|
Homoousion
Homoousion ( ; grc, ὁμοούσιον, lit=same in being, same in essence, from , , "same" and , , "being" or "essence") is a Christian theological term, most notably used in the Nicene Creed for describing Jesus (God the Son) as "same in being" or "same in essence" with God the Father (). The same term was later also applied to the Holy Spirit in order to designate him as being "same in essence" with the Father and the Son. Those notions became cornerstones of theology in Nicene Christianity, and also represent one of the most important theological concepts within the Trinitarian doctrinal understanding of God. Terminology The term , the accusative case form of (, "consubstantial"), was adopted at the First Council of Nicaea (325) in order to clarify the ontology of Christ. From its Greek original, the term was translated into other languages. In Latin, which is lacking a present participle of the verb 'to be', two main corresponding variants occurred. Since the Aristotel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Council Of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea (; grc, Νίκαια ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I in AD 325. This ecumenical council was the first effort to attain consensus in the church through an assembly representing all Christendom. Hosius of Corduba may have presided over its deliberations. Its main accomplishments were settlement of the Christological issue of the divine nature of God the Son and his relationship to God the Father, the construction of the first part of the Nicene Creed, mandating uniform observance of the date of Easter, and promulgation of early canon law. Overview The First Council of Nicaea was the first ecumenical council of the church. Most significantly, it resulted in the first uniform Christian doctrine, called the Nicene Creed. With the creation of the creed, a precedent was established for subsequent local and regional councils of bishops (synods) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ousia
''Ousia'' (; grc, οὐσία) is a philosophical and theological term, originally used in ancient Greek philosophy, then later in Christian theology. It was used by various ancient Greek philosophers, like Plato and Aristotle, as a primary designation for philosophical concepts of ''essence'' or '' substance''. In contemporary philosophy, it is analogous to English concepts of '' being'' and ''ontic''. In Christian theology, the concept of (''divine essence'') is one of the most important doctrinal concepts, central to the development of trinitarian doctrine. The Ancient Greek term (; ''divine essence'') was translated in Latin as or , and hence in English as ''essence'' or '' substance''. Etymology The term is an Ancient Greek noun, formed on the feminine present participle of the verb , , meaning "to be, I am", so similar grammatically to the English noun "being". There was no equivalent grammatical formation in Latin, and it was translated as or . Cicero coined and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicene Christianity
The original Nicene Creed (; grc-gre, Σύμβολον τῆς Νικαίας; la, Symbolum Nicaenum) was first adopted at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. In 381, it was amended at the First Council of Constantinople. The amended form is also referred to as the Nicene Creed, or the Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed for disambiguation. The Nicene Creed is the defining statement of belief of Nicene or mainstream Christianity and in those Christian denominations that adhere to it. The Nicene Creed is part of the profession of faith required of those undertaking important functions within the Orthodox and Catholic Churches. Nicene Christianity regards Jesus as divine and "begotten of the Father". Various non-Nicene doctrines, beliefs, and creeds have been formed since the fourth century, all of which are considered heresies by adherents of Nicene Christianity. In Western Christianity, the Nicene Creed is in use alongside the less widespread Apostles' Creed. In musical setting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ousia
''Ousia'' (; grc, οὐσία) is a philosophical and theological term, originally used in ancient Greek philosophy, then later in Christian theology. It was used by various ancient Greek philosophers, like Plato and Aristotle, as a primary designation for philosophical concepts of ''essence'' or '' substance''. In contemporary philosophy, it is analogous to English concepts of '' being'' and ''ontic''. In Christian theology, the concept of (''divine essence'') is one of the most important doctrinal concepts, central to the development of trinitarian doctrine. The Ancient Greek term (; ''divine essence'') was translated in Latin as or , and hence in English as ''essence'' or '' substance''. Etymology The term is an Ancient Greek noun, formed on the feminine present participle of the verb , , meaning "to be, I am", so similar grammatically to the English noun "being". There was no equivalent grammatical formation in Latin, and it was translated as or . Cicero coined and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God The Son
God the Son ( el, Θεὸς ὁ υἱός, la, Deus Filius) is the second person of the Trinity in Christian theology. The doctrine of the Trinity identifies Jesus as the incarnation of God, united in essence (consubstantial) but distinct in person with regard to God the Father and God the Holy Spirit (the first and third persons of the Trinity). Source The phrase "God the Son" is not found in the Bible, but is found in later Christian sources. By scribal error the term is in one medieval manuscript, MS No.1985, where Galatians 2:20 has "Son of God" changed to "God the Son". The term in English follows Latin usage as found in the Athanasian Creed and other texts of the early church: In Greek "God the Son" is ''ho Theos ho huios'' (ὁ Θεός ὁ υἱός) as distinct from ''ho huios'' nominative ''tou Theou'' genitive, ὁ υἱός τοῦ Θεοῦ, " Son of God". In Latin "God the Son" is Deus (nominative) Filius (nominative). The term ''deus filius'' is found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicene Creed
The original Nicene Creed (; grc-gre, Σύμβολον τῆς Νικαίας; la, Symbolum Nicaenum) was first adopted at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. In 381, it was amended at the First Council of Constantinople. The amended form is also referred to as the Nicene Creed, or the Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed for disambiguation. The Nicene Creed is the defining statement of belief of Nicene or mainstream Christianity and in those Christian denominations that adhere to it. The Nicene Creed is part of the profession of faith required of those undertaking important functions within the Orthodox and Catholic Churches. Nicene Christianity regards Jesus as divine and "begotten of the Father". Various non-Nicene doctrines, beliefs, and creeds have been formed since the fourth century, all of which are considered heresies by adherents of Nicene Christianity. In Western Christianity, the Nicene Creed is in use alongside the less widespread Apostles' Creed. In musical setting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heresiologists
In theology or the history of religion, heresiology is the study of heresy, and heresiographies are writings about the topic. Heresiographical works were common in both medieval Christianity and Islam. Heresiology developed as a part of the emerging orthodoxy in the Christian state church of the Roman Empire. Church scholars studied and documented the teachings of various Christian sects in order to clearly distinguish between those they accepted as orthodox and those they rejected as heretical. Other Christian communions developed their own competing heresiological traditions as well. In Islam, heresiology surveyed both the various Muslim sects, and also other religions such as Christianity and Judaism. Some like Abu Mansur al-Baghdadi and Ibn Hazm wrote polemical works, arguing the falseness of sects and religions other than their own. Others like Al-Shahrastani's ''Al-Milal wa al-Nihal'' took a more impartial approach closer to modern religious studies works. See also *Doxogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentinianism
Valentinianism was one of the major Gnostic Christian movements. Founded by Valentinus in the 2nd century AD, its influence spread widely, not just within Rome but also from Northwest Africa to Egypt through to Asia Minor and Syria in the East. Later in the movement's history it broke into an Eastern and a Western school. Disciples of Valentinus continued to be active into the 4th century AD, after the Roman Emperor Theodosius I issued the Edict of Thessalonica (380 AD), which declared Nicene Christianity as the State church of the Roman Empire. The doctrine, practices and beliefs of Valentinus and the Gnostic movement that bore his name were condemned as heretical by proto-orthodox Christian leaders and scholars. Prominent Church Fathers such as Irenaeus of Lyons and Hippolytus of Rome wrote against Gnosticism. Because early church leaders encouraged the destruction of Gnostic texts, most evidence for the Valentinian theory comes from its critics and detractors, most notably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance Theory
Substance theory, or substance–attribute theory, is an ontological theory positing that objects are constituted each by a ''substance'' and properties borne by the substance but distinct from it. In this role, a substance can be referred to as a ''substratum'' or a ''thing-in-itself''. ''Substances'' are particulars that are ontologically independent: they are able to exist all by themselves. Another defining feature often attributed to substances is their ability to ''undergo changes''. Changes involve something existing ''before'', ''during'' and ''after'' the change. They can be described in terms of a persisting substance gaining or losing properties. ''Attributes'' or ''properties'', on the other hand, are entities that can be exemplified by substances. Properties characterize their bearers, they express what their bearer is like. ''Substance'' is a key concept in ontology and metaphysics, which may be classified into monist, dualist, or pluralist varieties according to how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
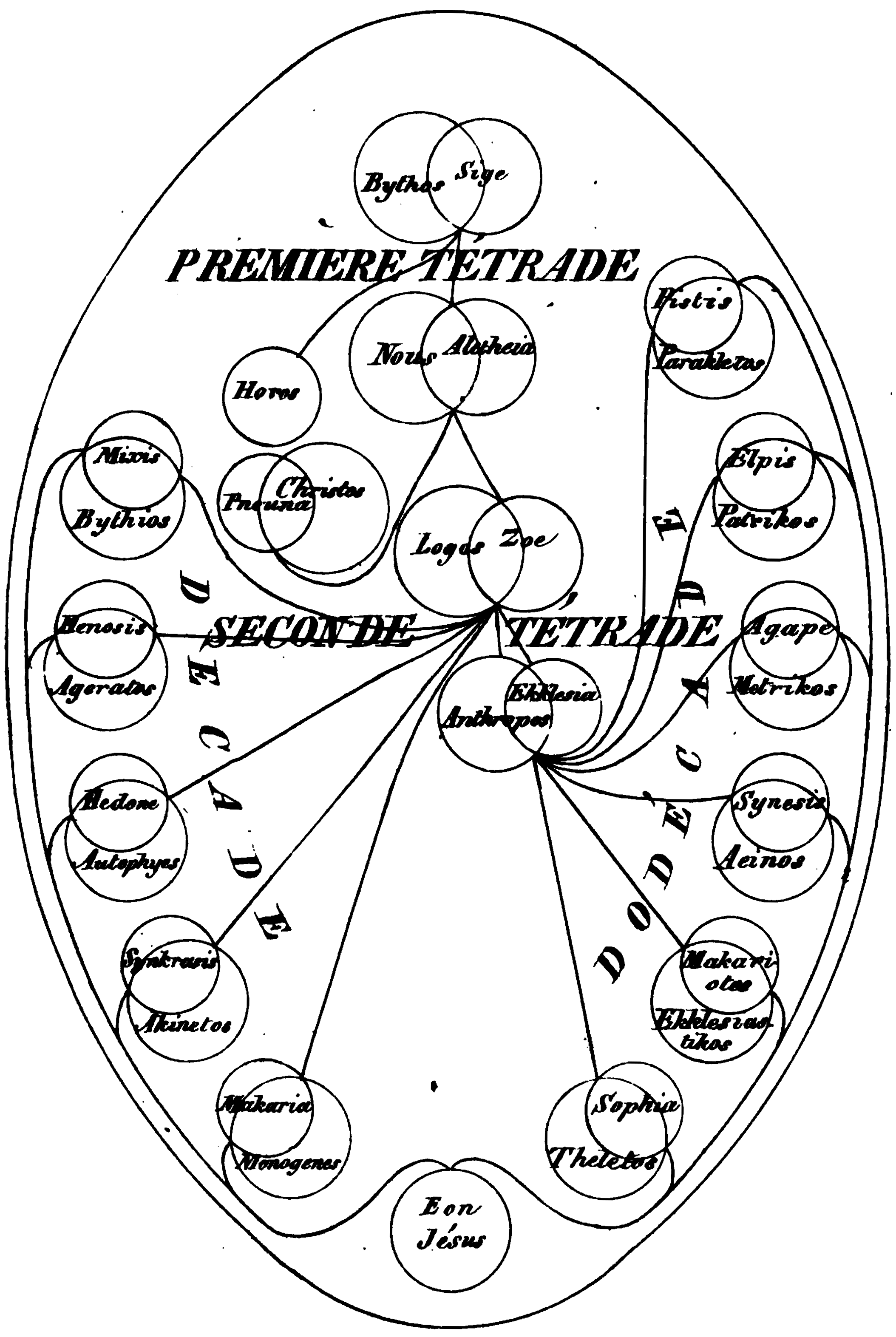
Syzygy (Gnosticism)
In many Gnostic systems, various emanations of God are known by such names as One, Monad, ''Aion teleos'' (αἰών τέλεος "The Broadest Aeon"), Bythos (, "depth" or "profundity"), ''Proarkhe'' ("before the beginning", ), ''Arkhe'' ("the beginning", ), and Aeons. In different systems these emanations are differently named, classified, and described, but emanation theory is common to all forms of Gnosticism. In Basilidian Gnosis they are called sonships (υἱότητες ''huiotetes''; sing.: υἱότης ''huiotes''); according to Marcus, they are numbers and sounds; in Valentinianism they form male/female pairs called syzygies (Greek , from σύζυγοι ''syzygoi'', lit. "yokings together"). This source of all being is an Aeon, in which an inner being dwells, known as ''Ennoea'' ("thought, intent", Greek ), ''Charis'' ("grace", Greek ), or ''Sige'' ("silence", Greek ). The split perfect being conceives the second Aeon, ''Nous'' ("mind", Greek Νους), within its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)