|
History Of Tbilisi
The history of Tbilisi, the capital of Georgia, dates back to at least the 5th century AD. Since its foundation by the monarch of Georgia's ancient precursor Kingdom of Iberia, Tbilisi has been an important cultural, political and economic center of the Caucasus and served, with intermissions, as the capital of various Georgian kingdoms and republics. Under the Russian rule, from 1801 to 1917 it was called Tiflis and held the seat of the Imperial Viceroy governing both sides of the entire Caucasus. Tbilisi's proximity to lucrative east–west trade routes often made the city a point of contention between various rival empires, and its location to this day ensures an important transit role. Tbilisi's varied history is reflected in its architecture, which is a mix of medieval, classical, and Soviet structures. Early history Legend has it that the present-day territory of Tbilisi was uninhabited and covered by forest as late as 458 AD, the date medieval Georgian chronicles assig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the Capital city, capital and the List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city of Georgia (country), Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura (Caspian Sea), Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million people. Tbilisi was founded in the 5th century Anno Domini, AD by Vakhtang I of Iberia, and since then has served as the capital of various Georgian kingdoms and republics. Between 1801 and 1917, then part of the Russian Empire, Tiflis was the seat of the Caucasus Viceroyalty (1801–1917), Caucasus Viceroyalty, governing both the North Caucasus, northern and the Transcaucasia, southern parts of the Caucasus. Because of its location on the crossroads between Europe and Asia, and its proximity to the lucrative Silk Road, throughout history Tbilisi was a point of contention among various global powers. The city's location to this day ensures its p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
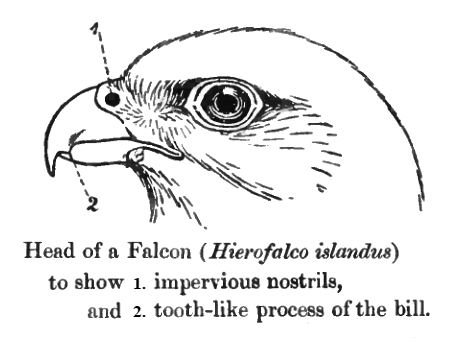
Falcon
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene. Adult falcons have thin, tapered wings, which enable them to fly at high speed and change direction rapidly. Fledgling falcons, in their first year of flying, have longer flight feathers, which make their configuration more like that of a general-purpose bird such as a broad wing. This makes flying easier while learning the exceptional skills required to be effective hunters as adults. The falcons are the largest genus in the Falconinae subfamily of Falconidae, which itself also includes another subfamily comprising caracaras and a few other species. All these birds kill with their beaks, using a tomial "tooth" on the side of their beaks—unlike the hawks, eagles, and other birds of prey in the Accipitridae, which use their feet. The largest fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Perso-Turkic War
The Third Perso-Turkic War was the third and final conflict between the Sassanian Empire and the Western Turkic Khaganate. Unlike the previous two wars, it was not fought in Central Asia, but in Transcaucasia. Hostilities were initiated in 627 AD by Tong Yabghu Qaghan of the Western Göktürks and Emperor Heraclius of the Byzantine Empire. Opposing them were the Sassanid Persians, allied with the Avars. The war was fought against the background of the last Byzantine-Sassanid War and served as a prelude to the dramatic events that changed the balance of powers in the Middle East for centuries to come ( Battle of Nineveh, Islamic conquest of Persia). Background Following the First Siege of Constantinople by the Avars and Persians, the beleaguered Byzantine Emperor Heraclius found himself politically isolated. He could not rely on the Christian Armenian potentates of Transcaucasia, since they were branded as heretics by the Orthodox Church, and even the king of Iberia preferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmenistan to the north, by Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and by the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. It covers an area of , making it the 17th-largest country. Iran has a population of 86 million, making it the 17th-most populous country in the world, and the second-largest in the Middle East. Its largest cities, in descending order, are the capital Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, Karaj, Shiraz, and Tabriz. The country is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, beginning with the formation of the Elamite kingdoms in the fourth millennium BC. It was first unified by the Medes, an ancient Iranian people, in the seventh century BC, and reached its territorial height in the sixth century BC, when Cyrus the Great fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mtskheta
Mtskheta ( ka, მცხეთა, tr ) is a city in Mtskheta-Mtianeti province of Georgia. It is one of the oldest cities in Georgia as well as one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the World. Itis located approximately north of Tbilisi, at the confluence of the Mtkvari and Aragvi rivers. Currently a small provincial capital, for nearly a millennium until the 5th century AD, Mtskheta was a large fortified city, a significant economical and political centre of the Kingdom of Iberia. Due to the historical significance of the town and its several outstanding churches and cultural monuments, the "Historical Monuments of Mtskheta" became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994. As the birthplace and one of the most vibrant centers of Christianity in Georgia, Mtskheta was declared as the "Holy City" by the Georgian Orthodox Church in 2014. In 2016 the Historical Monuments of Mtskheta were placed by UNESCO under Enhanced Protection, a mechanism established by the 1999 Seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dachi Of Iberia
Dachi ( ka, დაჩი, also Darchi, დარჩი, or Darchil, დარჩილი), of the Chosroid Dynasty, was the king of Caucasian Iberia, Iberia (Kartli, eastern Georgia (country), Georgia) reigning, according to a medieval Georgian literary tradition, for 12 years, from c. 522 to 534. He was given a territorial epithet ''Ujarmeli'' (უჯარმელი, i.e., "of/from Ujarma") for having spent years at his residence at Ujarma fortress, Ujarma. The name Dachi derives from Middle Persian ''Dārčīhr'', itself being a compound of the Iranian words ''dar'' ("court, palace") and ''čihr[ag]'' ("seed, origin"). According to the medieval Georgian chronicles, Dachi was the eldest son of King Vakhtang I of Iberia, Vakhtang I Gorgasal by Balendukht, daughter of the Sassanid Empire, Iranian Sassanid king Hormizd III. He succeeded his father, who had launched an abortive rebellion against the Sassanid hegemony, and took a more conciliatory line with his Iranian suzerains. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metekhi
Metekhi (Metechi; ka, მეტეხი) is a historic neighborhood of Tbilisi, Georgia, located (42.92N 44.34E) on the elevated cliff that overlooks the Mtkvari river. The neighborhood is home to the eponymous Metekhi Church of Assumption. History The district was one of the earliest inhabited areas on the city's territory. According to traditional accounts, King Vakhtang I Gorgasali erected here a church and a fort which served also as a king's residence; hence comes the name Metekhi which dates back to the 12th century and literally means “the area around the palace”. Tradition holds that it was also a site where the 5th-century martyr lady Saint Shushanik was buried. However, none of these structures have survived the Mongol invasion of 1235. The extant Metekhi Church of Assumption, resting upon the top of the hill, was built by the Georgian king St Demetrius II circa 1278–1284 and is somewhat an unusual example of domed Georgian Orthodox church. It was later d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abanotubani
Abanotubani ( ka, აბანოთუბანი, literally "bath district") is the ancient district of Tbilisi, Georgia, known for its sulphuric baths. Located at the eastern bank of the Mtkvari River at the foot of Narikala fort across Metekhisubani, Abanotubani is an important historic part of the city: it is where according to a legend the King of Iberia, Vakhtang Gorgasali’s falcon Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene. Adult falcons ... fell, leading to a discovery of the hot springs and, subsequently, to founding of a new capital. References {{Georgia-geo-stub Neighborhoods of Tbilisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Bathing
Public baths originated when most people in population centers did not have access to private bathing facilities. Though termed "public", they have often been restricted according to gender, religious affiliation, personal membership, and other criteria. In addition to their hygienic function, public baths have also been social meeting places. They have included saunas, massages, and other relaxation therapies, as are found in modern day spas. As the percentage of dwellings containing private bathrooms has increased in some societies, the need for public baths has diminished, and they are now almost exclusively used recreationally. History Public facilities for bathing were constructed, as excavations have provided evidence for, in the 3rd millennium BC, as with the Great Bath, Mohenjo-daro. Ancient Greece In Greece by the sixth century BC men and women washed in basins near places of physical and intellectual exercise. Later gymnasia had indoor basins set overhead, the open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


