian Plateau. The plateau is located in largely uninhabited area, the village of Noginsk was .... ''A. hyperboreus'' differs from ''Homosteus'' in that the former's marginal plate has a ridge where the central plate would have overlapped it, and in the infragnathal, which is curved sigmoidally, and bears at least seven tooth-like prongs nearer to the functional anterior end (the plate, which is fragmentary, suggests that the intact plate would have born several more). The living ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachythoraci
Brachythoraci is an extinct suborder of arthrodire placoderms, armored fish most diverse during the Devonian. Phylogeny Arthrodira is divided into three main groups: the paraphyletic Actinolepida and Phlyctaenii, and then the monophyletic Brachythoraci. Brachythoraci is then further divided into the large derived clade Eubrachythoraci and several basal groups: Buchanosteoidea, Homosteidae, and Holonematidae. (Although Holonematidae's membership in Brachythoraci is disputed.) Below is a cladogram from the 2016 Zhu ''et al.'' phylogenetic In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... study: References Arthrodires Prehistoric animal suborders Fish suborders {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
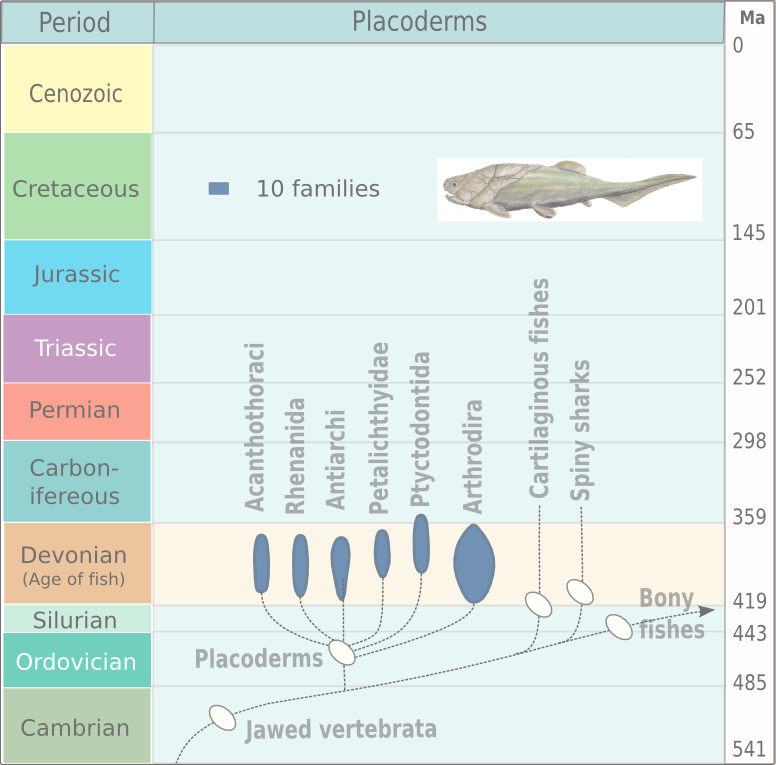
Arthrodire
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an Order (biology), order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of Placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are protected by a bony ring, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus ''Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, ''Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed ''Rolfosteus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |