|
History Of The Oil Shale Industry In The United States
The history of the oil shale industry in the United States goes back to the 1850s; it dates back farther as a major enterprise than the petroleum industry. But although the United States contains the world's largest known resource of oil shale, the US has not been a significant producer of shale oil since 1861. There were three major past attempts to establish an American oil shale industry: the 1850s; in the years during and after World War I; and in the 1970s and early 1980s. Each time, the oil shale industry failed because of competition from cheaper petroleum. As of 2014, there are a number of companies doing research and development on oil shale deposits in Colorado and Utah, but there is no commercial production of oil from shale in the United States. US oil shale resources The United States has not had a viable oil shale industry for more than 150 years, yet it contains the largest oil shale resource in the world. Eastern resources There are two types of oil shale resourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Shale
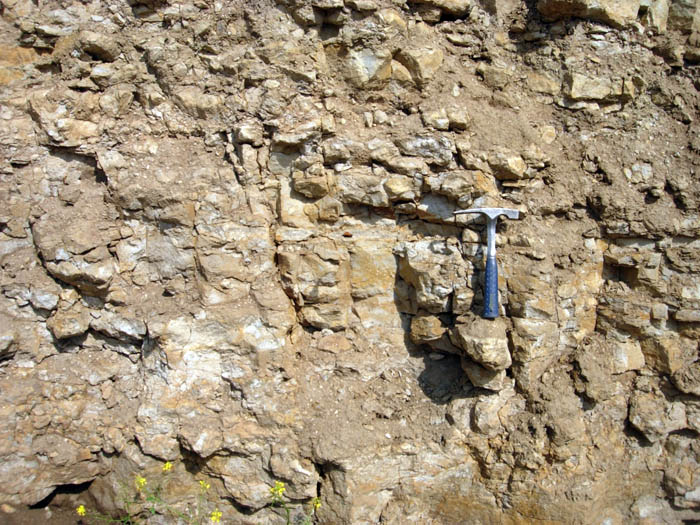
Oil shale is an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock containing kerogen (a solid mixture of organic chemical compounds) from which liquid hydrocarbons can be produced. In addition to kerogen, general composition of oil shales constitutes inorganic substance and bitumens. Based on their deposition environment, oil shales are classified as marine, lacustrine and terrestrial oil shales. Oil shales differ from oil-''bearing'' shales, shale deposits that contain petroleum (tight oil) that is sometimes produced from drilled wells. Examples of oil-''bearing'' shales are the Bakken Formation, Pierre Shale, Niobrara Formation, and Eagle Ford Formation. Accordingly, shale oil produced from oil shale should not be confused with tight oil, which is also frequently called shale oil. Deposits of oil shale occur around the world, including major deposits in the United States. A 2016 estimate of global deposits set the total world resources of oil shale equivalent of of oil in place. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Albany Shale
The New Albany Shale is an organic-rich geologic formation of Devonian and Mississippian age in the Illinois Basin of the United States. It is a major source of hydrocarbons. Stratigraphy The New Albany formation consists of brown, black, and green shale with minor beds of dolomite and sandstone. It was deposited under anoxic marine conditions. Pyrite is a common accessory mineral, and parts of the shale have greater than 4% by weight of organic carbon. The black shale layers have anomalously high radioactivity (due to uranium), phosphorus, and heavy metals. The formation was named for outcrops near New Albany, Indiana. It is one of a number of organic-rich shales of upper Devonian and lower Mississippian age in North America. It is correlative with the Antrim Shale of the Michigan Basin, the Ohio Shale of Ohio and eastern Kentucky, and the Chattanooga Shale of Tennessee and central Kentucky. The formation is composed of six members. These members in ascending strat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoria Formation
The Phosphoria Formation of the western United States is a geological formation of Early Permian age.Behnken, F.H., Wardlaw, B.R. and Stout, L.N., 1986, Conodont biostratigraphy of the Permian Meade Peak Phosphatic Shale Member, Phosphoria Formation, southeastern Idaho. University of Wyoming Contributions to Geology, v. 24, no. 2, p. 169-190. It represents some 15 million years of sedimentation, reaches a thickness of and covers an area of .Blatt, Harvey and Robert J. Tracy, ''Petrology'', Freeman, 1996, 2nd ed. pp. 345-349 The Phosphoria includes phosphorite beds that are an important source of phosphorus. Many of its shales are rich in organic matter and are petroleum source rocks, and some of its dolomites include petroleum reservoirs. Environment of deposition The Phosphoria Formation was deposited under marine conditions in a foreland basin located between the Paleozoic continental margin and the North American cratonic shelf.Maughan, E.K. 1984. Geological setting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elko County, Nevada
Elko County is a county in the northeastern corner of Nevada, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 53,702. Its county seat is Elko. The county was established on March 5, 1869, from Lander County. Elko County is the fourth-largest county by area in the contiguous United States, ranking lower when the boroughs of Alaska are included. It is one of only 10 counties in the U.S. with more than of area. Elko County is part of the Elko, NV Micropolitan Statistical Area. It contains 49.8 percent of the Duck Valley Indian Reservation, set up in the late 19th century for the Shoshone-Paiute peoples; they are a federally recognized tribe. Although slightly more than 50% of the reservation is across the border in Owyhee County, Idaho, the majority of tribal members live on the Nevada side. The reservation's land area is . History This area was long inhabited by Native American tribes of the Plateau, particularly the Western Shoshone, Northern Paiute, and Bannock p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''olígos'', "few") and (''kainós'', "new"), and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major changes during the Oligocene included a global expansion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elko Formation
The Elko Formation, also known as Elko Shale(s), is an oil shale geologic formation in Elko County, northern Nevada, United States. The deltaic and lacustrine shales and limestones preserve fossils dating back to the Middle Eocene of the Paleogene to Middle Miocene of the Neogene period. The frog genus '' Elkobatrachus'' and ant species '' Pseudocamponotus elkoanus'' were named after the formation. Description The formation ranges in age from the Middle Eocene (Uintan), with the underlying lower member dated at 46.1 ± 0.1 Ma and the upper member of the Eocene section dated at 38.9 ± 0.3 Ma.''Elkobatrachus'' type locality at .org A younger section is dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, clays, and silt. When hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae. Marl makes up the lower part of the cliffs of Dover, and the Channel Tunnel follows these marl layers between France and the United Kingdom. Marl is also a common sediment in post-glacial lakes, such as the marl ponds of the northeastern United States. Marl has been used as a soil conditioner and neutralizing agent for acid soil and in the manufacture of cement. Description Marl or marlstone is a carbonate-rich mud or mudstone which contains variable amounts of clays and silt. The term was originally loosely applied to a variety of materials, most of which occur as loose, earthy deposits consisting chiefly of an intimate mixture of clay and calcium carbonate, formed under freshwater conditions. These typically contain 35–65% clay and 65–35% carbonate. The te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
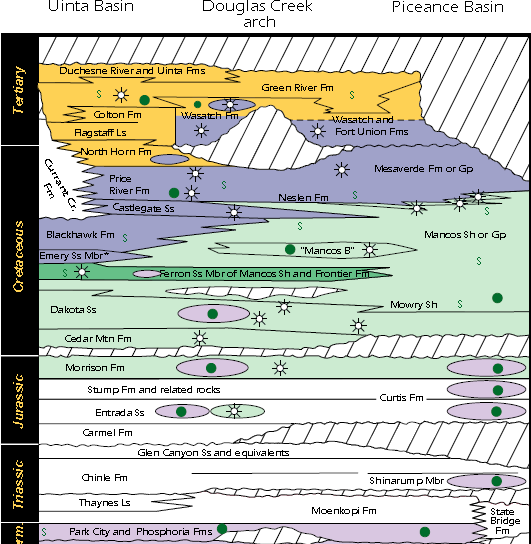
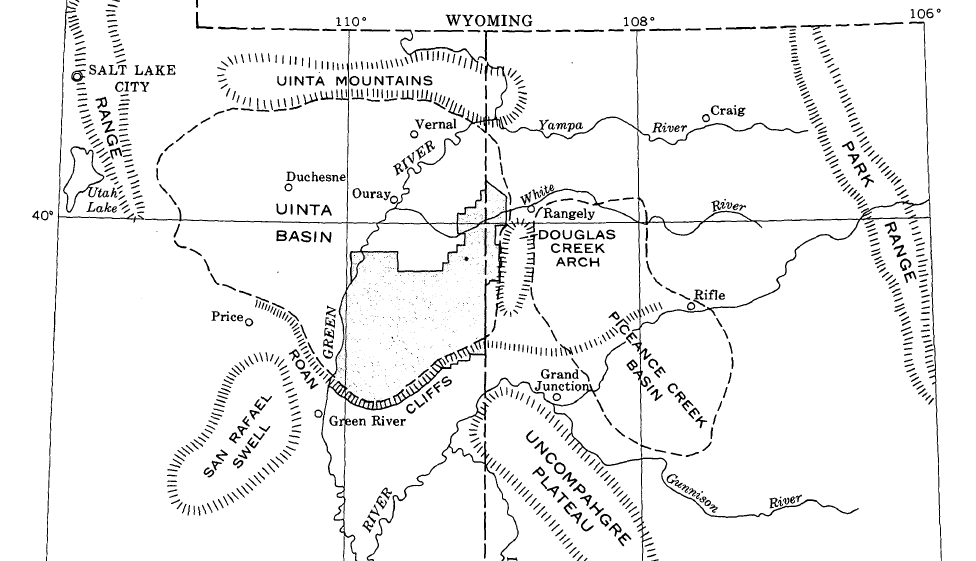
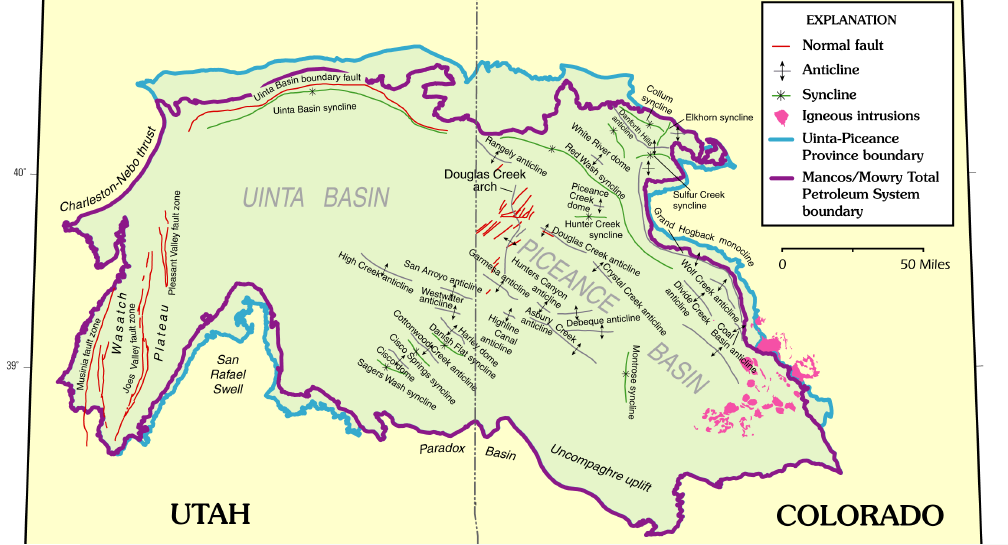
Uinta Basin
The Uinta Basin (also known as the Uintah Basin) is a physiographic section of the larger Colorado Plateaus province, which in turn is part of the larger Intermontane Plateaus physiographic division. It is also a geologic structural basin in eastern Utah, east of the Wasatch Mountains and south of the Uinta Mountains. The Uinta Basin is fed by creeks and rivers flowing south from the Uinta Mountains. Many of the principal rivers (Strawberry River, Currant Creek, Rock Creek, Lake Fork River, and Uintah River) flow into the Duchesne River which feeds the Green River—a tributary of the Colorado River. The Uinta Mountains forms the northern border of the Uinta Basin. They contain the highest point in Utah, Kings Peak, with a summit 13,528 feet (4123 metres) above sea level. The climate of the Uinta Basin is semi-arid, with occasionally severe winter cold. History Father Escalante's expedition visited the Uinta Basin in September 1776. 1822–1840 French Canadian tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green River Basin
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combination of yellow and cyan; in the RGB color model, used on television and computer screens, it is one of the additive primary colors, along with red and blue, which are mixed in different combinations to create all other colors. By far the largest contributor to green in nature is chlorophyll, the chemical by which plants photosynthesize and convert sunlight into chemical energy. Many creatures have adapted to their green environments by taking on a green hue themselves as camouflage. Several minerals have a green color, including the emerald, which is colored green by its chromium content. During post-classical and early modern Europe, green was the color commonly associated with wealth, merchants, bankers, and the gentry, while red was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piceance Basin
The Piceance Basin is a geologic structural basin in northwestern Colorado, in the United States. It includes geologic formations from Cambrian to Holocene in age, but the thickest section is made up of rocks from the Cretaceous Period. The basin contains reserves of coal, natural gas, and oil shale. The name likely derives from the Shoshoni word ''/piasonittsi/'' meaning “tall grass” (''/pia-/'' ‘big’ and ''/soni-/'' ‘grass’). Hydrocarbon resources In 2016 USGS released an assessment of the resources of the Mancos Shale of the Piceance Basin in Colorado and Utah, "a total of assessed technically recoverable mean resources of 74 million barrels of shale oil, 66.3 trillion cubic feet of gas, and 45 million barrels of natural gas liquids." Natural gas The basin has come to increasing public attention in recent years because of widespread drilling to extract natural gas. The primary target of gas development has been the Williams Fork Formation of the Mesaverde Group, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green River Formation
The Green River Formation is an Eocene geologic formation that records the sedimentation in a group of intermountain lakes in three basins along the present-day Green River in Colorado, Wyoming, and Utah. The sediments are deposited in very fine layers, a dark layer during the growing season and a light-hue inorganic layer in the dry season. Each pair of layers is called a varve and represents one year. The sediments of the Green River Formation present a continuous record of six million years. The mean thickness of a varve here is 0.18 mm, with a minimum thickness of 0.014 mm and maximum of 9.8 mm.Bradley, W. H. The varves and climate of the Green River epoch: U.S. Geol. Survey Prof. Paper 158, pp 87–110, 1929. The sedimentary layers were formed in a large area named for the Green River, a tributary of the Colorado River. The three separate basins lie around the Uinta Mountains (north, east, and south) of northeastern Utah: * an area in northwestern Colorado east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |