|
Hohenzollern Redoubt (fortification)
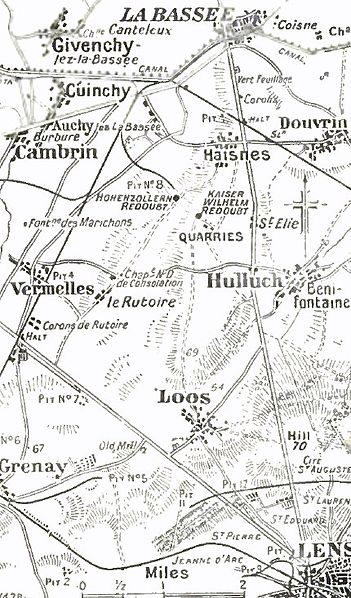
The Hohenzollern Redoubt () was a strongpoint of the German 6th Army on the Western Front during the First World War, at Auchy-les-Mines near Loos-en-Gohelle in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region of France. Named after the House of Hohenzollern, the redoubt was fought for by German and British forces. Engagements took place from the Battle of Loos to the beginning of the Battle of the Somme on 1 July 1916, including the action of the Hohenzollern Redoubt in 1915 and the British Attack at the Hohenzollern Redoubt from 2 to 18 March 1916. Background In the summer of 1915 the German armies continued the strengthening of front trenches, communication trenches and strong-points ordered by Chief of the General Staff General Erich von Falkenhayn, who on 25 January had also ordered the building of more defensive lines behind the front trench. Crown Prince Rupprecht the Sixth Army commander and some Western Front generals had objected to this policy, as an invitation to Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Von Falkenhayn
General Erich Georg Sebastian Anton von Falkenhayn (11 September 1861 – 8 April 1922) was the second Chief of the German General Staff of the First World War from September 1914 until 29 August 1916. He was removed on 29 August 1916 after the failure at the Battle of Verdun, the opening of the Battle of the Somme, the Brusilov Offensive and the entry of Romania into the war on the Allied side undid his strategy to end the war before 1917. He was later given important field commands in Romania and Syria. His reputation as a war leader was attacked in Germany during and after the war, especially by the faction supporting Paul von Hindenburg. Falkenhayn held that Germany could not win the war by a decisive battle but would have to reach a compromise peace; his enemies said he lacked the resolve necessary to win a decisive victory. Falkenhayn's relations with the Chancellor Theobald von Bethmann-Hollweg were troubled and undercut Falkenhayn's plans. Early life Falkenhayn was b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Attacks At Hulluch
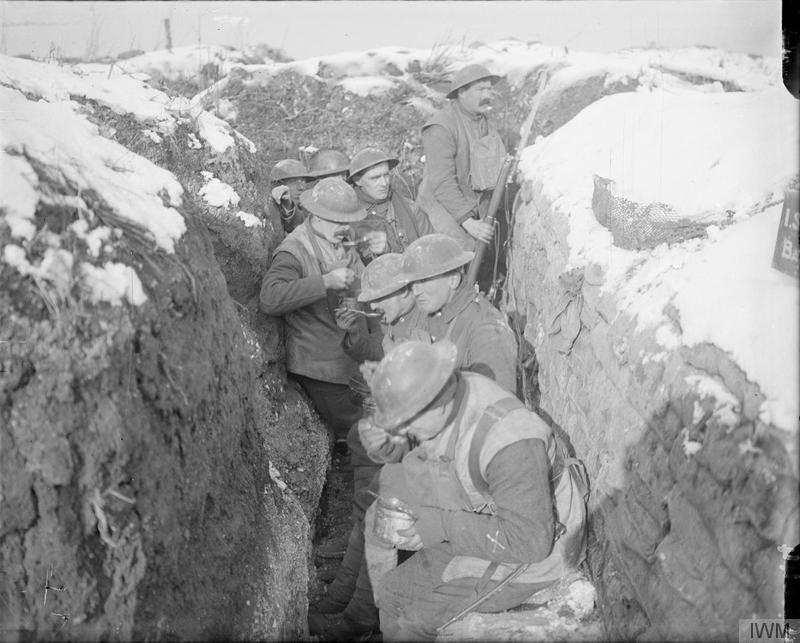
The Gas Attacks at Hulluch were two German cloud gas attacks on British troops during World War I, from 27 to 29 April 1916, near the village of Hulluch, north of Loos in northern France. The gas attacks were part of an engagement between divisions of the II Royal Bavarian Corps and divisions of the British I Corps. Just before dawn on 27 April, the 16th (Irish) Division and part of the 15th (Scottish) Division were subjected to a cloud gas attack near Hulluch. The gas cloud and artillery bombardment were followed by raiding parties, which made temporary lodgements in the British lines. Two days later the Germans began another gas attack but the wind turned and blew the gas back over the German lines. A large number of German casualties were caused by the change in the wind direction and the decision to go ahead despite protests by local officers. German casualties were increased by the British, who fired on German soldiers as they fled in the open. The gas used by the Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
35th Brigade (United Kingdom)
The 35th Brigade was an infantry brigade formation of the British Army that saw active service in both the First and the Second World Wars. First World War It was one of the ''New Army'' or ''Kitchener's Army'' brigades, and assigned to the 12th (Eastern) Division and served on the Western Front during the First World War. Order of battle, First World War * 7th (Service) Battalion, Norfolk Regiment * 7th (Service) Battalion, Suffolk Regiment * 9th (Service) Battalion, Essex Regiment * 5th (Service) Battalion, Princess Charlotte of Wales's (Royal Berkshire Regiment) * 1/1st Battalion, Cambridgeshire Regiment * 35th Machine Gun Company, Machine Gun Corps * 35th Trench Mortar Battery Second World War The brigade was disbanded after the war in 1919. However, it was reformed in the Territorial Army, now as the 35th Infantry Brigade, in 1939 when the Territorial Army was doubled in size. The brigade was raised as a duplicate of the 131st Infantry Brigade and consisted of three 2nd Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
37th Brigade (United Kingdom)
The 37th Brigade was an infantry brigade of the British Army that served in both the First and the Second World Wars. First World War The 37th Brigade was one of the ''New Army'' or '' Kitchener's Army'' brigades, and was assigned to the 12th (Eastern) Division and served on the Western Front during the First World War. The brigade was raised in August 1914 from the thousands of men volunteering for Kitchener's New Armies. Order of battle The 37th Brigade was constituted as follows during the war: * 6th (Service) Battalion, Queen's (Royal West Surrey Regiment) * 6th (Service) Battalion, Buffs (East Kent Regiment) * 7th (Service) Battalion, East Surrey Regiment ''(disbanded February 1918)'' * 6th (Service) Battalion, Queen's Own (Royal West Kent Regiment) * 37th Machine Gun Company, Machine Gun Corps ''(formed 4 February 1916, moved to 12th Battalion, Machine Gun Corps on 1 March 1918)'' * 37th Trench Mortar Battery ''(formed 15 June 1916)'' Second World War The 37th Infantry B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th (Eastern) Division
The 12th (Eastern) Division was an infantry division raised by the British Army during the First World War from men volunteering for Kitchener's New Armies. The division saw service in the trenches of the Western Front from June 1915 to the end of the war. Formation and First World War The 12th (Eastern) Division, was one of the first Kitchener's Army divisions raised from volunteers by Lord Kitchener. It was formed within Eastern Command as a result of Army Order No. 324 of 21 August 1914, as part of the K1 wave of divisions. It fought on the Western Front for the duration of the First World War. One of its most notable actions was the Battle of Épehy where there is a memorial cross to the 12th Division. In the First World War, the division's insignia was the Ace of Spades, which has since been adopted by the present 12th Armoured Infantry Brigade. Order of Battle 35th Brigade * 7th (Service) Battalion, Norfolk Regiment * 7th (Service) Battalion, Suffolk Regime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
No Man's Land
No man's land is waste or unowned land or an uninhabited or desolate area that may be under dispute between parties who leave it unoccupied out of fear or uncertainty. The term was originally used to define a contested territory or a dumping ground for refuse between fiefdoms. In modern times, it is commonly associated with World War I to describe the area of land between two enemy trench systems, not controlled by either side. Coleman p. 268 The term is also used metaphorically, to refer to an ambiguous, anomalous, or indefinite area, in regards to an application, situation, or jurisdiction. It has sometimes been used to name a specific place. Origin According to Alasdair Pinkerton, an expert in human geography at Royal Holloway, University of London, the term is first mentioned in Domesday Book (1086), to describe parcels of land that were just beyond the London city walls. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' contains a reference to the term dating back to 1320, spell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slag
Slag is a by-product of smelting (pyrometallurgical) ores and used metals. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous (by-products of processing iron and steel), ferroalloy (by-product of ferroalloy production) or non-ferrous/base metals (by-products of recovering non-ferrous materials like copper, nickel, zinc and phosphorus). Within these general categories, slags can be further categorized by their precursor and processing conditions (e.g., Blast furnace (BF) slags, air-cooled blast furnace (ACBF) slag, basic oxygen furnace (BOF) slag, and electric arc furnace (EAF) slag) . Due to the large demand for these materials, slag production has also significantly increased throughout the years despite recycling (most notably in the iron and steelmaking industries) and upcycling efforts. The World Steel Association (WSA) estimates that 600 kg of by-products (~90 wt% is slags) are generated per tonne of steel produced. Composition Slag is usually a mixture of metal oxides and sili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
170th Tunnelling Company
The 170th Tunnelling Company was one of the tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers created by the British Army during World War I. The tunnelling units were occupied in offensive and defensive mining involving the placing and maintaining of mines under enemy lines, as well as other underground work such as the construction of deep dugouts for troop accommodation, the digging of subways, saps (a narrow trench dug to approach enemy trenches), cable trenches and underground chambers for signals and medical services.The Tunnelling Companies RE , access date 25 April 2015 Background By January 1915 it had become evident to the BEF at the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Haig, 1st Earl Haig
Field Marshal Douglas Haig, 1st Earl Haig, (; 19 June 1861 – 29 January 1928) was a senior officer of the British Army. During the First World War, he commanded the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) on the Western Front from late 1915 until the end of the war. He was commander during the Battle of the Somme, the Battle of Arras, the Third Battle of Ypres, the German Spring Offensive, and the Hundred Days Offensive.Sheffield 2002, p. 21.Sheffield 2002, p. 263.Hart 2008, p. 2. His military career included service in the War Office, where he was instrumental in the creation of the Territorial Force in 1908. In January 1917 he was raised up to the rank of Field Marshal, subsequently leading the BEF during the final Hundred Days Offensive, when it crossed the Canal du Nord and broke through the Hindenburg line, capturing 195,000 German prisoners. This campaign, in combination with the Kiel mutiny, the Wilhelmshaven mutiny, the proclamation of a republic on 9 November 1918, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th (Scottish) Division
The 9th (Scottish) Division, was an infantry division of the British Army during the First World War, one of the Kitchener's Army divisions raised from volunteers by Lord Kitchener to serve on the Western Front during the First World War. After the 1st South African Infantry Brigade Group joined in early 1916, the division was known colloquially as the '' Jock and Springboks''. History Background A 9th Division had been formed for service during the Second Boer War, and was commanded by Henry Edward Colvile. In 1902, a 9th Division was as formed and was commanded by Edward Pemberton Leach, but it was broken-up at some point prior to the start of the war. First World War In the Battle of Loos, notable for being the first battle in which British forces used poison gas, the 9th (Scottish) Division assaulted the Hohenzollern Redoubt, the 5th Camerons suffered horrific casualties, and Corporal James Dalgleish Pollock gained a Victoria Cross for his actions. The 9th (Sco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
117th Infantry Division (German Empire)
The 117th Infantry Division (''117. Infanterie-Division'') was a formation of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed on April 2, 1915, and organized over the next several weeks. It was part of a wave of new infantry divisions formed in the spring of 1915. The division was disbanded in 1919, during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. The division was formed primarily from the excess infantry regiments of regular infantry divisions that were being triangularized. The division's 233rd Infantry Brigade staff had been the staff of the 23rd Reserve Infantry Brigade of the 12th Reserve Division, which came to the new division along with the 22nd Reserve Infantry Regiment. The 11th Reserve Infantry Regiment had been part of the 11th Reserve Division. The 157th Infantry Regiment came from the 12th Infantry Division. The division was recruited in Silesia. Combat chronicle The 117th Infantry Division began fighting on the Western Front in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
