|
Hodgeman Islands
The Hodgeman Islands are a group of small islands lying close to the coast of Antarctica, west-southwest of Cape De la Motte, in the eastern part of the entrance to Watt Bay. They were discovered by the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (1911–14) under Douglas Mawson, who named the islands for Alfred Hodgeman Alfred Hodgeman (8 August 1885 – January 1964) was an Australian architect and cartographer known for his involvement in the Australasian Antarctic expedition. Biography Alfred James Hodgeman was born in Adelaide, South Australia on 8 August 1 ..., a cartographer and assistant meteorologist with the expedition. See also * List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands References Islands of George V Land {{GeorgeVLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
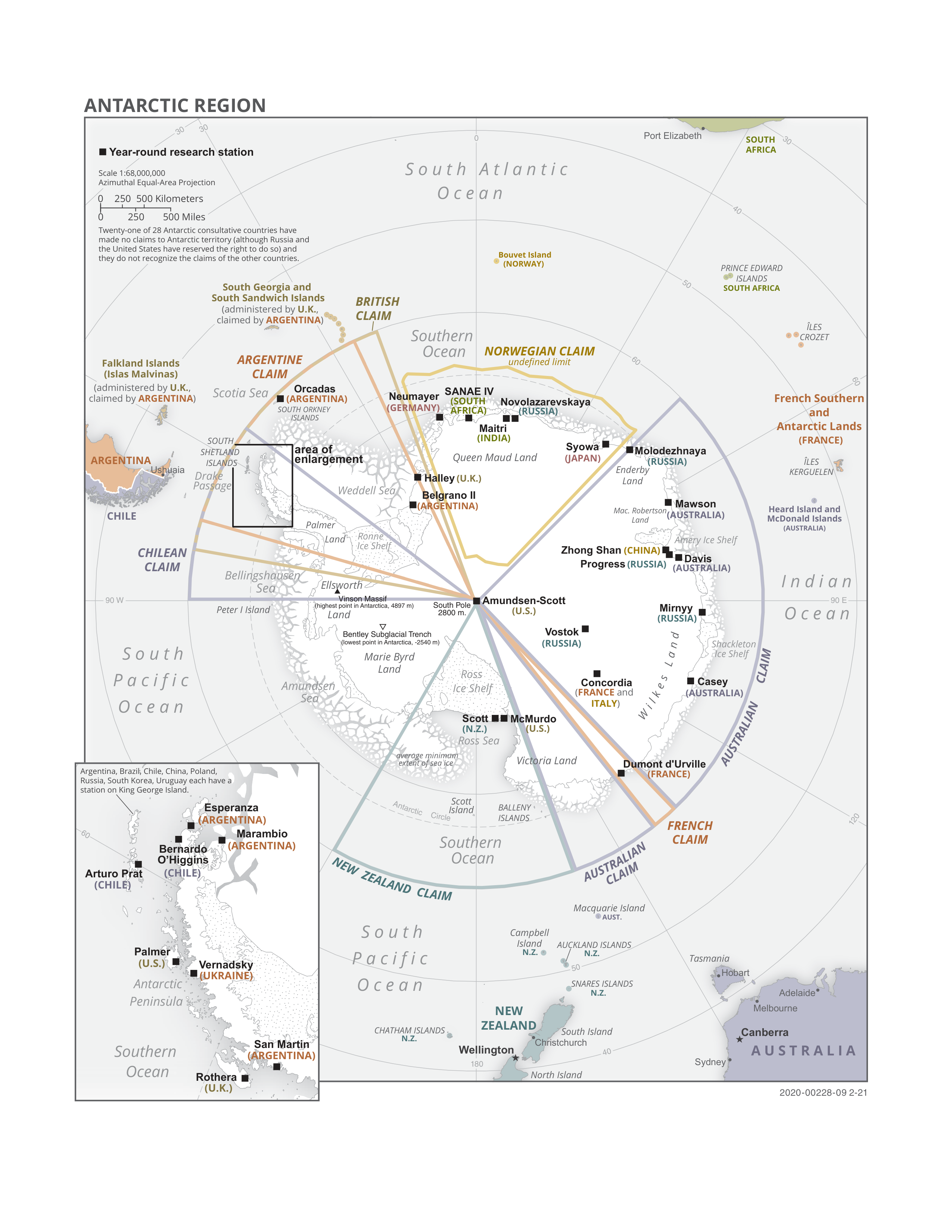
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape De La Motte
Cape De la Motte is a prominent cape in George V Land in Antarctica separating Watt Bay and Buchanan Bay. Just to the south, the continental ice surface rises at Mount Hunt. The cape was charted by the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (1911–14) under Douglas Mawson, who named it for C. P. de la Motte, third officer on the expedition ship ''Aurora''. It has been conjectured that the high land behind this cape is "Point Case", which the United States Exploring Expedition (1838–42) under Lieutenant Charles Wilkes Charles Wilkes (April 3, 1798 – February 8, 1877) was an American naval officer, ship's captain, and explorer. He led the United States Exploring Expedition (1838–1842). During the American Civil War (1861–1865), he commanded ' during the ... saw from what was called "Disappointment Bay" on January 23, 1840. References * Headlands of George V Land {{GeorgeVLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watt Bay
Watt Bay () is a bay about 16 nautical miles (30 km) wide indenting the coast between Garnet Point and Cape De la Motte. Discovered by the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (1911–14) under Douglas Mawson Sir Douglas Mawson OBE FRS FAA (5 May 1882 – 14 October 1958) was an Australian geologist, Antarctic explorer, and academic. Along with Roald Amundsen, Robert Falcon Scott, and Sir Ernest Shackleton, he was a key expedition leader during ..., who named it for W.A. Watt, Premier of Victoria in 1911. Bays of George V Land {{GeorgeVLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australasian Antarctic Expedition
The Australasian Antarctic Expedition was a 1911–1914 expedition headed by Douglas Mawson that explored the largely uncharted Antarctic coast due south of Australia. Mawson had been inspired to lead his own venture by his experiences on Ernest Shackleton's ''Nimrod'' expedition in 1907–1909. During its time in Antarctica, the expedition's sledging parties covered around of unexplored territory, while its ship, , navigated of unmapped coastline. Scientific activities included meteorological measurements, magnetic observations, an expansive oceanographic program, and the collection of many biological and geological samples, including the discovery of the first meteorite found in Antarctica. The expedition was the first to establish and maintain wireless contact between Antarctica and Australia. Another planned innovation – the use of an aircraft – was thwarted by an accident before the expedition sailed. The plane's fuselage was adapted to form a motorised sledge or "air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Mawson
Sir Douglas Mawson OBE FRS FAA (5 May 1882 – 14 October 1958) was an Australian geologist, Antarctic explorer, and academic. Along with Roald Amundsen, Robert Falcon Scott, and Sir Ernest Shackleton, he was a key expedition leader during the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration. Mawson was born in England and came to Australia as an infant. He completed degrees in mining engineering and geology at the University of Sydney. In 1905 he was made a lecturer in petrology and mineralogy at the University of Adelaide. Mawson's first experience in the Antarctic came as a member of Shackleton's ''Nimrod'' Expedition (1907–1909), alongside his mentor Edgeworth David. They were part of the expedition's northern party, which became the first to attain the South Magnetic Pole and to climb Mount Erebus. After his participation in Shackleton's expedition, Mawson became the principal instigator of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (1911–1914). The expedition explored thousand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Hodgeman
Alfred Hodgeman (8 August 1885 – January 1964) was an Australian architect and cartographer known for his involvement in the Australasian Antarctic expedition. Biography Alfred James Hodgeman was born in Adelaide, South Australia on 8 August 1885. His parents were Alfred Hodgeman and Helen Davidson Pennington. He was employed by the South Australian government as a draughtsman and was later an architect. Hodgeman was asked by Sir Douglas Mawson to design the huts for the Australasian Antarctic Expedition and selected to join the expedition. The huts were prefabricated in sections to allow for transport to Antarctica. As part of his role, Hodgeman oversaw the construction of the main hut at the main base and took part in several sledging expeditions, recording routes taken, coastlines and topography. He also remained behind awaiting the return of the Far Eastern Party, Mawson, Belgrave Edward Sutton Ninnis and Xavier Mertz. Mertz and Ninnis died on the journey and only Mawson r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |